Functions
2.47 Phase Rotation
SIPROTEC, 7UM62, Manual
C53000-G1176-C149-7, Release date 03.2010
325
2.47 Phase Rotation
A phase sequence reversal feature via binary input and parameter is implemented in the 7UM62. This permits
all protection and monitoring functions to operate correctly even with phase rotation reversal, without the need
for two phases to be reversed.
If an anti-clockwise rotating phase sequence permanently exists, this should be entered in the power system
data (see Section 2.5).
If phase rotation can reverse during operation (e.g. in a pumped storage power station, transition from gener-
ator to pumping operation is done by changing the phase rotation), then a reversal signal at the input allocated
is sufficient to inform the protection device of phase-sequence reversal.
2.47.1 Functional Description
Logic
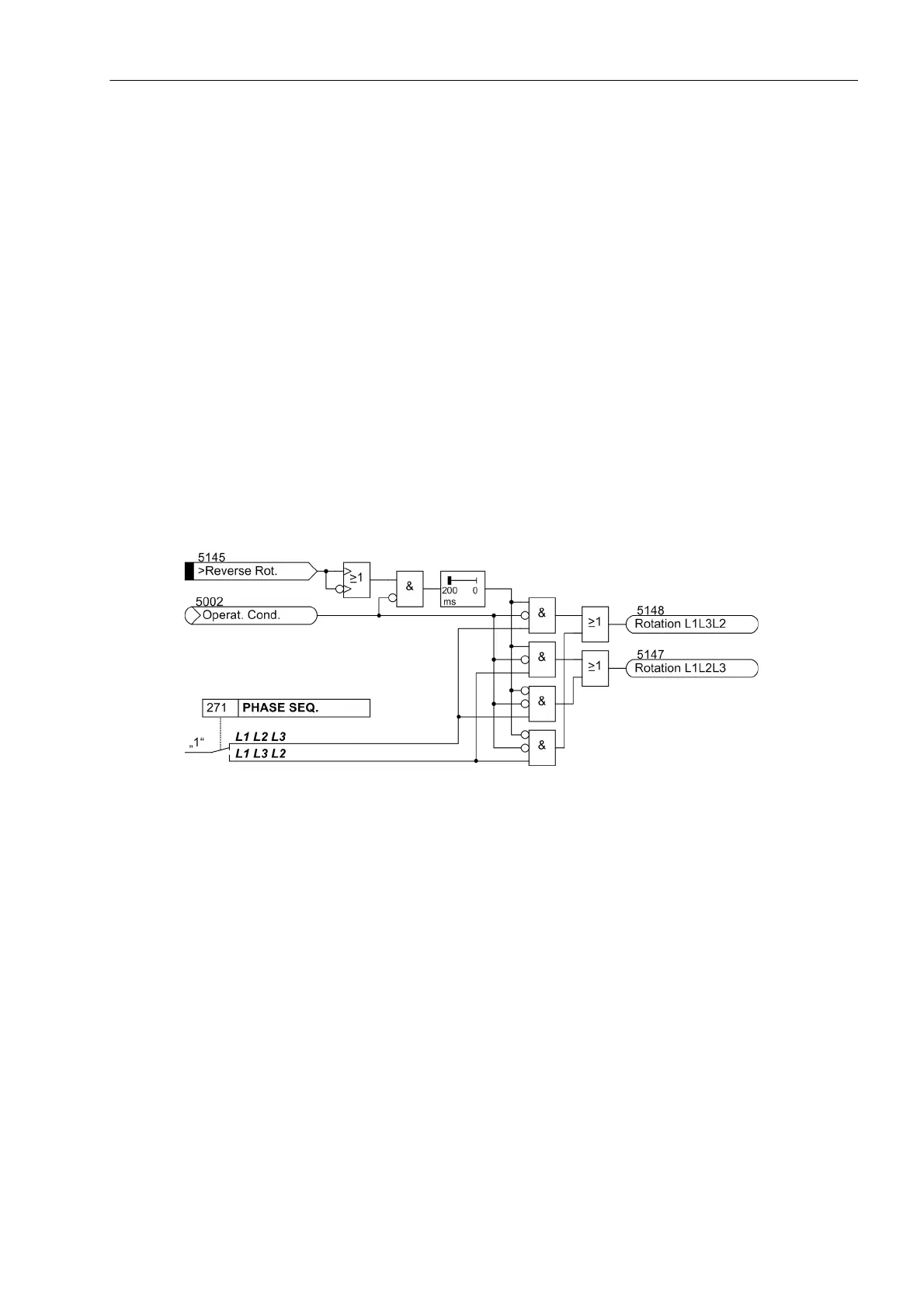
The phase rotation is permanently set in a parameter of the power system data at address 271 PHASE SEQ..
Binary input „>Reverse Rot.“ sets the phase rotation to the opposite of the parameter setting.
Figure 2-145 Message logic of the phase-sequence reversal
For safety reasons, the device accepts phase sequence reversal only when no usable measured quantities are
current. The binary input is scanned only if operational condition 1 is not current. If a reverse command is
present for at least 200 ms, the measured quantities of phases L2 and L3 are exchanged.
If operational condition 1 is reached before the minimum control time of 200 ms has expired, phase sequence
reversal does not become effective.
As no phase rotation reversal is possible in operational condition 1, the control signal could be retracted in op-
erational condition 1 without a phase rotation reversal occurring. For safety reasons, the control signal should
be permanently present in order to avoid malfunctions also on device reset (e.g. due to configuration change).
Influence on Protective Functions
Swapping phases with a phase sequence reversal affects exclusively calculation of positive and negative se-
quence quantities, as well as phase-to-phase voltages by subtraction of one phase-to-ground voltage from an-
other, so that phase related indications, fault values, and operating measurement values are not distorted. Thus
this function influences almost all protection functions and some of the monitoring functions (see Section
2.42.1) which issue an indication if the required and calculated phase rotations do not match.

 Loading...
Loading...











