Functions
2.33 Interturn Protection (ANSI 59N (IT))
SIPROTEC, 7UM62, Manual
C53000-G1176-C149-7, Release date 03.2010
236
2.33 Interturn Protection (ANSI 59N (IT))
The interturn fault protection detects faults between turns within a generator winding (phase). This situation
may involve relatively high circulating currents that flow in the short-circuited turns and damage the winding and
the stator. The protective function is characterized by a high sensitivity.
Given the way the generators are constructed, it is rather unlikely that an interturn fault will occur.
Generators with a separate stator winding (e.g. large-sized hydro-electric generators) are more likely to be af-
fected. In this configuration, the transverse differential protection or the zero sequence current protection are
used instead between the connected starpoints.
2.33.1 Functional Description
Basic Principle
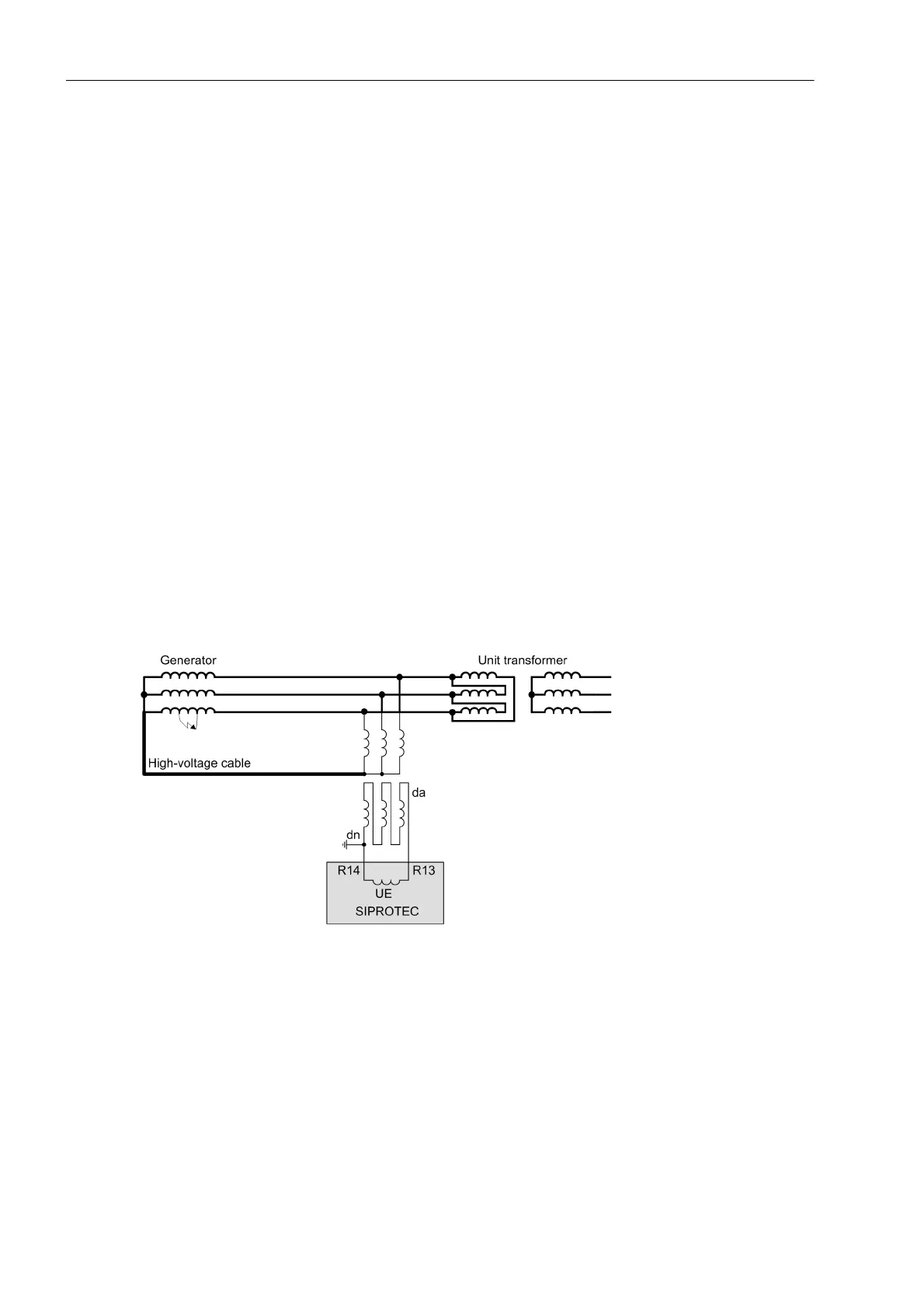
Figure 2-104 shows the basic principle of measurement. The displacement voltage is measured at the open
delta winding by means of 3 two-phase isolated voltage transformers. So as to be insensitive towards earth
faults, the isolated voltage transformer starpoint has to be connected to the generator starpoint by means of a
high-voltage cable. The voltage transformer starpoint must not be earthed since this implies that the generator
starpoint, too, would be earthed with the consequence that each fault would lead to a single-pole earth fault.
In the event of an interturn fault, the voltage in the affected phase will be reduced ultimately causing a displace-
ment voltage that is detected at the broken delta winding. The sensitivity is limited rather by the winding asym-
metries than by the protection device.
Figure 2-104 Standard connection of the interturn fault protection
Figure 2-105 shows an alternative connection example with limited sensitivity. The loading resistor is located
at the generator starpoint and the displacement voltage is measured via the voltage transformer. This voltage
transformer is equally used for the stator earth fault protection. The voltage transformer on the outgoing side is
earthed and has additionally a broken delta winding. The connection example shown in figure 2-105 has the
effect that the displacement voltage becomes zero at the measurement input of the interturn fault protection in
the event of an earth fault. In the event of an interturn fault, the displacement voltage occurs only at the open-
delta winding that is open on the outgoing side.

 Loading...
Loading...











