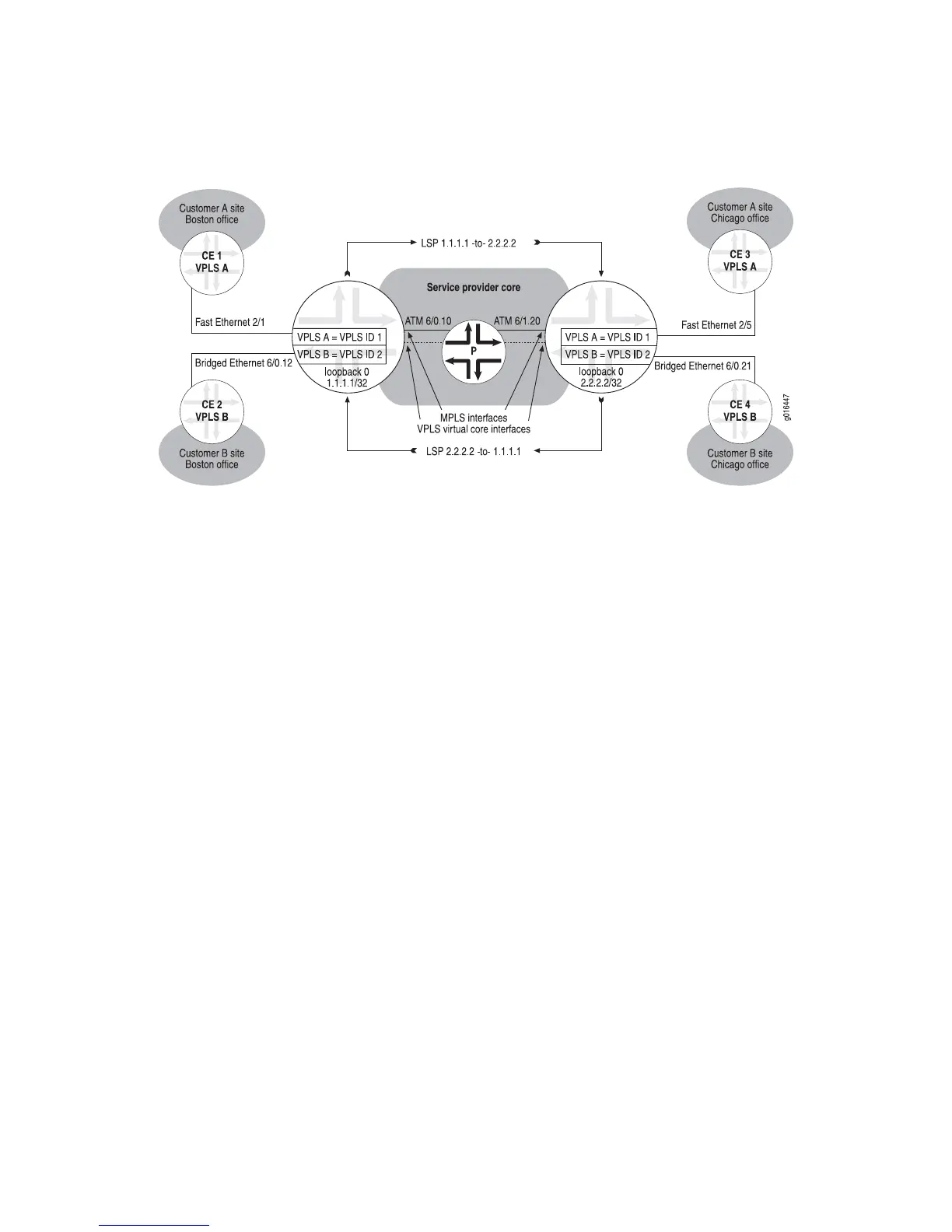
Figure 130: Topology for VPLS Configuration Example with LDP Signaling
PE 1
Default virtual router
PE 2
Default virtual router
Topology Overview of VPLS with LDP Signaling
Because the basic components of a VPLS network are the same regardless of whether
BGP signaling or LDP signaling is used, the sample topology shown for LDP signaling
in Figure 130 on page 609 is almost identical to the sample topology shown for BGP
signaling in Figure 129 on page 602. Figure 130 on page 609 includes two VPLS
domains: VPLS A, which connects CE 1 and CE 3, and VPLS B, which connects CE 2
and CE 4. The local PE router, PE 1, and the remote PE router, PE 2, each participate
in both the VPLS A domain and the VPLS B domain, and have one VPLS instance
associated with each domain configured on each router.
Unlike a VPLS configuration with BGP signaling, a VPLS configuration with LDP
signaling requires that you configure a VPLS ID for each VPLS instance to uniquely
identify each VPLS domain. In the sample topology in Figure 130 on page 609, instance
vplsA is assigned VPLS ID 1, and instance vplsB is assigned VPLS ID 2 on both the
local PE router and the remote PE router. You must also configure a list of remote
neighbor (peer) addresses to which LDP can send or from which LDP can receive
targeted hello messages. In the sample topology, the remote neighbor configured
for PE 1 is PE 2 with IP address 2.2.2.2, and the remote neighbor configured for PE 2
is PE 1 with IP address 1.1.1.1.
The Ethernet and bridged Ethernet network interfaces, ATM core-facing interfaces,
VPLS virtual core interfaces, and MPLS LSPs play the same role in a VPLS topology
with LDP signaling as they do in a VPLS topology with BGP signaling. For more
information about these components, see “Topology Overview of VPLS with BGP
Signaling” on page 602.
Configuration on PE 1 (Local PE Router)
Use the following commands on the local PE router (PE 1) to configure the VPLS
topology shown in Figure 130 on page 609.
! Configure VPLS instance vplsA.
VPLS Configuration Example with LDP Signaling ■ 609
Chapter 10: Configuring VPLS

 Loading...
Loading...