Functions
2.14 Differential Protection and Its Protected Objects
SIPROTEC, 7UM62, Manual
C53000-G1176-C149-7, Release date 03.2010
104
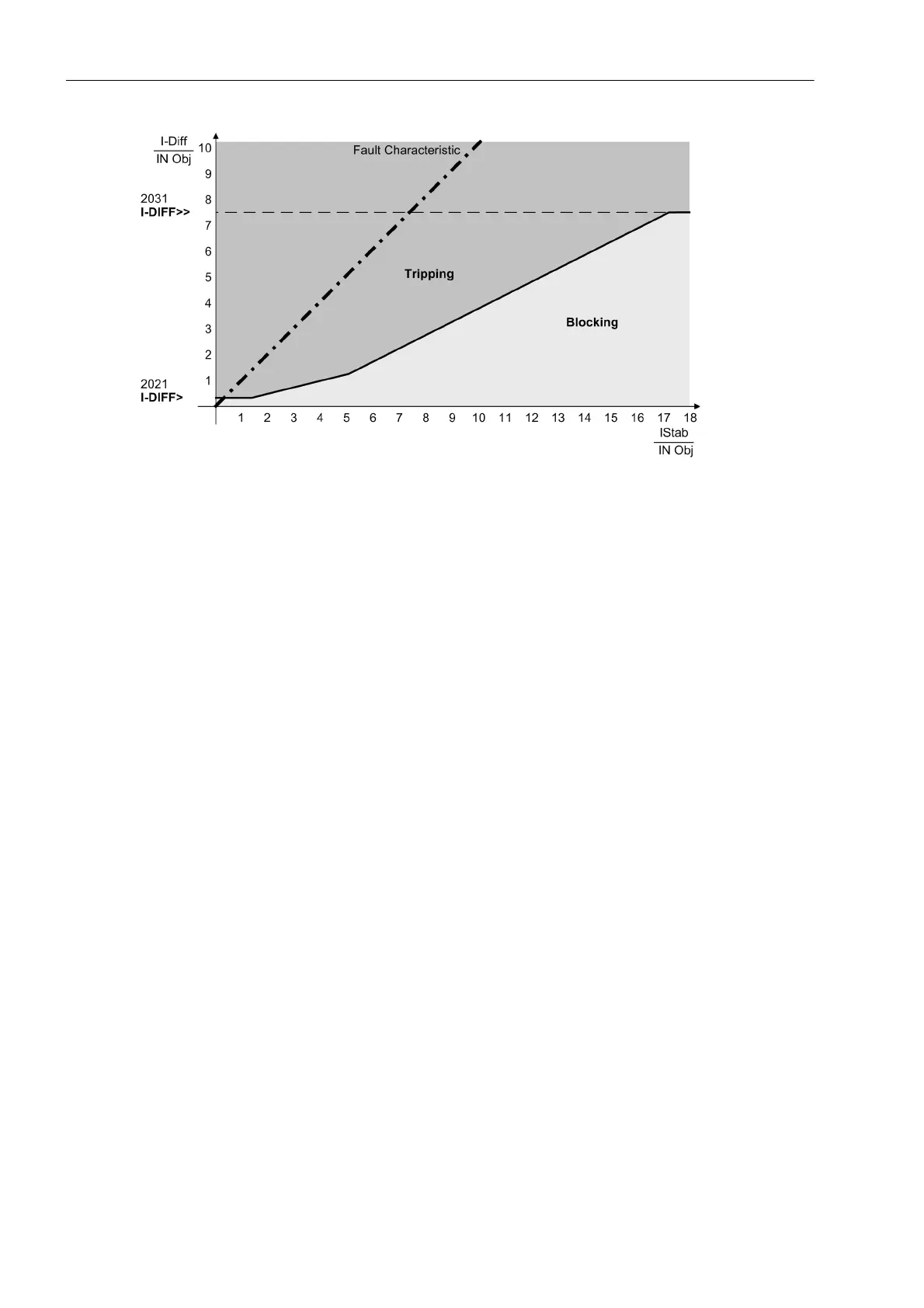
Figure 2-32 Tripping Characteristic of the Differential Protection with Fault Characteristic
Quantitative Matching of Measured values
The rated CT currents are matched to the rated current of the protected object, regardless of what that object
is. As a result, all currents are referred to the protected object. To match the currents, the characteristic values
of the protected object (apparent power, rated voltage) and the rated primary currents of the CTs are entered
in the protective device for each side of the protected object.
Evaluation of Measured Values
The measured values are calculated at each sampling instant and from them the instantaneous values of dif-
ferential and stabilizing current established. From the differential current, the fundamental frequency compo-
nent is determined using a Fourier filter, which effectively attenuates interference and aperiodic DC compo-
nents.
The stabilizing quantity is calculated from the arithmetic average of a rectified value, so that the filter effect is
less in this case. As a result, with interference quantities, compared with the differential current, the stabilization
component predominates, especially with aperiodic DC components.
Tripping Characteristic
This result shows that for internal fault I
diff
= I
stab
. Thus the characteristic of internal faults in the tripping diagram
(see following figure) is a straight line with a slope of 45°. The following figure illustrates the complete stabili-
zation characteristic of the 7UM62. The characteristic branch a represents the sensitivity threshold of the dif-
ferential protection (setting I-DIFF>) and considers constant error currents such as magnetizing currents.
Branch b considers current-proportional errors which may result from transformation errors of the main CTs
and the input CTs of the device, or which for example may be caused by mismatchings or by the influence of
tap changers in transformers with voltage control.
For high currents which may give rise to current transformer saturation, characteristic branch c provides for
additional stabilization.
In the presence of differential currents above branch d a trip command is issued regardless of stabilizing current
and harmonic stabilization. This is the operating range of the „High Speed Trip StageI
Diff
>>“.
The area of add-on stabilization is determined by the saturation indicator (see margin title "Add-on Stabiliza-
tion with CT saturation").

 Loading...
Loading...











