NXP Semiconductors
UM11227
NTM88 family of tire pressure monitor sensors
UM11227 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP B.V. 2020. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 6 — 24 April 2020
11 / 205
• Many instructions treat X as a second general-purpose 8-bit register
• Seven addressing modes:
– Inherent — Operands in internal registers
– Relative — 8-bit signed offset to branch destination
– Immediate — Operand in next object code byte(s)
– Direct — Operand in memory at 0x0000–0x00FF
– Extended — Operand anywhere in 64 kB address space
– Indexed relative to H:X — Five submodes including auto-increment
– Indexed relative to SP — Improves C efficiency dramatically
• Memory-to-memory data move instructions with four address mode combinations
• Overflow, half-carry, negative, zero, and carry condition codes support conditional
branching on the results of signed, unsigned, and binary-coded decimal (BCD)
operations
• Efficient bit manipulation instructions
• Fast 8-bit by 8-bit multiply and 16-bit by 8-bit divide instructions
• STOP and WAIT instructions to invoke low-power operating modes
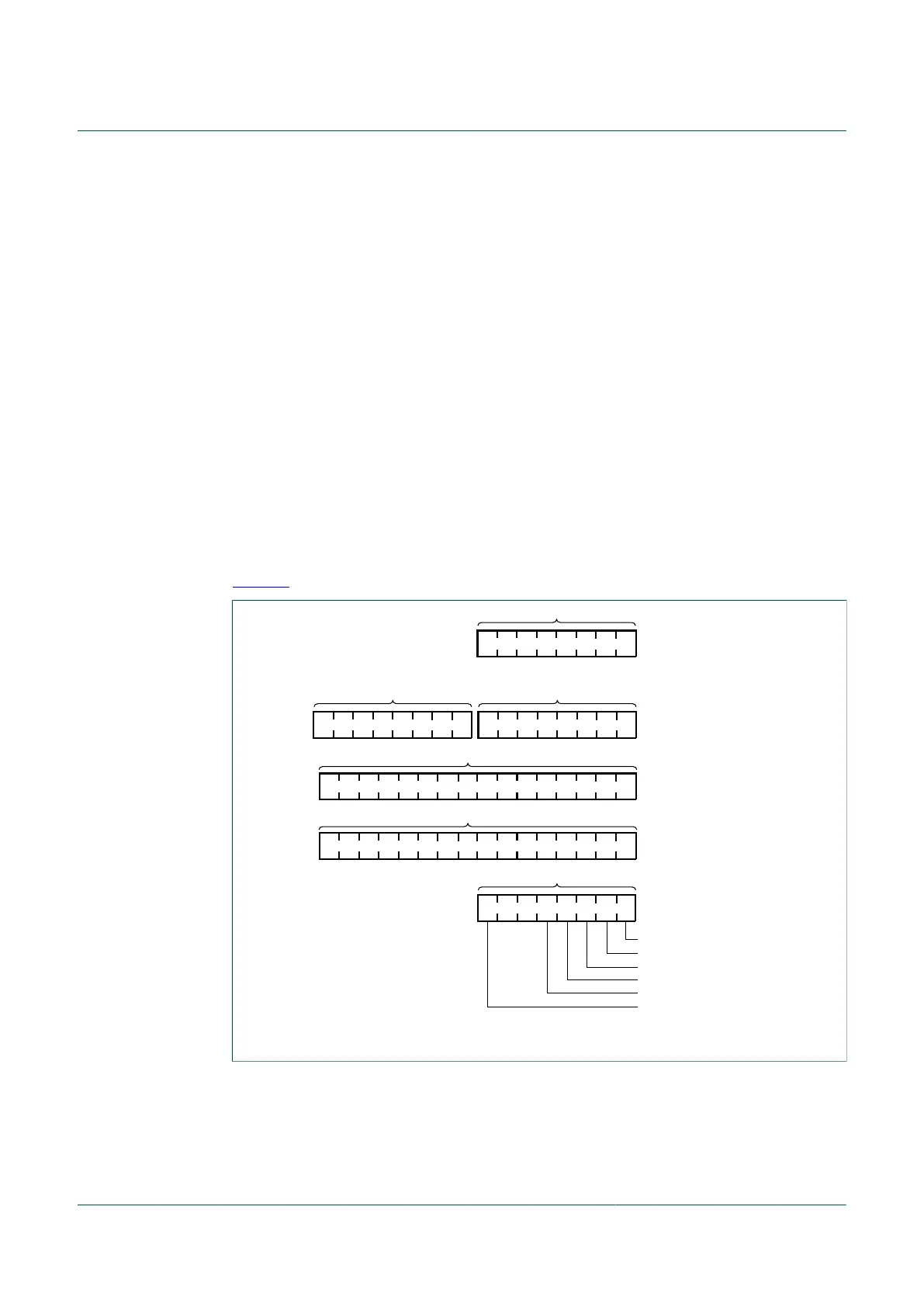
8.3 Programmer’s model and CPU registers
Figure 5 shows the five CPU registers. CPU registers are not part of the memory map.
aaa-028004
accumulator
A
index register (low)index register (high)
16-bit index register H:X
XH
stack pointer
condition code register
V 1 1 H I N Z C
SP
CCR
Carry
Zero
Interrupt mask
Two's complement overflow
Half-carry (from bit 3)
Negative
program counter pointer
PC
Figure 5. CPU registers
8.3.1 Accumulator (A)
The A accumulator is a general-purpose 8-bit register. One operand input to the
arithmetic logic unit (ALU) is connected to the accumulator and the ALU results are often
stored into the A accumulator after arithmetic and logical operations. The accumulator
 Loading...
Loading...