Page F–4
DuRApulse GS4 AC Drive User Manual – 1st Ed, Rev A - 10/20/2017
Appendix F: PID Control
deFinitions and inForMation For high-Functioning Pid ParaMeters
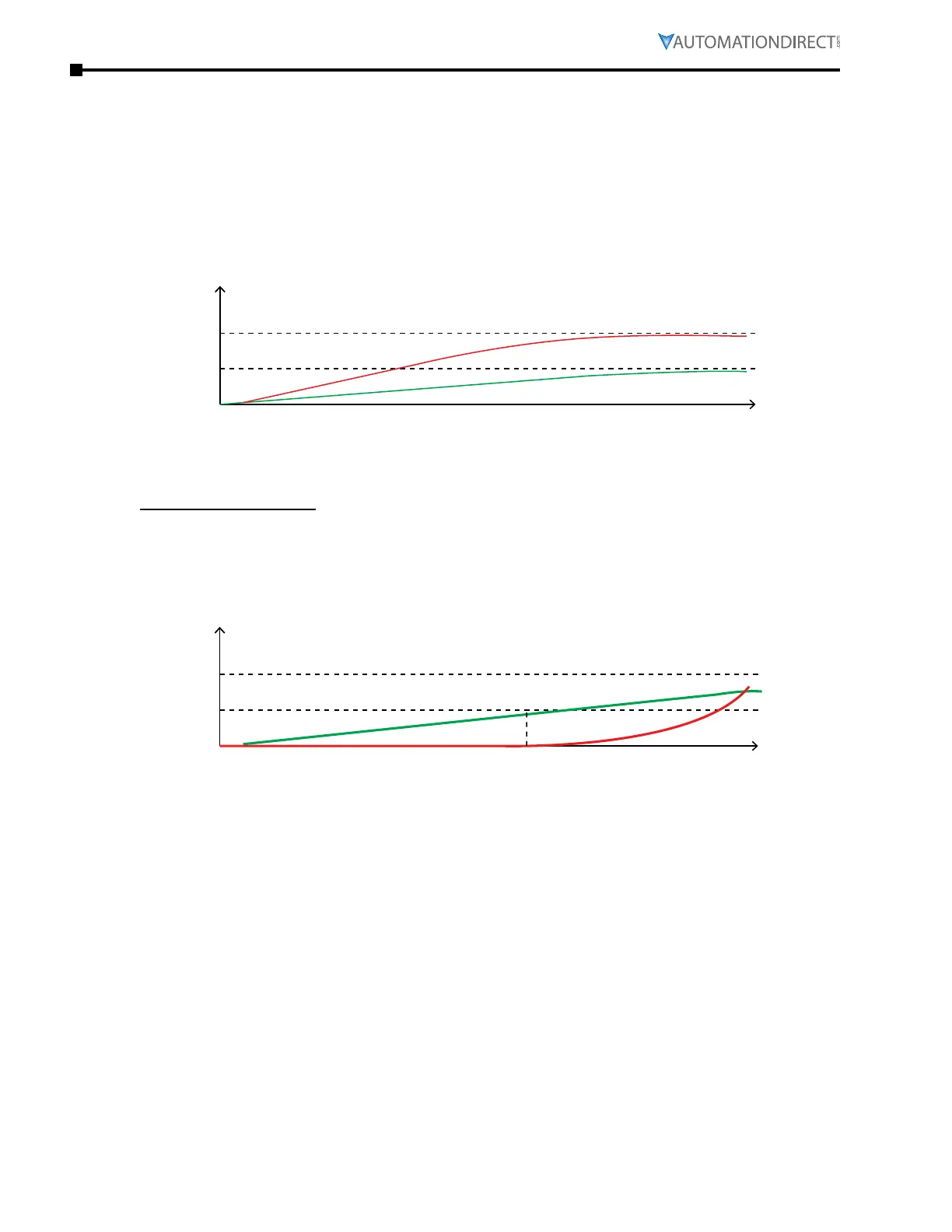
The PID function controls the output frequency of the inverter according to PID calculation, which
is based on the deviation between target and feedback. The inverter adjusts its output frequency
to correct the deviation. PID can be configured for Negative or Positive Feedback.
negative Feedback (Pid Forward)
Output frequency increases if deviation value is negative. Output frequency will increase quickly
if the negative deviation value is large (Setpoint > Feedback). Otherwise, output frequency will
increase gently if the negative deviation value is small.
Please see picture below for example.
Output
Frequen
Feedback
Max
equency
Setpoint
Positive Feedback (Pid reverse)
Deviation value decreases as output frequency decreases. This equals reverse acting control,
where controller output decreases as the process variable increases.
Positive Feedback means: -Target Value + Feedback. This is used to modify the detection or
deviation value which will be decreased by increasing the output frequency.
Output frequency increases if deviation value is positive. Output frequency will increase quickly if
the positive deviation value is large (Setpoint < Feedback). Otherwise, it will increase gently if the
positive deviation value is small.
Please see picture below for example.
Output Frequency
Feedbac
Max
equency
Setpoint

 Loading...
Loading...