COMMAND RANGING & TELEMETRY UNIT CORTEX
CRT QUANTUM USER'S MANUAL
Ref. DTU 100042
Is.Rev. 5.17
Date: Dec.
03, 2021Sept. 30, 2021
This document is the property of Safran Data Systems.
It cannot be duplicated or distributed without expressed written consent.
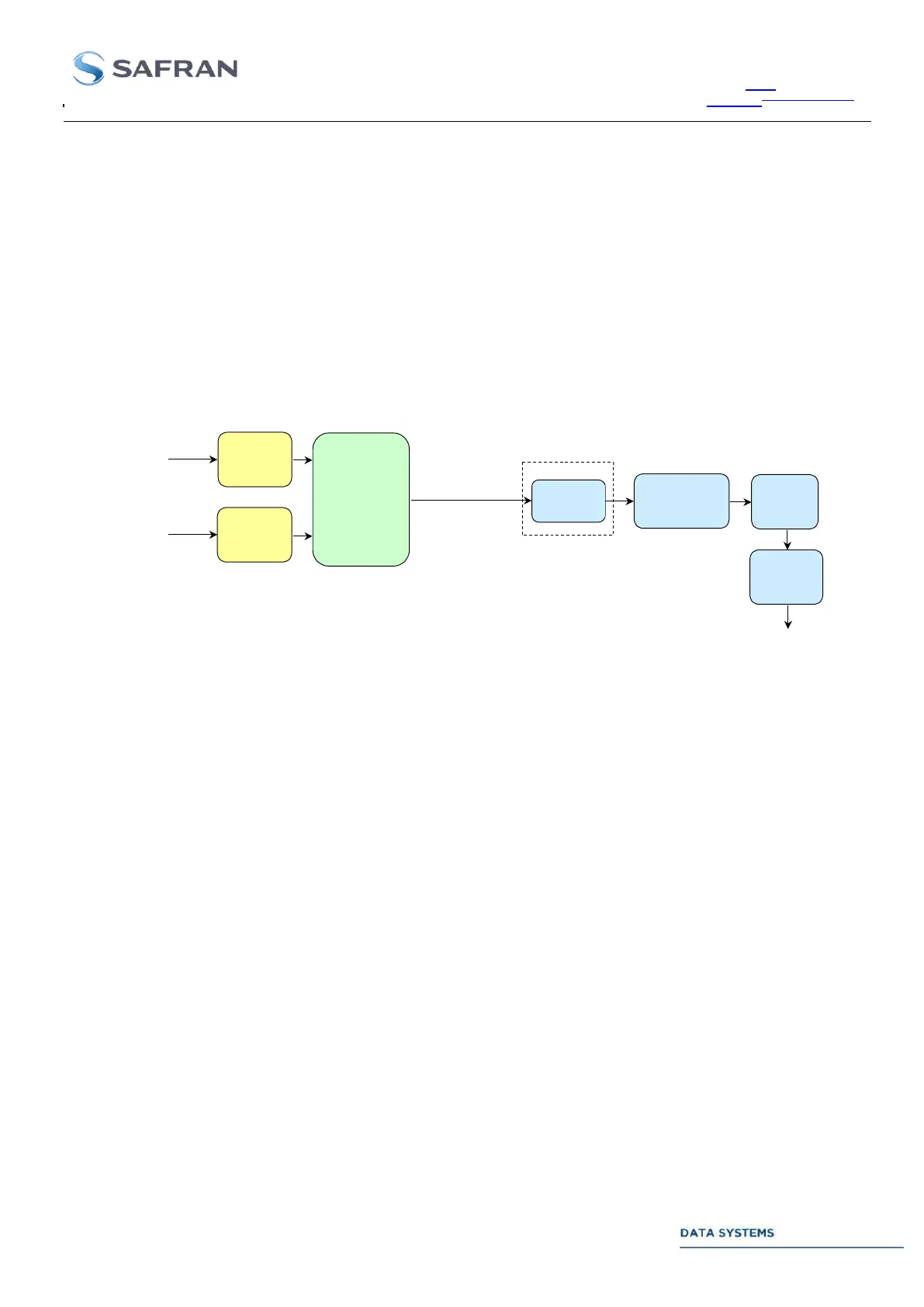
3.3.5.1.1. Post Detection Diversity Combining
The combining system is based on two independent IF Receivers (called Channel A and Channel B) which
outputs are weighted from the IF level information in Video mode or Eb/N0 information in PCM mode, and then
added to produce a PCM or Video signal which is then processed by the Frame Synchronizer (PCM mode) or
BPSK demodulator(s) (Video mode). The Frame Synchronizer or BPSK demodulator(s) can also be directly
connected to the output of any one of the two channels. Diversity combining is available for these types of
modulation schemes:
Video mode: PM demodulation,
PCM mode : PCM/PM, PCM/BPSK, PCM/QPSK or PCM/OQPSK (not yet supported in
PCM/AQPSK mode).
Sub Carrier
Demodulators
Frame
Synchronizer
(only with video demodulation)
PM,FM
BPSK,QPSK
demodulators
Channel A
IF input
Post Detection
Diversity
Combining
PM,FM
BPSK,QPSK
demodulators
Channel B
IF input
Viterbi decoder
Differential decoder
Turbo decoder
RS decoder
Figure 26: Post detection Diversity Combining : functional block diagram
For fast locking, as soon as an IF Receiver gets locked, the second receiver automatically by-passes the carrier
acquisition phase and attempts to phase lock onto a carrier which frequency is given by the first receiver
(expected IF + computed IF offset). The same process applies when a receiver unlocks: it then attempts to
directly phase-lock onto the carrier since its frequency is accurately measured by the other Receiver.
 Loading...
Loading...