OPERATION
Carl Zeiss Illumination and Contrasting Method Axio Scope.A1
80 M60-2-0007 e 05/08
• Bring the object to be examined into the field of view and turn it with the rotary stage. Normally,
birefringent (anisotropic) objects will now show the same color and intensity variations as described
above during rotation between crossed polarizers. Optically anotropic substances may remain dark
when an isotropic direction, e.g. from optically single-axle or double-axle crystals, is put parallel to the
observation direction.
4.1.6.2 Determination of the Polarization Direction n
γ '
(1) Application
The determination of the polarization direction of n
γ
or n
γ'
respectively (polarization direction with the
absolute or relative largest index of refraction) and n
α
or n
α'
respectively (polarization direction with the
absolute or relative smallest index of refraction) relative to the morphological directions, e.g. of crystal
surfaces, crystal needles or fibers, provide an important signature of the material. This method is also
used in the diagnosis of bio-crystals (e.g. gout and pseudo-gout).
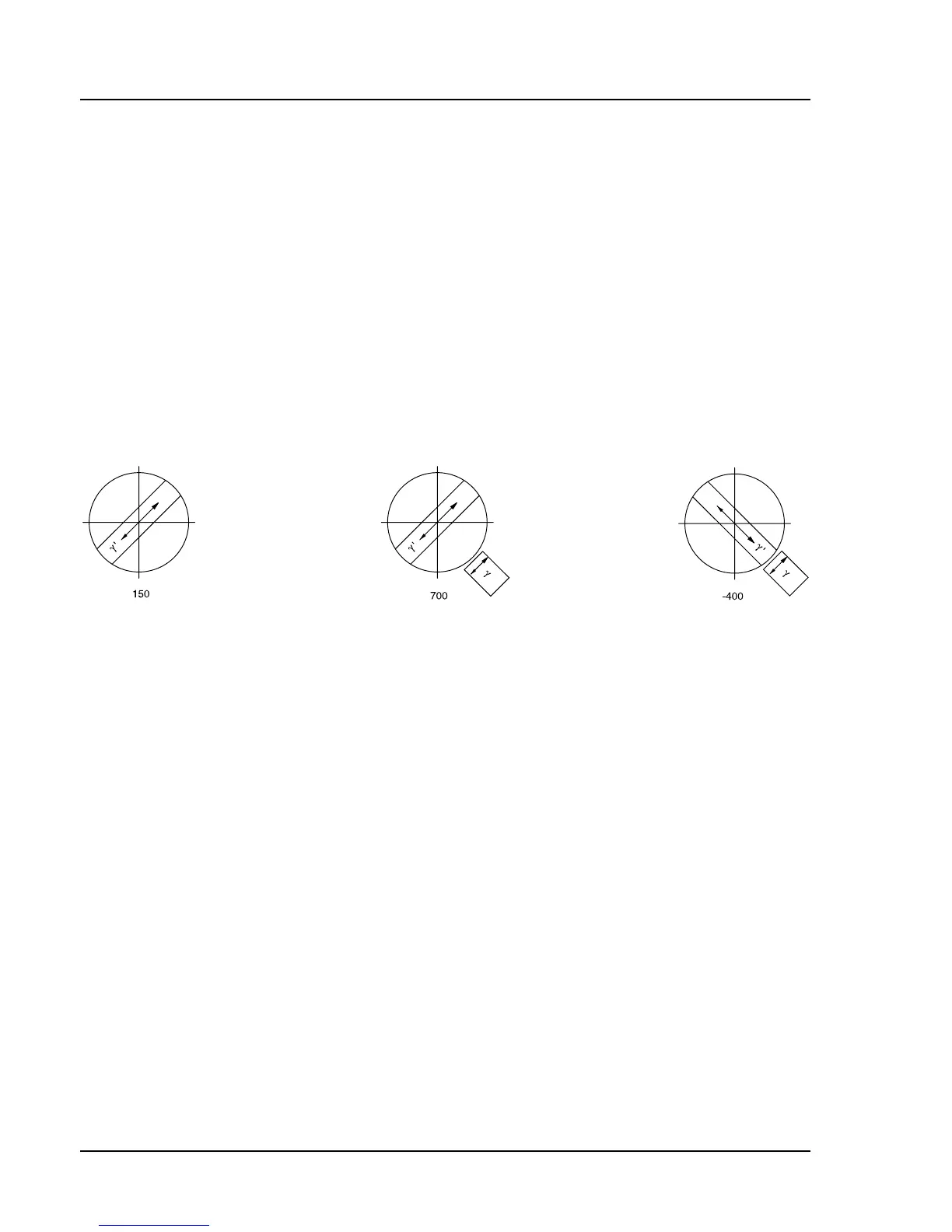
Fig. 4-8 Determination of the polarization direction n
γ'
in a synthetic fiber
(2) Instrumentation
− Eyepiece with graticule
− Tension-free objectives
− Rotary stage (
649H649HFig. 4-7/1)
− Polarizer D (rotatable or fixed), if not using a condenser with an integrated polarizer
− Analyzer module ACR P&C for transmitted light in the reflector turret/slider or analyzer slider D
fixed or with Lambda plate
− Adjustment sample for polarization microscopy (453679-0000-000)

 Loading...
Loading...