Appendix A
552
NOTE The computer has no idea which spectral region represents the
original signal. The signal processing routines simply use the
primitive values, that means the components in the Nyquist band.
So, if you are sampling a band-limited signal at bandpass
conditions, that means with a rate that is lower than twice the
highest frequency contained in that signal, you need to consider
that the DSP processes and reports the frequency components in
the Nyquist band.
Undersampling
Most often, lowpass conditions apply. That means, the signal to be
sampled has only an upper frequency limit F
in
. If the sampling
frequency F
s
is lower than twice the highest signal frequency, this
is called undersampling.
Undersampling
causes Aliasing
Undersampling is characterized by a phenomenon called aliasing
or foldover.
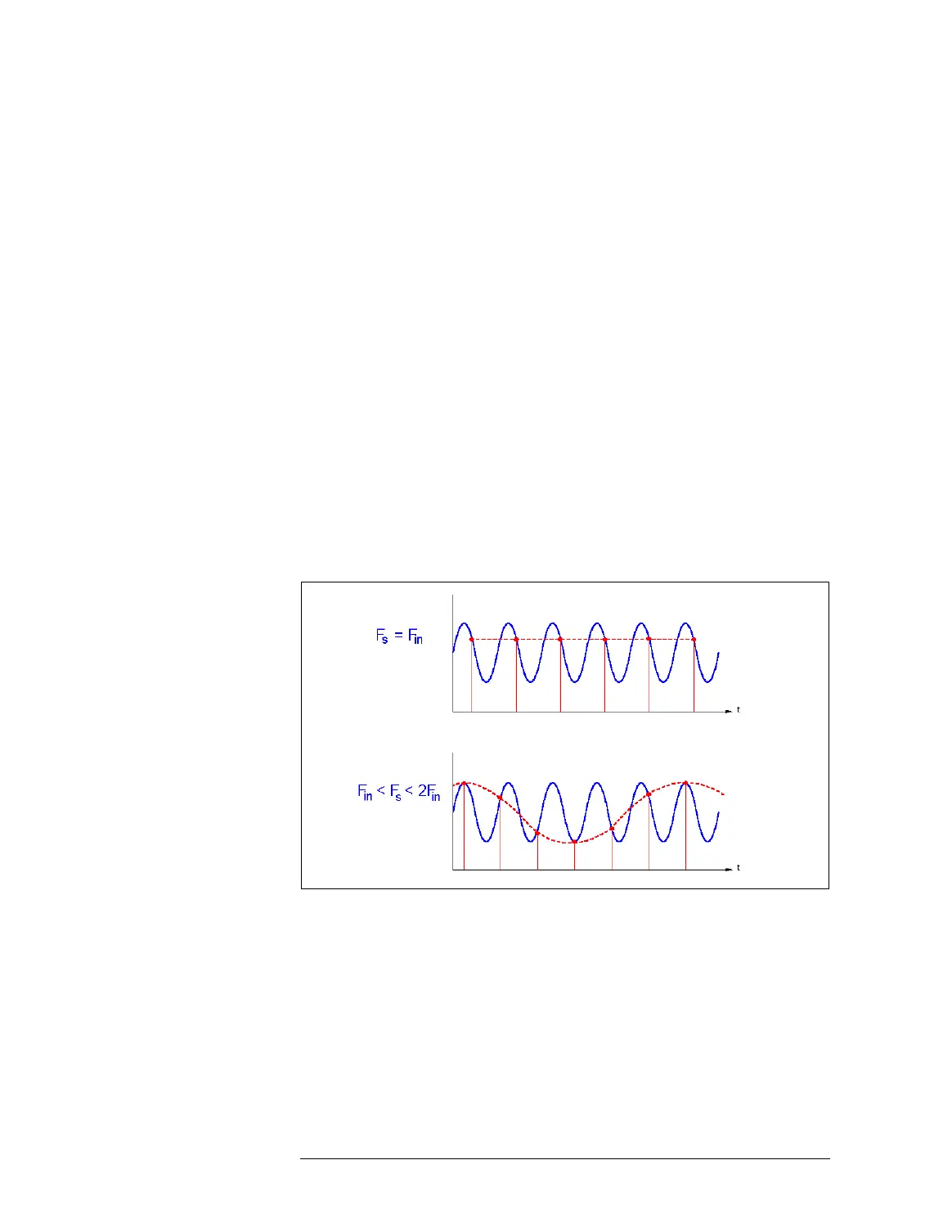
If we would sample a sinewave with its own base frequency F
in
, we
would get N points of equal value as shown in the figure below.
Undersampling Examples in Time Domain
If we would use a sampling frequency F
s
between F
in
and 2F
in
, the
samples will form a sinewave, but with a significantly lower
frequency than F
in
. This frequency is called the alias of the
original. It is caused by foldover (a kind of mirroring).
The alias frequency is |F
s
– F
in
|.

 Loading...
Loading...