MDS 05-6632A01, Rev. F MDS Orbit MCR/ECR Technical Manual 203
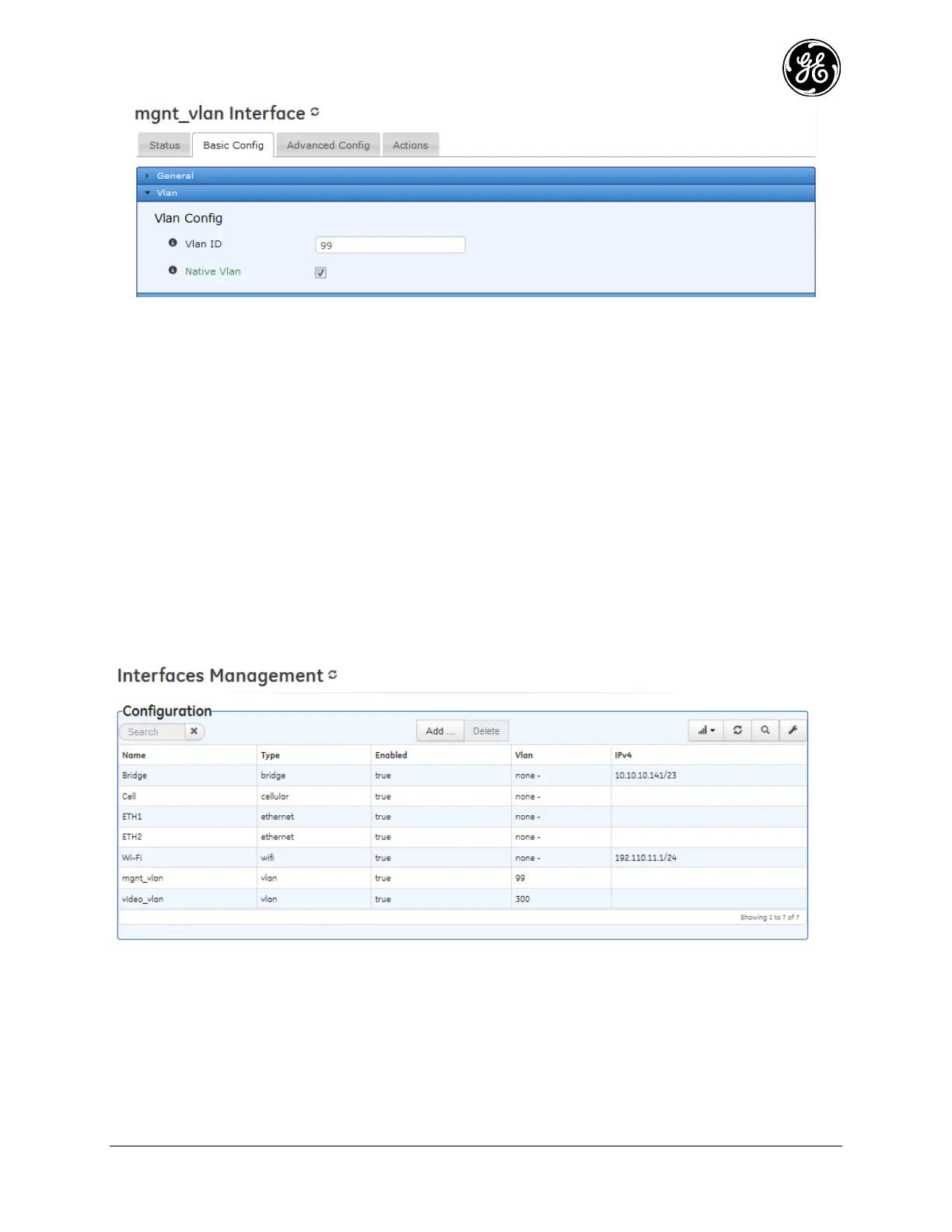
Figure 3-108. VLAN Configuration - VLAN Id
Or, using the CLI with this set command:
% set interfaces interface my_native_vlan type vlan vlan-config vlan-id 99 native-vlan true
A native VLAN is conceptually the same as a standard VLAN except that the packets will never be
tagged. The purpose of a native VLAN is to segregate untagged packets on a VLAN trunk port that
normally only contains tagged traffic. If a VLAN trunk port receives an untagged packet, and the trunk is
a member of the native VLAN, that packet will be treated as if it came from the native VLAN. If the
trunk port is not a member of the native VLAN and an untagged packet arrives on that port, the packet
will be dropped.
As VLANs are implemented as bridges, and it is not valid for a bridge to be a member of another bridge,
it follows that a VLAN interface cannot be configured as a member of a bridge. VLANs can be
configured with IP addresses just as any other interface in the system.
Monitoring
As shown previously once VLANs are created they may be monitored on the Interface status screen the
same way physical interfaces appear:
Figure 3-109. Interface Status Screen
Bridging 3.8.5
Understanding
The unit supports transparent bridging of LAN, WiFi/900Mhz networks. The bridge forwards traffic
between LAN and WiFi/900Mhz networks at the layer-2 of OSI model. This allows LAN and
WiFi/900Mhz clients to be in the same IP sub-network.
 Loading...
Loading...