Part II: Settings and Measurements
9-3
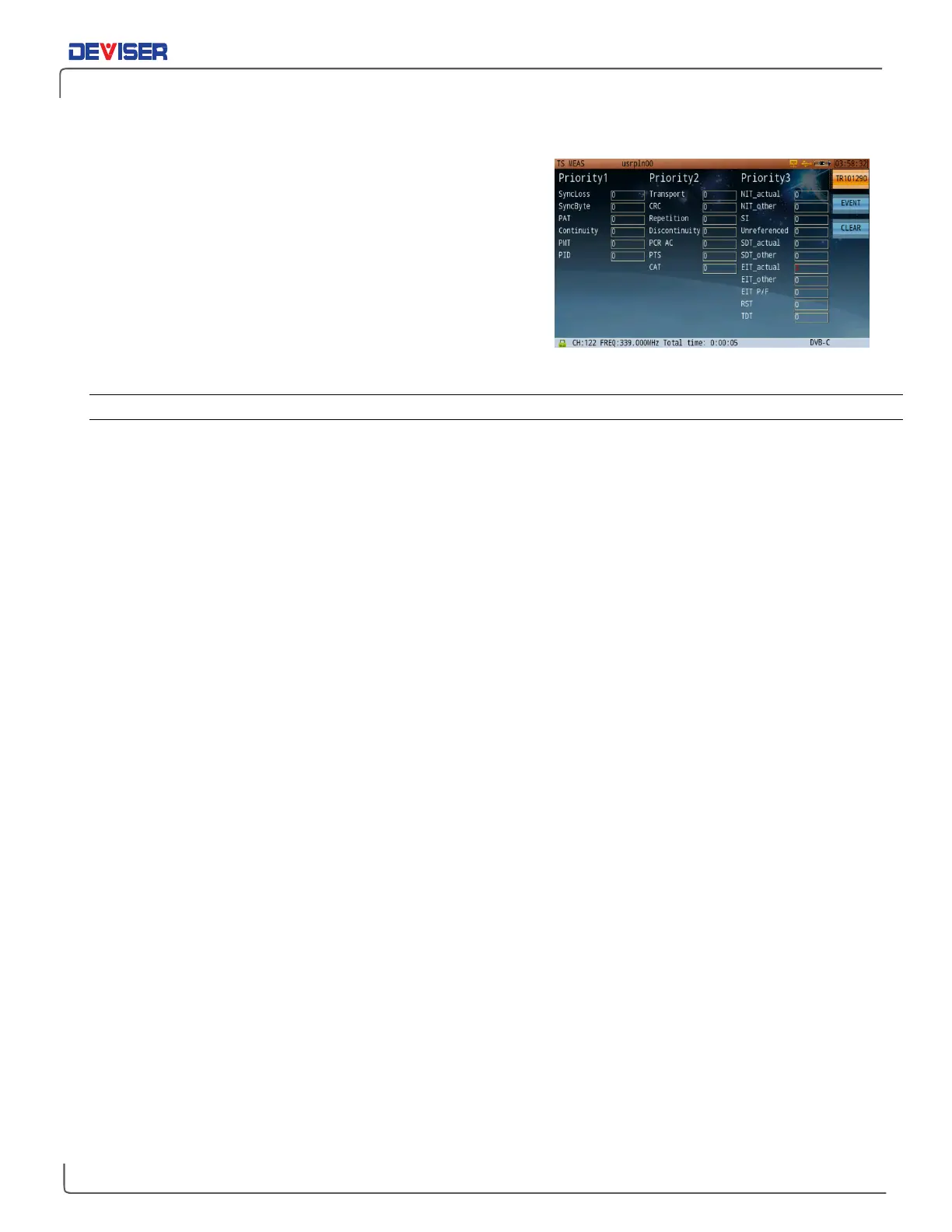
TR 101 290 Priority 1, 2 and 3 Tests
The DVB group has established a battery of recommended
measurements to perform on transport streams, set forth in the
ETSI TR101290 document. Based on TR 101 290 advisories, errors
to be detected by means of these recommended tests are
graded into three levels of priority: Priority 1, 2, and 3.
Priority 1 – no decidability
Priority 2 – partially no decidability
Priority 3 – errors in the supplementary information/SI
Due to hardware resource limits, the DS2831’s TS analysis does not include buffer-test-related parameters.
9-3.1 Priority 1 Parameters
(1) TS_sync_loss: It is suggested that five consecutive correct sync bytes are sufficient for sync acquisition,
and two or more consecutive corrupted sync bytes indicate a sync loss. The loss of transport stream
synchronization, which may occur either because of severe interference or simply because of a break in
the line, is called “TS_sync_loss”. “TS_sync_loss” occurs when the content of the sync bytes of at least 3
successful transport stream packets is not equal to 0x47.
(2) Sync_byte_error: is set as soon as the correct sync byte (0x47) does not appear after 188 or 204 bytes.
This is fundamental since this structure is used throughout the channel encoder and decoder chains for
synchronization. It is also important for the decoder to check every sync byte for correctness since the
encoders may not necessarily check the sync byte. Some encoders may use the sync byte flag signal on
a parallel interface to control the randomizer re-sending a byte inversion without checking that the
corresponding byte is a valid sync byte. A “sync_byte_error” occurs when the content of a sync byte in
the transport stream header is not equal to 0x47.
(3) PAT_error: The Program Association Table (PAT), only appears in PID 0x0000 packets, tells the decoder
what programs are in the TS and points to the Program Map Tables (PMT) which in turn point to the
component video, audio and data streams that make up the program. If the PAT is missing then the
decoder can decode no programs.
A PAT error occurs when: 1.- the PAT is missing, 2.- the repetition rate is greater than 500 ms, 3.- the PAT is
scrambled or 4.- the table ID is not equal to zero.
(4) Continuity_count_error: Each transport stream packet contains a 4-byte-long header, a 4-bit counter
which counts from 0 to 15 in a loop, and then begins at zero again after an overflow (modulo 16
counter). However, each transport stream packet for each PID has its own continuity counter, i.e.
packets with a PID=100, e.g., have a different counter, as do packets with a PID=200. It is the purpose of
this counter to enable one to recognize missing or repeated transport stream packets of the same PID in
order to draw attention to any multiplexer problems.
Such problems can also arise as a result of errors in remultiplexing or due to random bit errors in the
transmission link. Although MPEG-2 allows discontinuities in the transport stream, they must be indicated
in the adaptation field, e.g. after a switch-over (discontinuity indicator=1). In the case of zero packets
(PID=0x1FF), discontinuities are allowed and are not verified.
A continuity_error occurs when
•
The same TS packet is transmitted twice without a discontinuity being indicated, or
•
If a packet is missing (count incremented by 2) without a discontinuity being indicated, or
•
The sequence of packets is wrong.
 Loading...
Loading...