CHAPTER16 Services
Mediant 800 Gateway & E-SBC | User's Manual
● The SIP-based Media Recording feature is available only if the device is installed
with a License Key that includes this feature. The License Key specifies the
maximum number of supported SIP recording sessions. For installing a License
Key, see License Key.
● The device supports up to 200 concurrent SIPRec sessions. This capacity
assumes that there are no other concurrent, regular (non-SIPRec) voice sessions.
Session recording is a critical requirement in many business communications environments such
as call centers and financial trading floors. In some of these environments, all calls must be
recorded for regulatory and compliance reasons. In others, calls may be recorded for quality control
or business analytics. Recording is typically performed by sending a copy of the session media to
the recording devices.
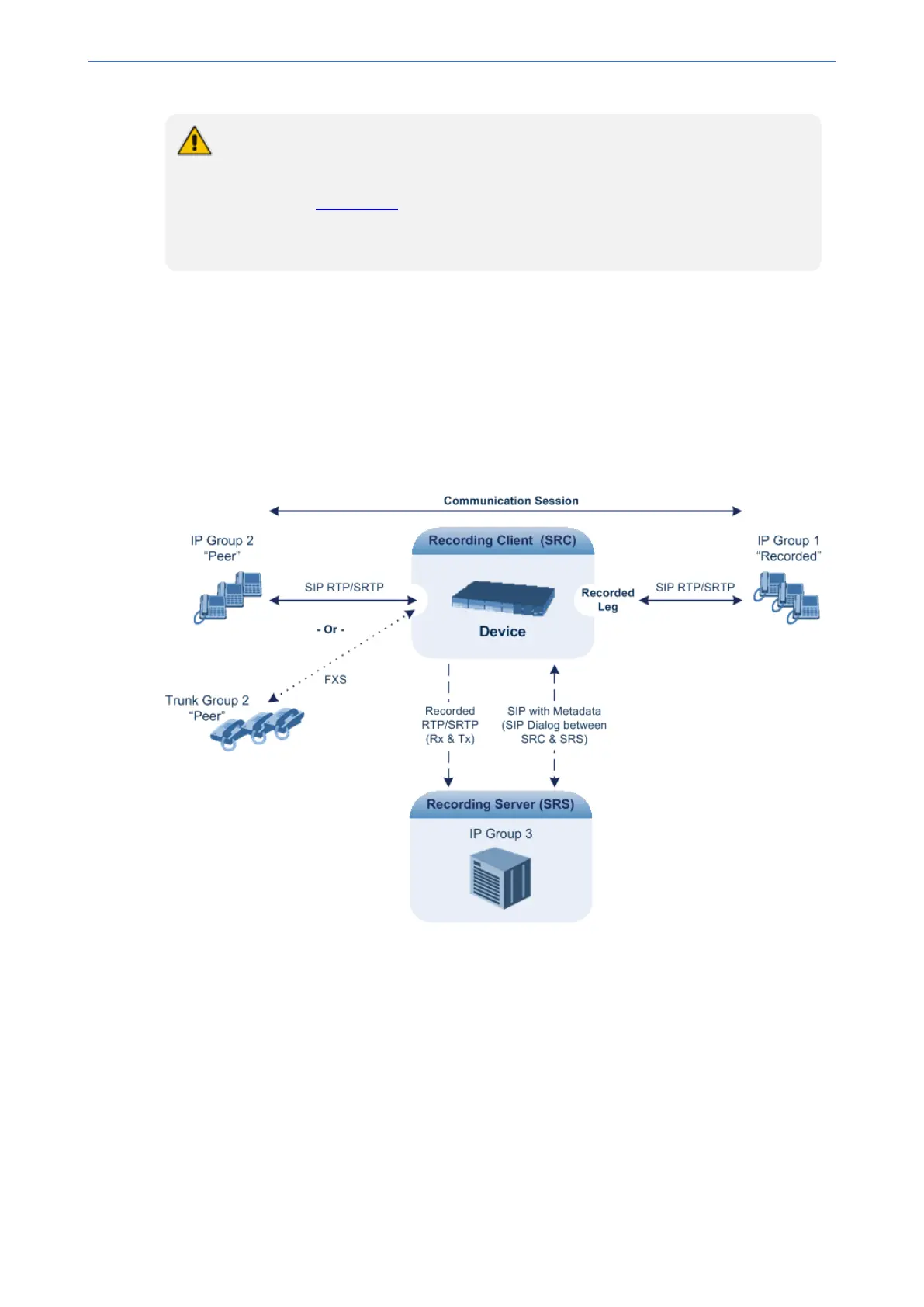
The SIPRec protocol specifies the use of SIP, SDP, and RTP to establish a Recording Session
(RS) from the Session Recording Client (SRC), which is on the path of the Communication
Session (CS), to a Session Recording Server (SRS) at the recording equipment. The device
functions as the SRC, sending recording sessions to a third-party SRS, as shown in the figure
below.
The device can record calls between two IP Groups, or between an IP Group and a Trunk Group for
Gateway calls. The type of calls to record can be specified by source and/or destination prefix
number or SIP Request-URI, as well as by call initiator. The side ("leg") on which the recording is
done must be specified. Specifying the leg is important as it determines the various call media
attributes of the recorded RTP (or SRTP) such as coder type.
The device can also record SRTP calls and send it to the SRS in SRTP. In such scenarios, the
SRTP is used on the IP leg. For an SBC RTP-SRTP session, the recorded IP Group in the SIP
Recording table must be set to the RTP leg if recording is required to be RTP, or set to the SRTP
leg if recording is required to be SRTP.
For SBC calls, the device can also be located between an SRS and an SRC and act as an RTP-
SRTP translator. In such a setup, the device receives SIP recording sessions (as a server) from
the SRC and translates SRTP media to RTP, or vice versa, and then forwards the recording to the
SRS in the translated media format.
- 203 -

 Loading...
Loading...
















