78
Creating a Rhythm Set
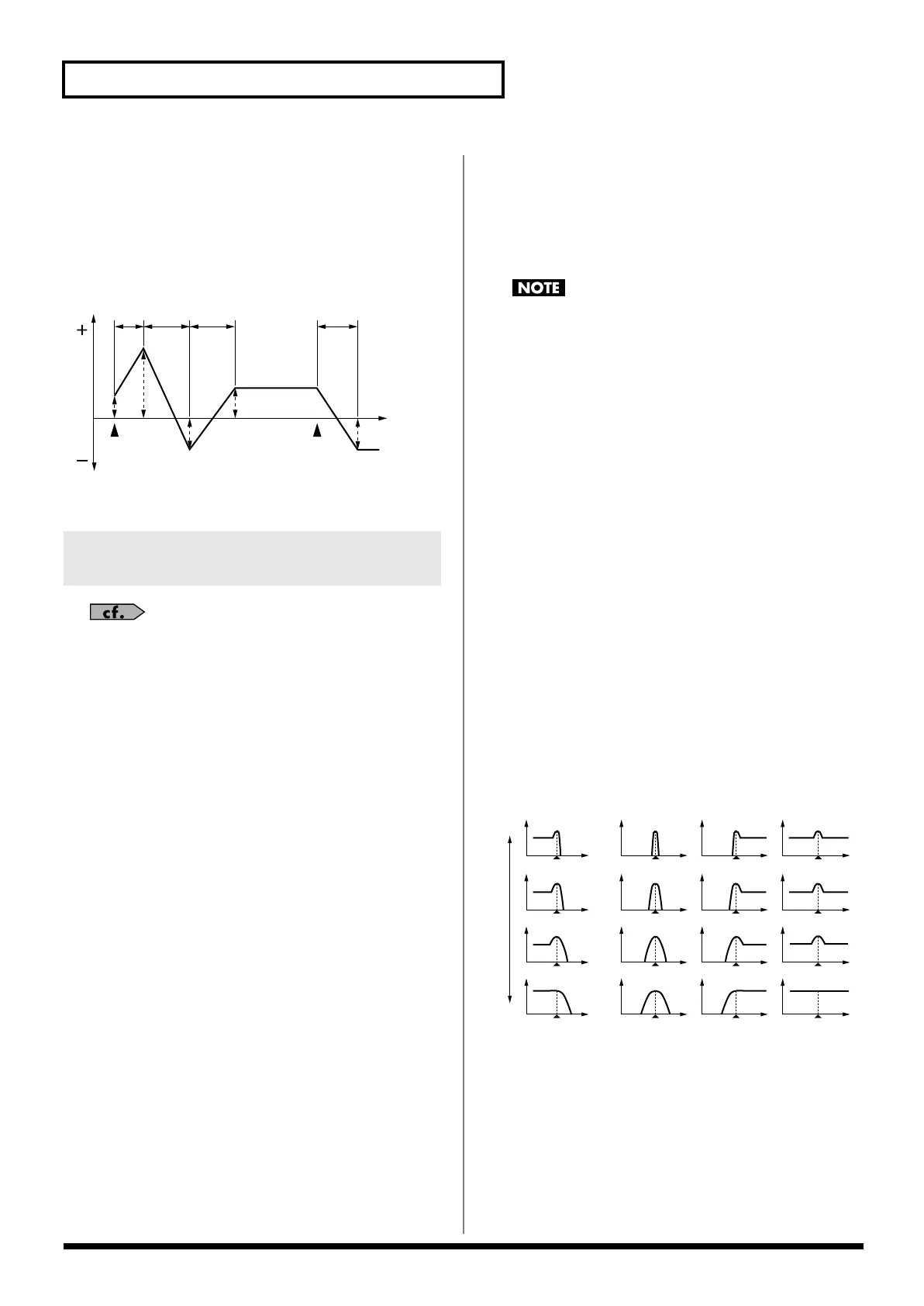
P-Env Level 0–4 (Pitch Envelope Level 0–4)
Specify the pitch envelope levels (Level 0–Level 4). It determines
how much the pitch changes from the reference pitch (the value set
with Coarse Tune or Fine Tune on the Pitch screen) at each point.
Positive (+) settings will cause the pitch to be higher than the
standard pitch, and negative (-) settings will cause it to be lower.
Value:
-63– +63
fig.06-032.e
For details on these settings, refer to
“How to Make Rhythm
Set Settings”
(p. 71).
Rhythm TVF
Filter Type
Selects the type of filter. A filter cuts or boosts a specific frequency
region to change a sound’s brightness, thickness, or other qualities.
Value
OFF:
No filter is used.
LPF:
Low Pass Filter. This reduces the volume of all
frequencies above the cutoff frequency (Cutoff Freq) in
order to round off, or un-brighten the sound. This is the
most common filter used in synthesizers.
BPF:
Band Pass Filter. This leaves only the frequencies in the
region of the cutoff frequency (Cutoff Frequency), and
cuts the rest. This can be useful when creating distinctive
sounds.
HPF:
High Pass Filter. This cuts the frequencies in the region
below the cutoff frequency (Cutoff Frequency). This is
suitable for creating percussive sounds emphasizing
their higher tones.
PKG:
Peaking Filter. This emphasizes the frequencies in the
region of the cutoff frequency (Cutoff Frequency). You
can use this to create wah-wah effects by employing an
LFO to change the cutoff frequency cyclically.
LPF2:
Low Pass Filter 2. Although frequency components
above the Cutoff frequency (Cutoff Frequency) are cut,
the sensitivity of this filter is half that of the LPF. This
makes it a comparatively warmer low pass filter. This
filter is good for use with simulated instrument sounds
such as the acoustic piano.
LPF3:
Low Pass Filter 3. Although frequency components
above the Cutoff frequency (Cutoff Frequency) are cut,
the sensitivity of this filter changes according to the
Cutoff frequency. While this filter is also good for use
with simulated acoustic instrument sounds, the nuance
it exhibits differs from that of the LPF2, even with the
same TVF Envelope settings.
If you set “LPF2” or “LPF3,” the setting for the Resonance
parameter will be ignored.
Cutoff Frequency
Selects the frequency at which the filter begins to have an effect on
the waveform’s frequency components.
Value:
0–127
With “LPF/LPF2/LPF3” selected for the Filter Type parameter,
lower cutoff frequency settings reduce a tone’s upper harmonics for
a more rounded, warmer sound. Higher settings make it sound
brighter.
If “BPF” is selected, harmonic components will change depending
on the TVF Cutoff Frequency setting. This can be useful when
creating distinctive sounds.
With “HPF” selected, higher Cutoff Frequency settings will reduce
lower harmonics to emphasize just the brighter components of the
sound.
With “PKG” selected, the harmonics to be emphasized will vary
depending on Cutoff Frequency setting.
Resonance
Emphasizes the portion of the sound in the region of the cutoff
frequency, adding character to the sound. Excessively high settings
can produce oscillation, causing the sound to distort.
Value:
0–127
fig.06-034.e
Modifying the Brightness of a
Sound with a Filter (TVF/TVF Env)
T1 T2 T3 T4
L3
L4
L2
L1
L0
Note off
Pitch
Time
Note on
T: Time L: Level
LPF BPF HPF PKG
parameter value
Level
Cutoff frequency
Frequency
High
Low
Fantom-XR_r_e.book 78 ページ 2006年4月4日 火曜日 午前10時14分

 Loading...
Loading...