Functions
2.14 Differential Protection and Its Protected Objects
SIPROTEC, 7UM62, Manual
C53000-G1176-C149-7, Release date 03.2010
105
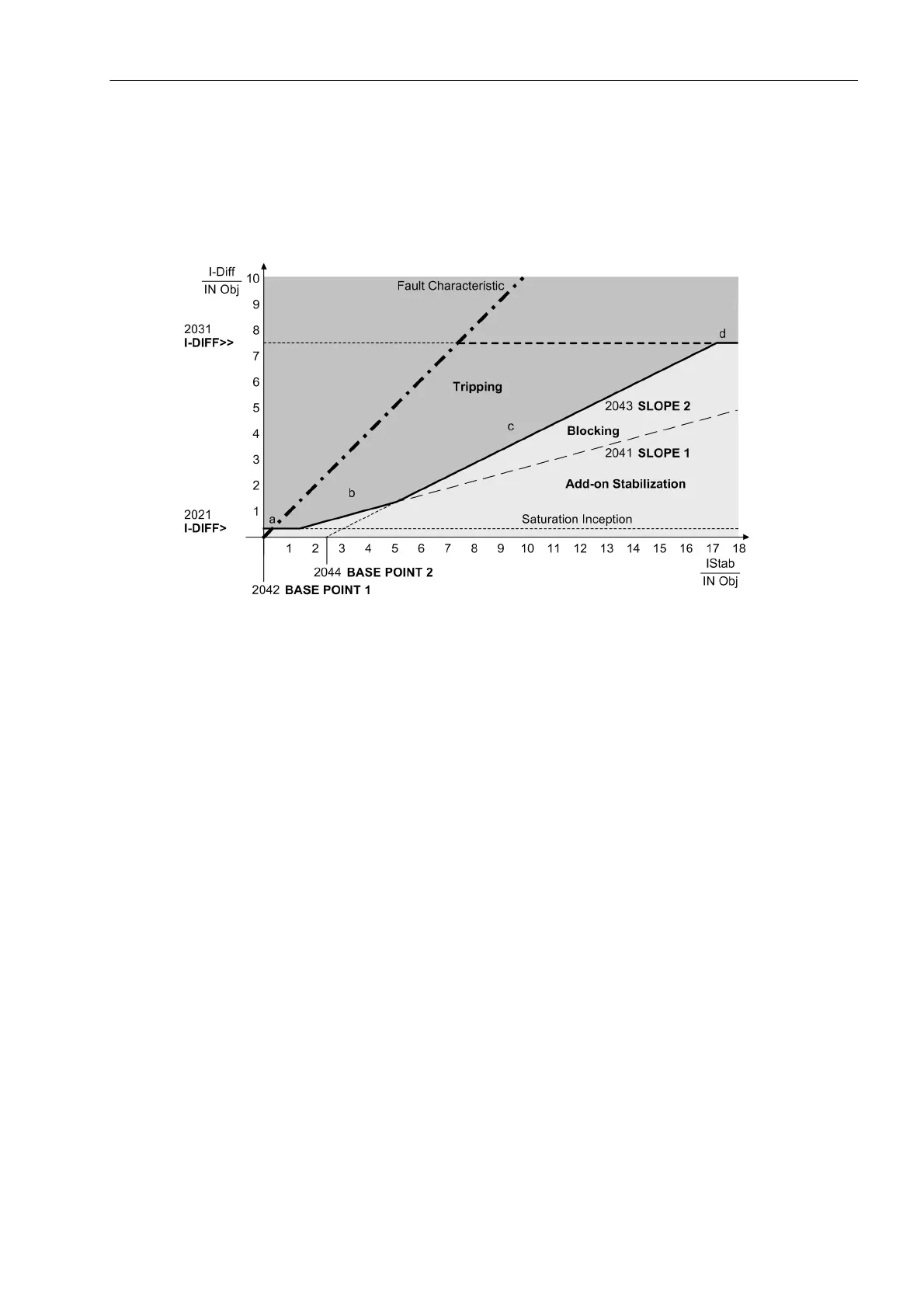
The currents II
diff
and I
stab
are compared by the differential protection with the operating characteristic according
to the following figure. If these values result result in a point within the tripping area, a trip signal is issued. If
the current conditions I
diff
/I
stab
appear near the fault characteristic (≥ 9 0 % of the slope of the fault character-
istic), tripping occurs even when the trip characteristic has been excessively increased due to add-on stabiliza-
tion, startup or DC current detection.
Figure 2-33 Operating Characteristic of the Differential Protection
High-Speed Tripping Stage I
diff
>>
The high-speed trip stage I
Diff
>> clears high-current internal faults instantaneously. As soon as the differential
current rises above the threshold I
Diff
>> (branch d), a trip signal is issued regardless of the magnitude of the
stabilizing current.
This stage can operate even when, for example, a considerable second harmonic is present in the differential
current caused by current transformer saturation by a DC component in the short-circuit current, and which
could be interpreted by the inrush stabilization function as an inrush current.
Fast tripping uses both the fundamental component of the differential current as well as instantaneous values.
Instantaneous value processing ensures fast tripping even if the current fundamental component was strongly
attenuated by current transformer saturation.
High-current internal faults in the protected transformer can be cleared instantaneously without regard to the
stabilizing currents whenever the current amplitude excludes an external fault. This is always the case when
the short-circuit current is higher than 1/u
SC
· I
N Transf
.

 Loading...
Loading...











