Xiotech—Proprietary 160337-000 Rev D, 30 September, 2013 Page 63
Initialize and Configure ISE User Guide
Command Line Interface (CLI)
To create a host using the CLI, use the create host command with the options shown in Table 18. To see
a list of assigned and unassigned HBA port WWIDs, enter the show hba command. If a name is not
specified, the CLI auto-generates a name in the format Hostnn, where nn is an incrementing number starting
from
01
. Any auto-generated names that already exist are skipped over.
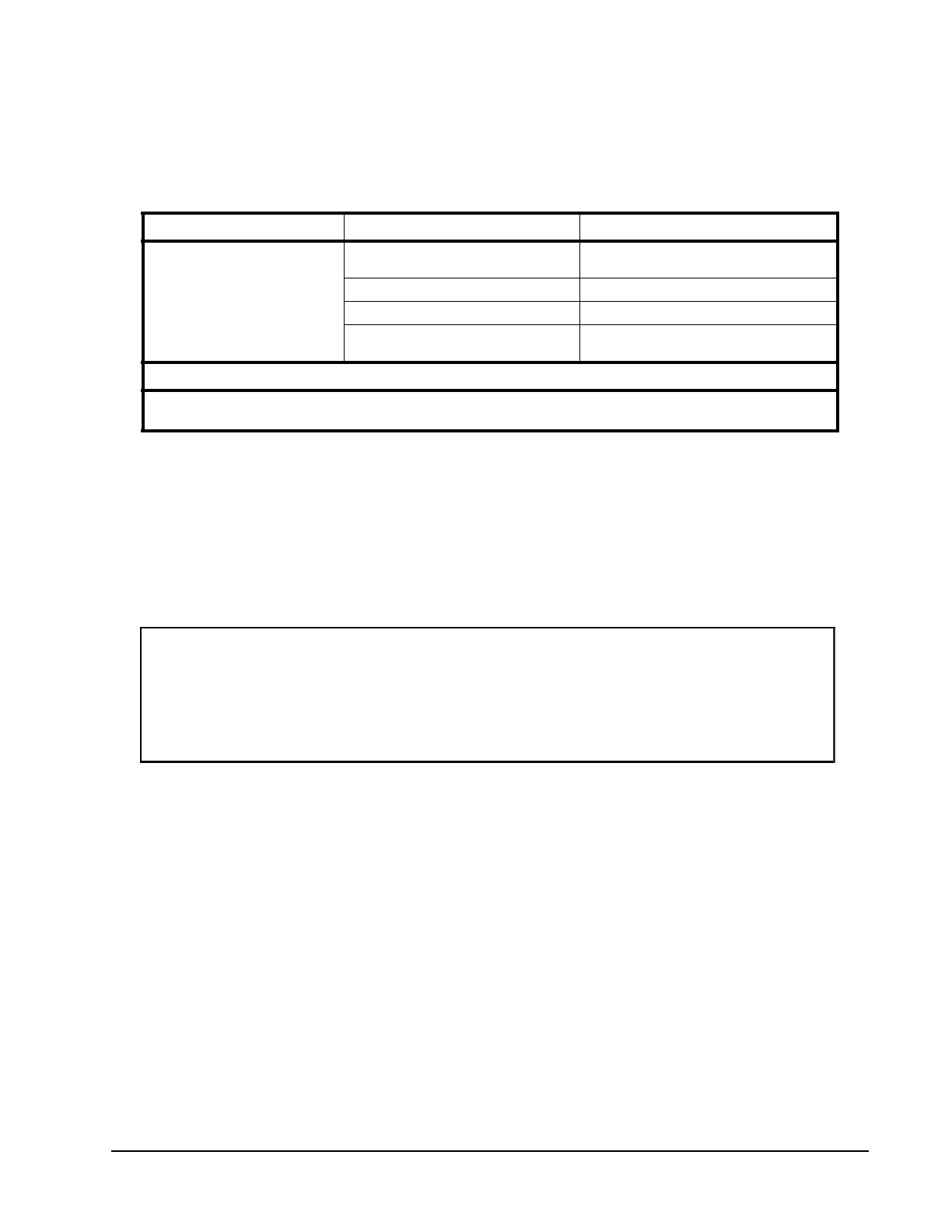
Table 18: Create Host Command
The example command in Table 18 creates a host named GEN01 with a Windows operating system and
containing HBA port WWIDs 10000000D94D0123 and 10000000A87D0902 and comment Test Host 1.
The host name may be up to thirty-two alphanumeric characters long but may not begin with a numeric
character. The comment may be up to sixty alphanumeric characters long. Special characters are accepted
except those listed in “Reserved Characters” on page 29. Text strings with embedded blanks must be
enclosed in quotes as shown in the example.
The ISE creates the host and displays a confirmation similar to that shown in the figure (45) below.
Figure 45. Host Created Confirmation
Volumes and hosts are mapped with the CLI using the present command. See “Command Line Interface
(CLI)” on page 64 for details.
Command Options Comment
create --host=<name>
or
create --host
--windows
For host using Windows operating system.
This option is the default
.
--linux
For host using Linux operating system.
--comment=<comment text>
Optional comment.
<list of HBA WWNs that
compose this host>
Separate multiple HBA WWIDs with spaces.
Example:
create
--host=GEN01
--windows
10000000D94D0123
10000000A87D0902
--comment= ”Test
Host
1”
GEN01 (Windows)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
Comment : Test_Host_1
HBAs : 10000000D94D0123, 10000000A87D0902
Volumes : <no volumes presented to this host>
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
Host created

 Loading...
Loading...