Part B - System description cobas p 512
2-20 Operator's Manual - Version 1.6 - 10/2015
means of infrared light. It then transmits the upper and lower level of the respective sample
material to the system's control computer.
In the second step, the camera module determines the tube's type (and thus its dimensions)
via cap color identification. The system then calculates the respective volume of the tube's
content on the basis of this information.
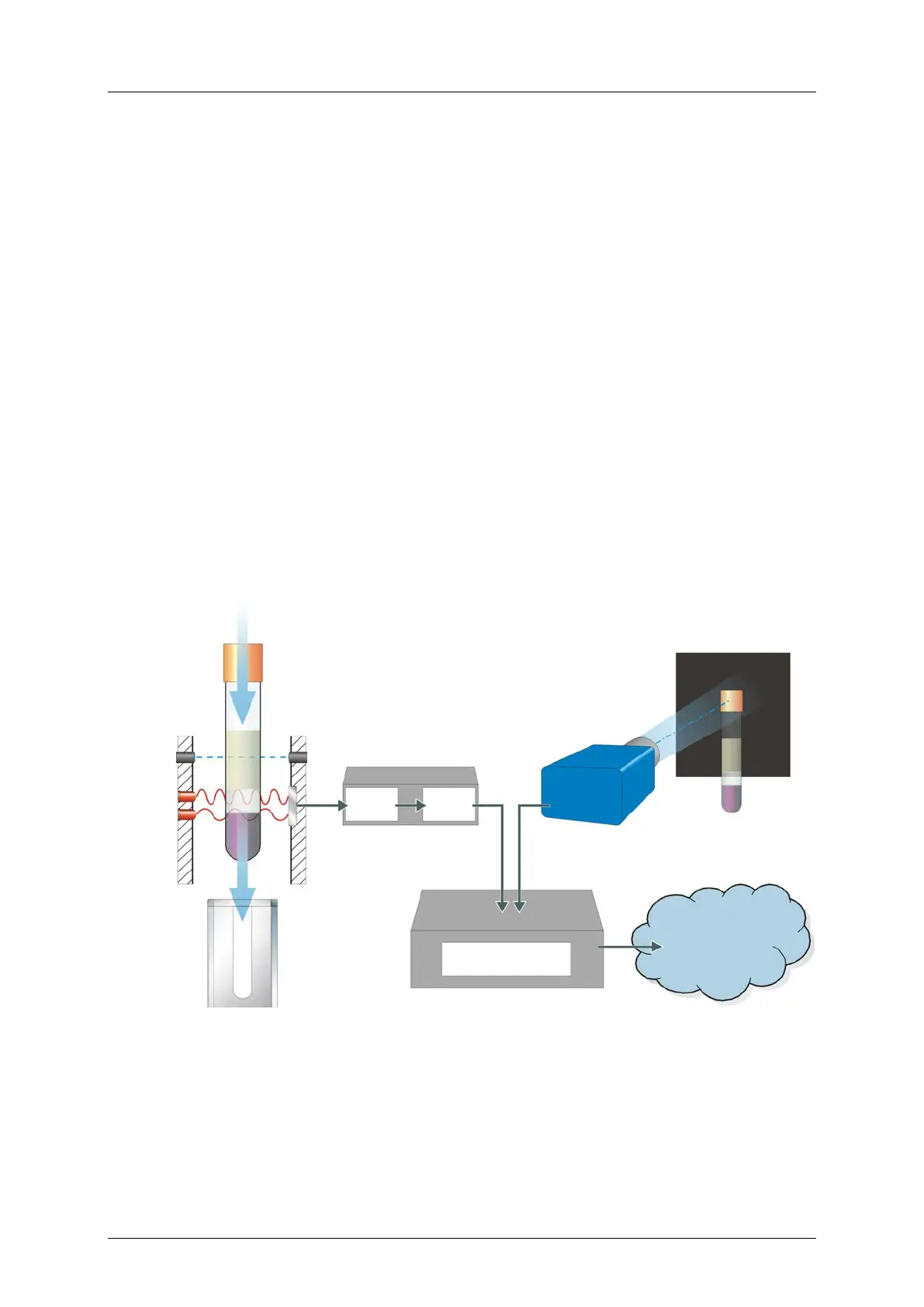
Measurement principle
An optical measuring procedure is used for determination of the material transitions within
the sample tube. This procedure works by two infrared emitters of different wavelength and a
receiver element sensitive for both wavelengths.
When starting the measurement, the emitters are pulsed by a microprocessor (µP) sending
the corresponding signals to a LED driver. Received signals from the sensor element are
supplied via an amplifier back to the microprocessor (µP) again. The availability of new
measuring data is then reported to the NetPC. Their transmission towards the NetPC is
initiated on request. Once the NetPC has evaluated the received measuring data, the results
are sent to the system's control computer.
In a second step, the system's camera module identifies the tube's type and thus determines
its dimensions. Both liquid level data and tube dimensions are then used to calculate the
volume of the sample material inside the tube.
The following schematic diagram provides an overview of the work steps described above:
Figure 2-15: Schematic diagram
camera (tube type identification module)
processor
control computer

 Loading...
Loading...