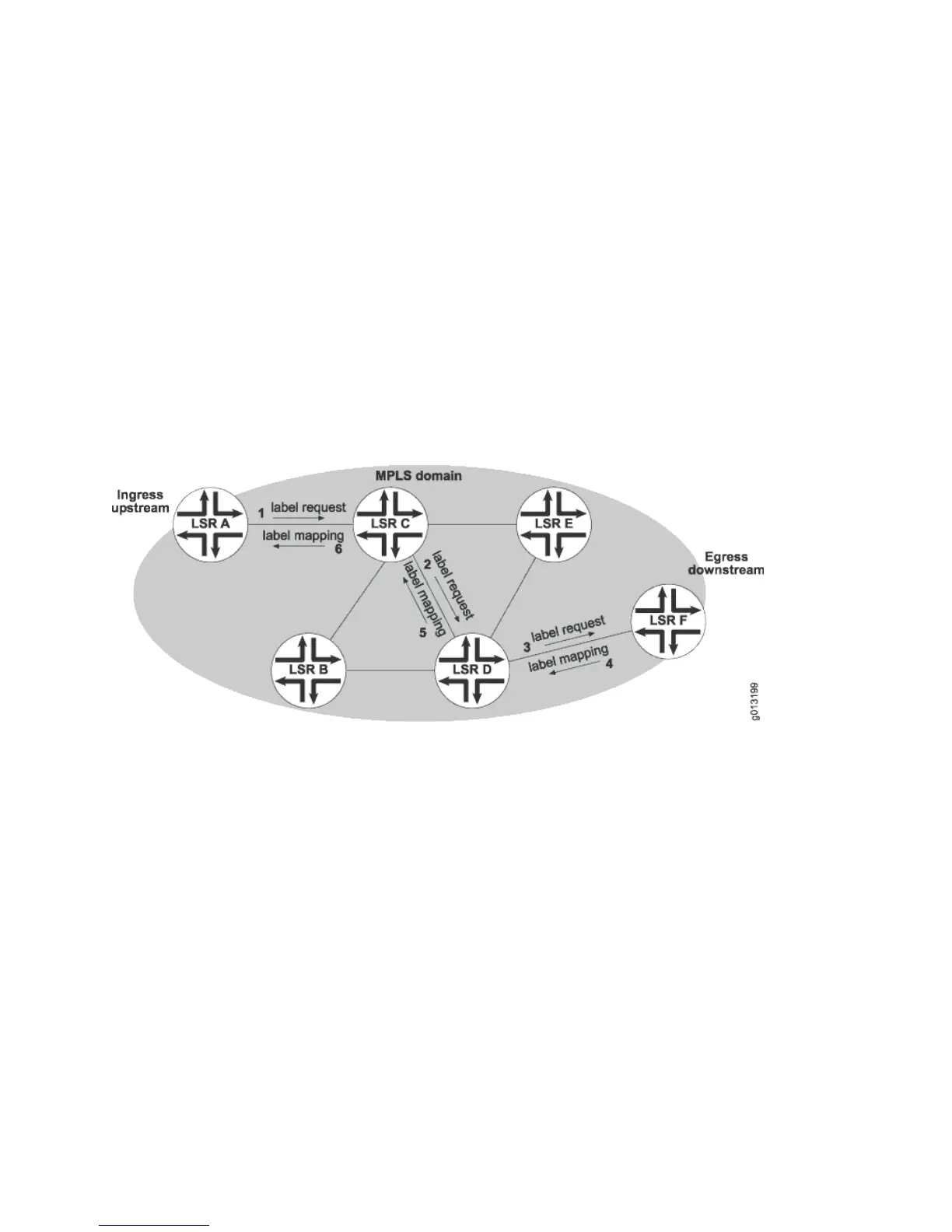
In Figure 53 on page 219, LSR A sends a label request to LSR C. Before LSR C responds,
it sends its own request to LSR D. LSR D in turn makes a request for a label to LSR
F. When LSR F returns an acceptable label to LSR D, that label is for use only between
LSRs D and F. LSR D sends a label back to LSR C that this pair of LSRs will use. Finally,
LSR C sends back to LSR A the label that they will use. This completes the
establishment of the LSP.
Downstream-unsolicited means that MPLS devices do not wait for a request from an
upstream device before signaling FEC-to-label bindings. As soon as the LSR learns a
route, it sends a binding for that route to all peer LSRs, both upstream and
downstream. Downstream-unsolicited does not conserve labels, because an LSR
receives label mappings from neighbors that might not be the next hop for the
destination; it is used by BGP or LDP when adjacent peers are configured to use the
platform label space.
Figure 53: LSP Creation, Downstream-on-Demand, Ordered Control
Independent control means that the LSR sending the label acts independently of its
downstream peer. It does not wait for a label from the downstream LSR before it
sends a label to its peers. When an LSR advertises a label to an upstream neighbor
before it has received a label for the FEC from the next-hop neighbor, the LSP is
terminated at the LSR. Traffic for the destination cannot be label-switched all the
way to the egress LSR. If no inner label is present, then the traffic is routed instead
of switched.
In Figure 54 on page 220, LSR D learns a route to some prefix. LSR D immediately
maps a label for this destination and sends the label to its peers, LSR B, LSR C, LSR
E, and LSR F. In the topology-driven network, the LSPs are created automatically
with each peer LSR.
MPLS Label Distribution Methodology ■ 219
Chapter 2: MPLS Overview

 Loading...
Loading...