Transporting Packets Across an IP Backbone with MPLS
As described in the previous section, PE 1 and PE 2 exchange routing information,
including MPLS labels for their customer sites, by means of a BGP session established
between them across the service provider core.
NOTE: To better understand MPLS before you read this section, see “Configuring
MPLS” on page 267.
Labels are employed in both the BGP control plane and the MPLS data plane. In the
control plane, BGP advertises a route with an in label; this in label is also the label
needed when MPLS traffic is received. BGP receives routes with an associated out
label; the out label is the label sent with MPLS traffic.
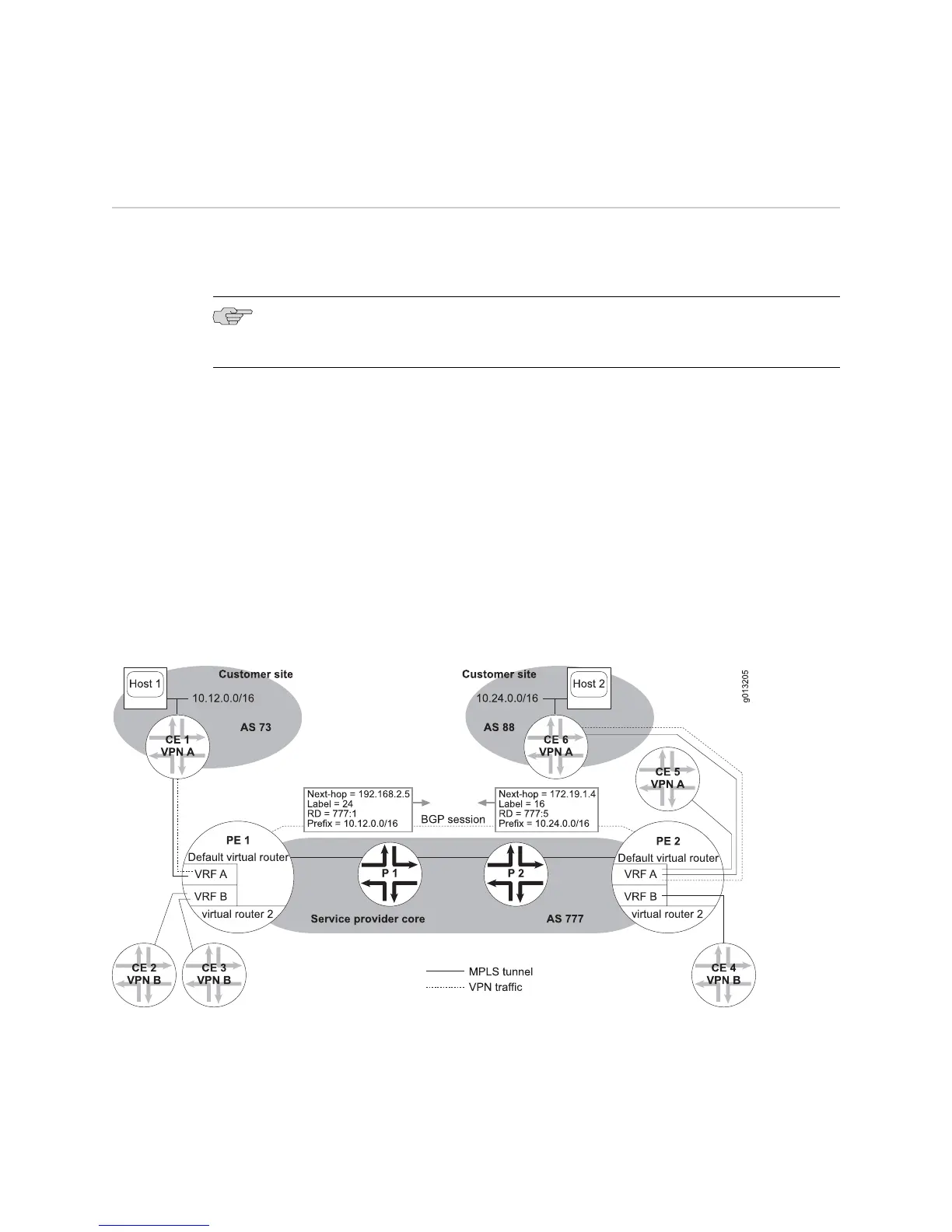
Consider the network shown in Figure 73 on page 390. If you display the in label on
PE 1, you see that MP-BGP advertises a labeled VPN-IPv4 prefix of 10.12.0.0/16 with
an in label of 24 (and an RD of 777:1, as shown in the illustration).
host1:pe1#show ip bgp vpn all field in-label
Prefix In-label
10.12.0.0/16 24
10.24.0.0/16 none
Figure 73: BGP/MPLS VPN Route Exchange
If you display the in label on PE 2, you see that MP-BGP advertises a labeled VPN-IPv4
prefix of 10.24.0.0/16 with an in label of 16 (and an RD of 777:5, as shown in the
illustration).
390 ■ Transporting Packets Across an IP Backbone with MPLS
JUNOSe 11.1.x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide

 Loading...
Loading...