8.1 Overview and Flow of Tuning
8.1.1 Tuning Function
8-3
8.1
Overview and Flow of Tuning
Tuning is performed to optimize response by adjusting the servo gains in the SERVOPACK.
The servo gains are set using a combination of parameters, such as parameters for the speed
loop gain, position loop gain, filters, and moment of inertia ratio. These parameters influence
each other, so you must consider the balance between them.
The servo gains are set to stable settings by default. Use the various tuning functions to
increase the response even further for the conditions of your machine.
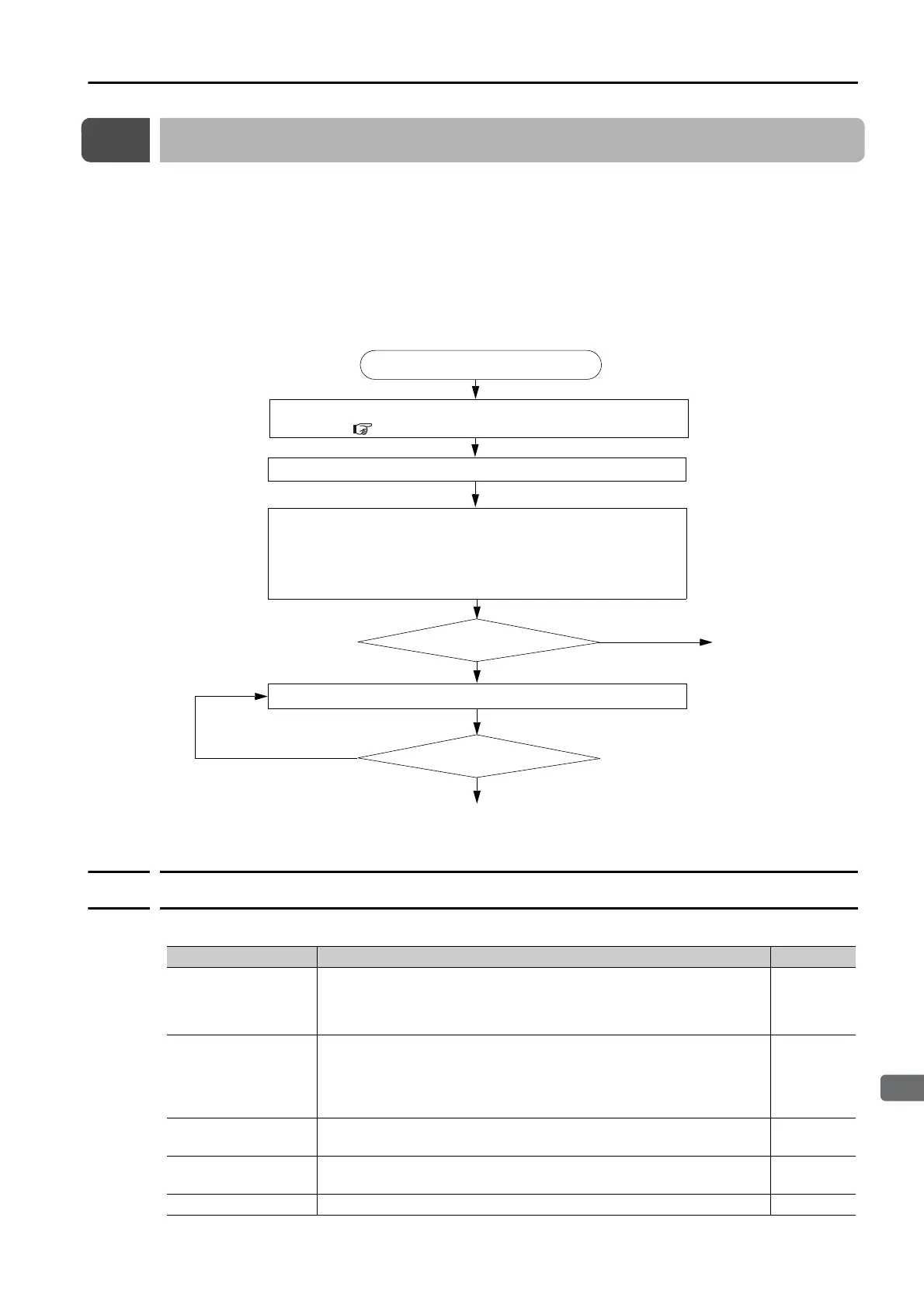
The basic tuning procedure is shown in the following flowchart. Make suitable adjustments
considering the conditions and operating requirements of your machine.
8.1.1
Tuning Function
The following table provides an overview of the tuning functions.
Start of Tuning
Results acceptable?
Yes
End
No
Results acceptable?
No
End
Yes
Perform custom tuning.
Continuous Vibration
Adjust anti-resonance control.
Residual Vibration When Positioning
Perform vibration suppression.
Estimating the Moment of Inertia
Initial Confirmations to Ensure Safe Tuning
8.3
Precautions to Ensure Safe Tuning
Manual Tuning
Tuning Functions Description Reference
Moment of Inertia
Estimation
The moment of inertia ratio is calculated by operating the Servomotor a
few times.
The moment of inertia ratio that is calculated here is used in other tun-
ing functions.
page 8-8
Custom Tuning
The following parameters are adjusted with the reference input from the
host controller while the machine is in operation.
• Gains (e.g., position loop gain and speed loop gain)
• Filters (torque reference filter and notch filters)
• Anti-resonance control
page 8-15
Anti-resonance
Control Adjustment
This function effectively suppresses continuous vibration.
page 8-24
Vibration
Suppression
This function effectively suppresses residual vibration if it occurs when
positioning.
page 8-28
Manual Tuning You can manually adjust the servo gains to adjust the response.
page 8-32

 Loading...
Loading...











