Functions
2.13 Startup Overcurrent Protection (ANSI 51)
SIPROTEC, 7UM62, Manual
C53000-G1176-C149-7, Release date 03.2010
99
The startup overcurrent protection is a short-circuit protection function that operates below 10 Hz. Its operating
range is designed for 2 Hz to approx. 10 Hz (change to operational condition 1). Beyond this range the above
short-circuit protection functions are active.
The function is also active above 70 Hz with reduced sensitivity, because at that frequency the protection is
again in operational condition 0.
Measuring Principle
At frequencies below 10 Hz, the protection works in operating condition 0, with the sampling frequency auto-
matically set to nominal conditions (f
A
= 800 Hz for 50 Hz networks and 960 Hz for 60 Hz networks). From the
sampled phase currents, a special algorithm determines the peak values. These are converted into values pro-
portional to the rms values, and compared with the set threshold value.
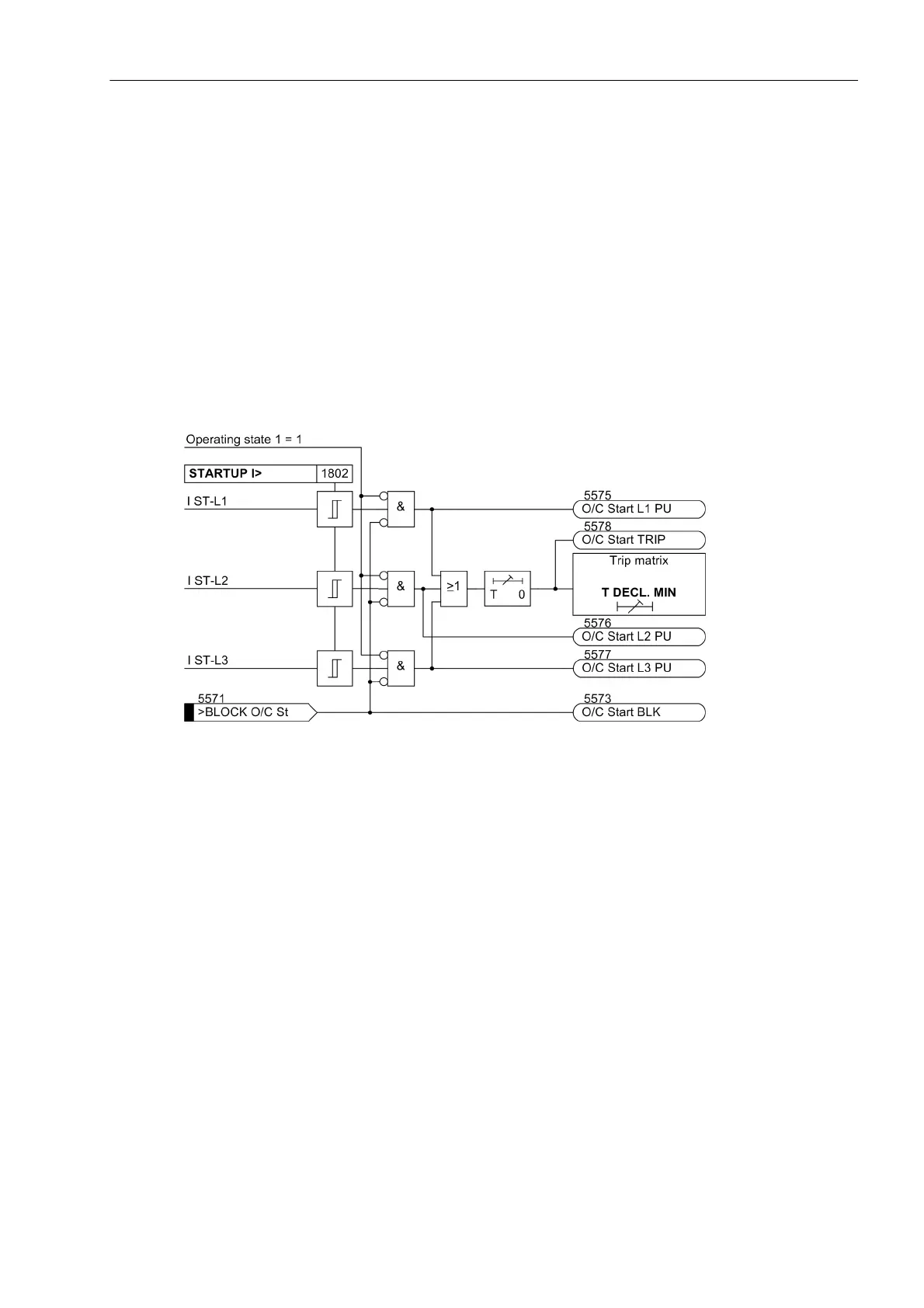
The logic is shown in the following picture.
Figure 2-27 Logic diagram of the startup overcurrent protection
2.13.2 Setting Notes
General
Startup overcurrent protection is only effective and available if address 118 O/C STARTUP is allocated to Side
1 or Side 2 during configuration. If the function is not needed it is set to Disabled.
Address 1801 serves to switch the function ON or OFF or to block only the trip command (Block relay).
Pick-up threshold
The characteristic of the startup procedure shows that the currents during startup amount to approx. 20 % of
the nominal currents. This allows the protection in principle to be set below nominal current. As shown in the
logic diagram, the function is blocked on change from operational state 0 to 1. Also blockage is to be provided
for via the binary input.
The figure below shows an example of the estimated short-circuit currents at different frequencies. Short-circuit
currents can be a multiple of the rated current. This permits the nominal current to be used for a setting which
could be between 1.2 and 1.4 I/I
NG
.

 Loading...
Loading...











