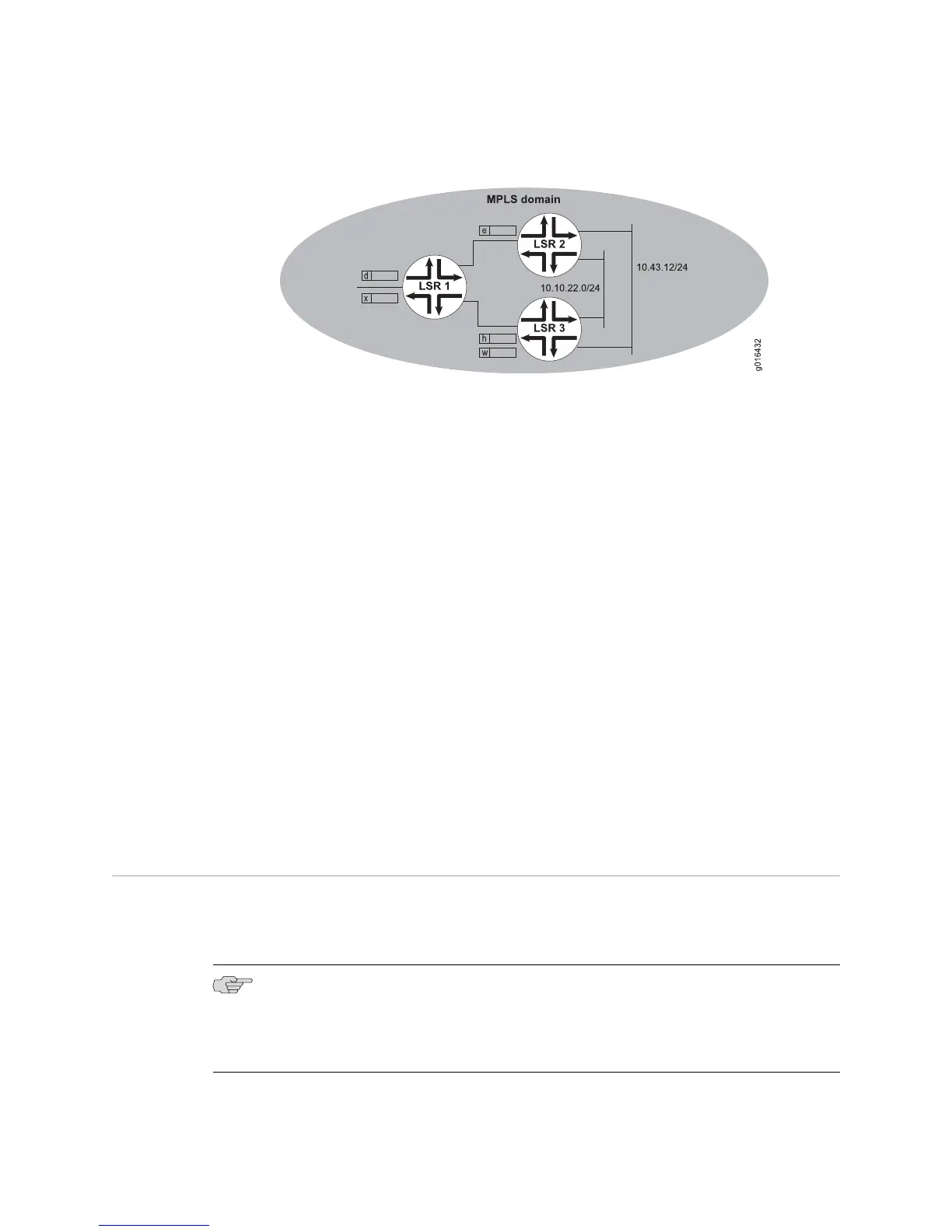
Figure 62: FEC Aggregation and Equal-Cost Paths
In this example, LSR 2 uses FEC aggregation, but LSR 3 does not. Consequently, LSR
2 advertises the single label e, mapped to a FEC that includes both prefixes,
10.10.22.0/24 and 10.43.12.0/24.
In contrast, LSR 3 has two FECs, one for 10.10.22.0/24 and one for 10.43.12.0/24.
A separate label is bound to each FEC. LSR 3 advertises label h for one FEC and
label w for the other FEC.
LSR 2 and LSR 3 are downstream routers for LSR 1. LSR 1 does not aggregate. Instead,
LSR 1 advertises label d for 10.10.22.0/24 and label x for 10.43.12.0/24.
To configure MPLS LDP FEC deaggregation to bind each prefix on the current virtual
router to a separate label:
■ Issue the mpls ldp deaggregate command:
host1(config)#mpls ldp deaggregate
Related Topics Basic MPLS Configuration Tasks on page 268■
■ Additional LDP Configuration Tasks on page 281
■ mpls ldp deaggregate
Configuring LDP Graceful Restart
The graceful restart mechanism minimizes the negative effect on MPLS forwarding
across an LSR restart by enabling neighbors to wait for the LSR to restart and causing
the LSR itself to restart gracefully.
NOTE: Successful operation of LDP graceful restart requires that stateful SRP
switchover (high availability) be configured on the router. Although you can configure
LDP graceful restart if stateful SRP switchover is not configured on the router, the
graceful restart capability will not function.
To configure LDP graceful restart:
282 ■ Configuring LDP Graceful Restart
JUNOSe 11.1.x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide

 Loading...
Loading...