Functions
2.37 Restart Inhibit for Motors (ANSI 66, 49Rotor)
SIPROTEC, 7UM62, Manual
C53000-G1176-C149-7, Release date 03.2010
255
2.37 Restart Inhibit for Motors (ANSI 66, 49Rotor)
The rotor temperature of a motor generally remains well below its admissible limit temperature during normal
operation and also under increased load conditions. However, with startups and resulting high startup currents
caused by small thermal time constants of the rotor it may suffer more thermal damage than the stator. To avoid
that multiple starting attempts result in tripping, a new motor start must be prevented if it can be expected that
the allowed rotor heating would be violated by this starting attempt. Therefore the 7UM62 device provides a
motor restart blocking feature. An inhibit signal is issued until a new motor start is admissible (restarting thresh-
old). This blocking signal must be configured to a binary output of the device whose contact is inserted in the
motor starting circuit.
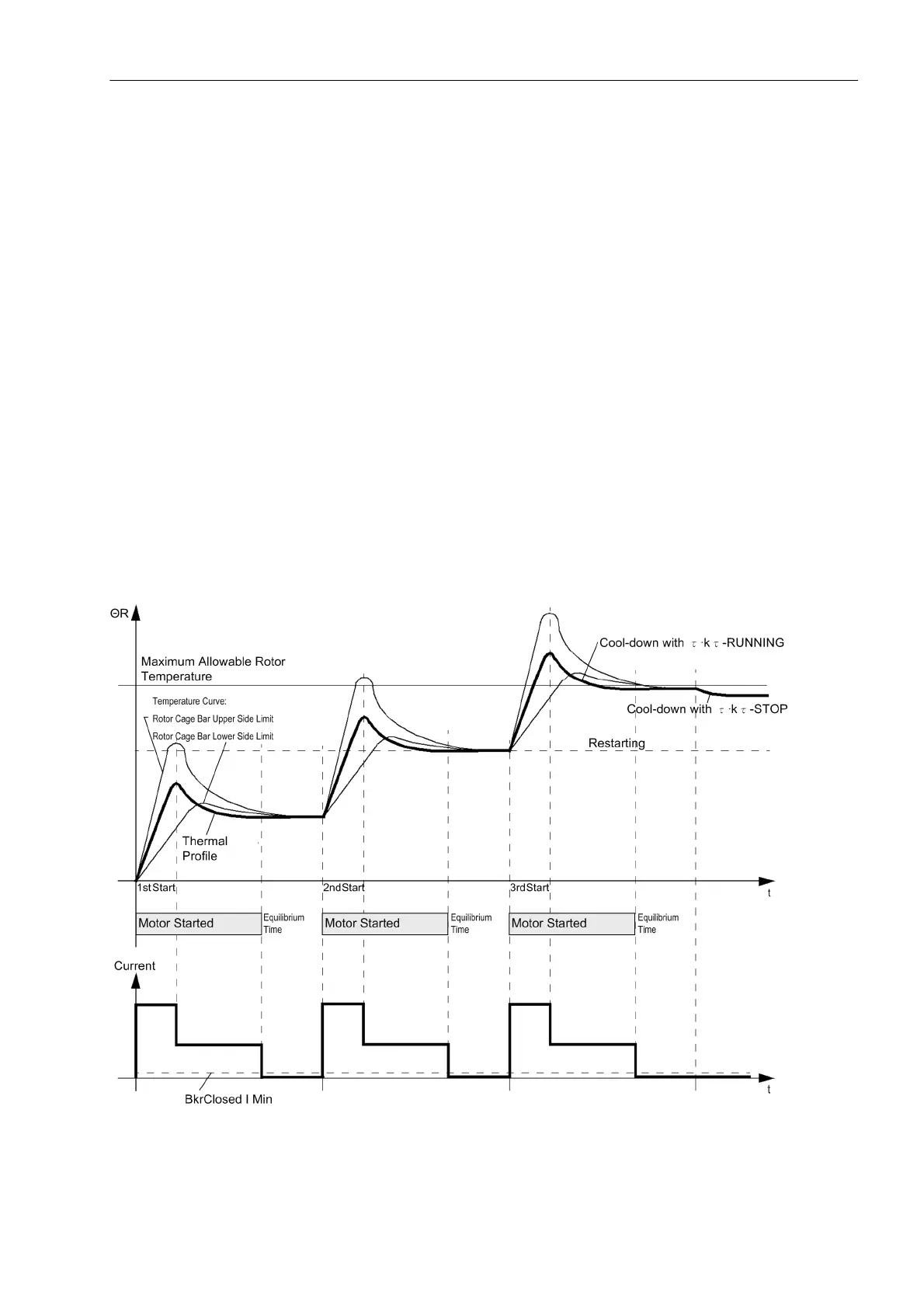
2.37.1 Functional Description
Determining the Rotor Overtemperature
Because rotor current cannot be measured directly, stator currents must be used. The rms values of the cur-
rents are used for this. Rotor overtemperature Θ
R
is calculated using the highest of the three phase currents.
For this it is assumed that the thermal limits for the rotor winding according to the manufacturer's data regarding
nominal startup current, maximum admissible starting time, and the number of starts permitted from cold (n
cold
)
and warm (n
warm
) state are just reached. From this data, the device calculates values for the thermal rotor profile
and issues a blocking signal until this profile decreases below the restarting threshold allowing restart.
Figure 2-116 Temperature Curve at the Rotor and the Thermal Profile during Repeated Start-Up Attempts

 Loading...
Loading...











