CHAPTER13 Network
Mediant 800 Gateway & E-SBC | User's Manual
First Incoming Packet Mechanism
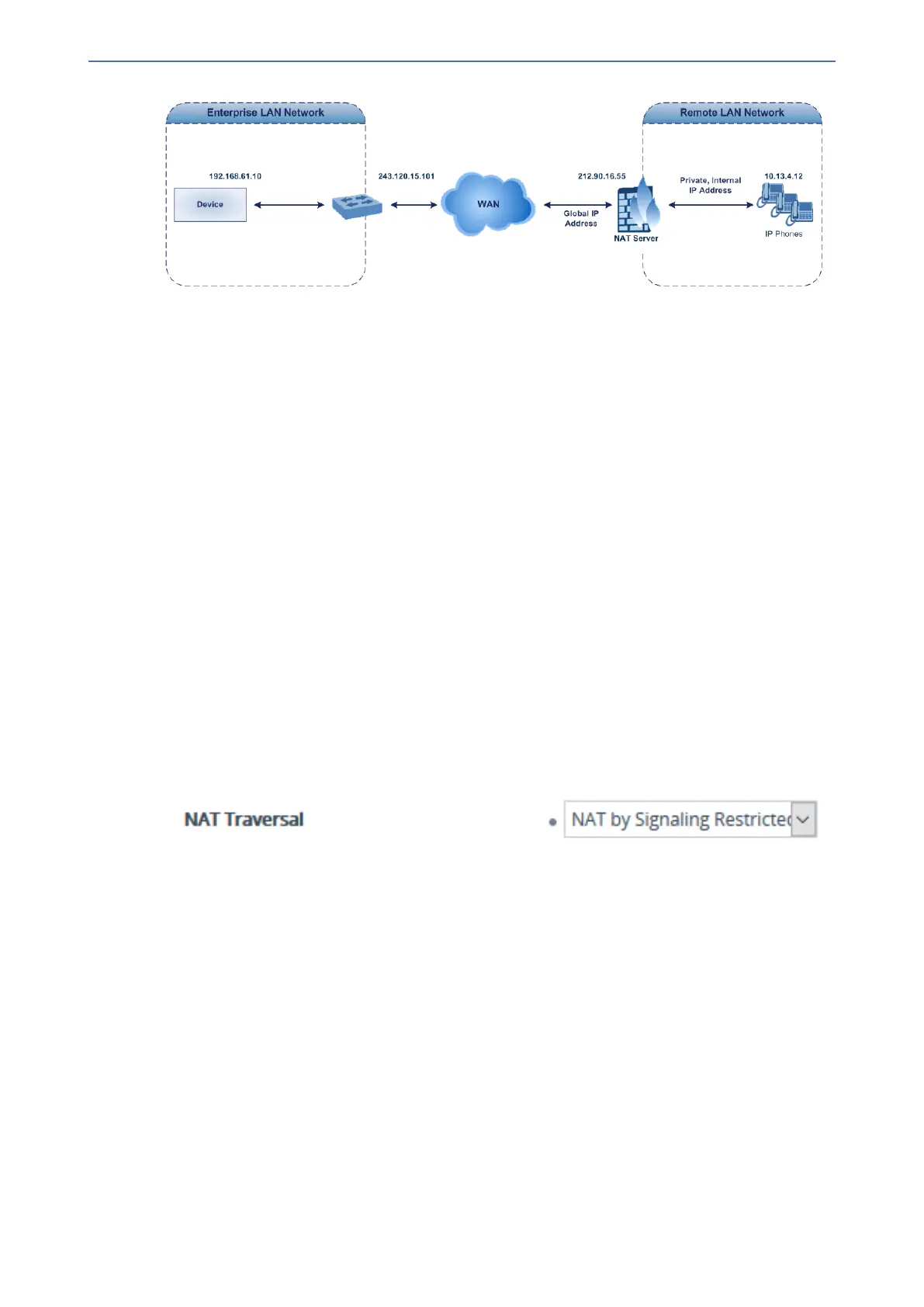
In scenarios where the remote user agent (UA) resides behind a NAT server, it’s possible that the
device, if not configured for NAT traversal, will send the media (RTP, RTCP and T.38) streams to
an invalid IP address and UDP port. In other words, it will send the media to the private IP
address:port of the UA and not the public address (of the NAT server) and therefore, the media will
not reach the UA. When the UA is located behind NAT, although the UA sends its private IP
address:port in the original SIP message (INVITE), the device receives the media packets with a
source address of a public IP address:port (i.e., allocated by the NAT server). Therefore, to ensure
that the media reaches the UA, the device must send it to the public address.
The device identifies whether the UA is located behind NAT by comparing the source IP address of
the first received media packet with the IP address and UDP port of the first received SIP message
(INVITE) when the SIP session was started. This is done for each media type--RTP, RTCP and
T.38--and therefore, they can have different destination IP addresses and UDP ports than one
another.
The device supports various NAT traversal methods, which you can configure using the 'NAT
Traversal' (NATMode) parameter. For more information on the different options provided by this
parameter, see NAT and STUN Parameters on page1180.
➢ To enable NAT resolution using the First Incoming Packet mechanism:
1. Open the Media Settings page (Setup menu > Signaling & Media tab > Media folder >
Media Settings).
2. From the 'NAT Traversal' drop-down list (NATMode), select the required NAT option.
3. Click Apply.
No-Op Packets
The device can send No-Op packets to verify Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP) and T.38
connectivity, and to keep NAT bindings and Firewall pinholes open. The No-Op packets can be
sent in RTP and T.38 formats:
■ RTP No-Op: The RTP No-Op support complies with IETF Internet-Draft draft-wing-avt-rtp-
noop-03 ("A No-Op Payload Format for RTP"). The IETF document defines a No-Op payload
format for RTP. The draft defines the RTP payload type as dynamic. You can configure the
payload type as described in the following procedure (default is 120).
■ T.38 No-Op: T.38 No-Op packets are sent only while a T.38 session is activated. Sent
packets are a duplication of the previously sent frame (including duplication of the sequence
number).
➢ To configure the No-Op packet feature:
1. Enable the feature, using the [NoOpEnable] parameter.
- 112 -

 Loading...
Loading...
















