Section 3 — Stack and Intake Vent Sizing and Installation
3-10 Part No. 750-363
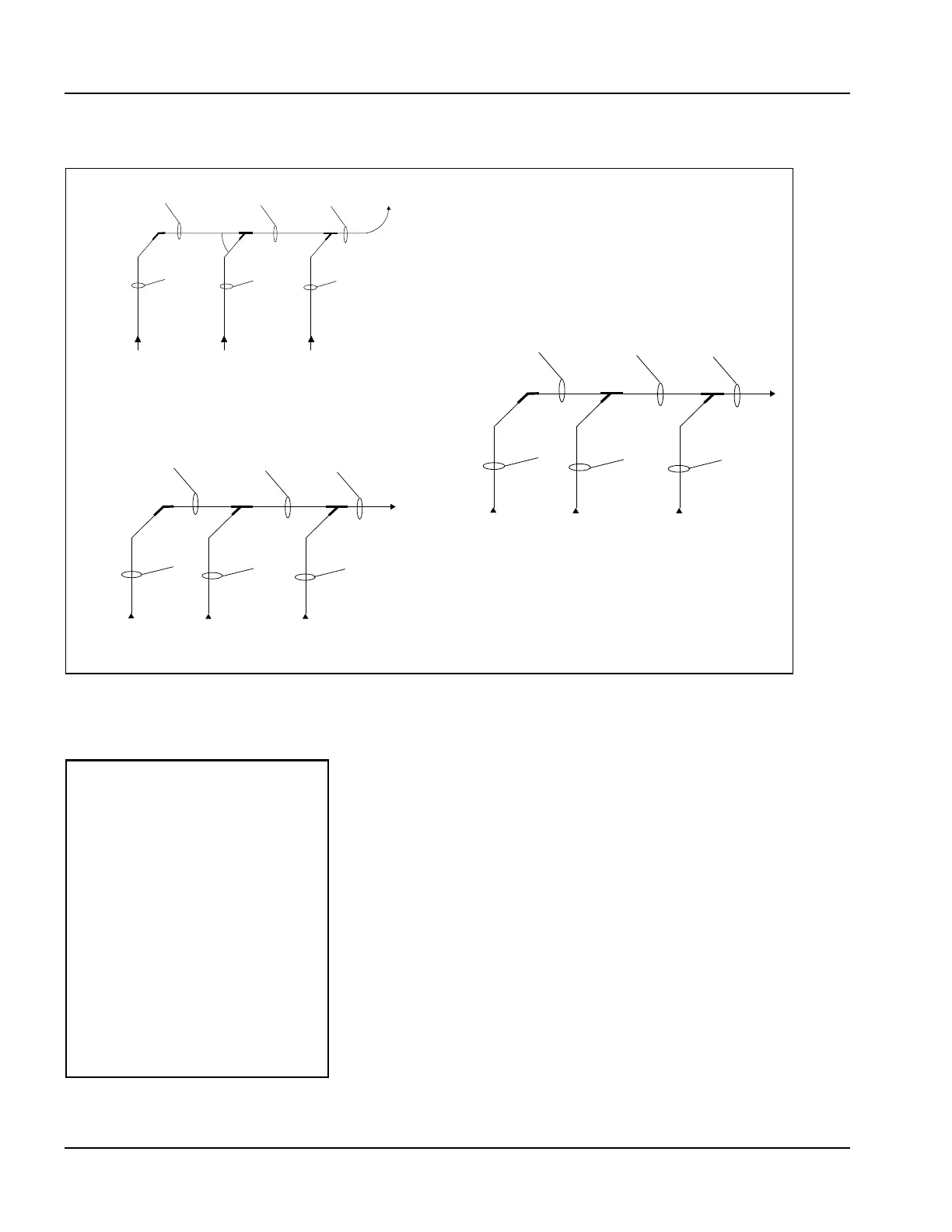
EXAMPLE 3
3.5 COMBUSTI0N AIR/BOILER ROOM
VENTILATION REQUIREMENTS
The boiler(s) must be supplied with adequate quantities of
uncontaminated air to support proper combustion and equipment
ventilation. Air shall be free of chlorides, halogens, fluorocarbons,
construction dust or other contaminants that are detrimental to the
burner/boiler. If these contaminants are present, we recommend the
use of direct vent combustion provided the outside air source is
uncontaminated.
Combustion air can be supplied by means of conventional boiler
room venting, where ambient combustion air is drawn from the area
immediately surrounding the boiler (boiler room must be positive
pressure*), or with air ducted from the outdoors to the burner
cabinet (direct venting) or burner air intake (sealed combustion). All
installations must comply with local Codes and with NFPA 54 (the
National Fuel Gas Code - NFGC) for the U.S. and for Canada, CAN/
CGA B 149.1 and B 149.2.
*A boiler room exhaust fan is not recommended as this type of device can cause
a negative pressure in the boiler room if using a conventional wall louvered air
intake.
14”
14” 14”
14”
From Boilers
14”
14”
16”
24”
30”
16” 16”
16”
From Boilers
45
o
26”
26”
26”
14” 14”
14”
3
From boilers
to roof
vent
GOOD
BAD
GOOD
Combustion air methods
ROOM AIR
Air is drawn from the boiler room.
DIRECT VENTING
Air is ducted from the outdoors to
the burner cabinet. No direct
connection to burner air intake.
SEALED COMBUSTION
Outside air is ducted directly to
the burner air intake.

 Loading...
Loading...