Functions
2.37 Restart Inhibit for Motors (ANSI 66, 49Rotor)
SIPROTEC, 7UM62, Manual
C53000-G1176-C149-7, Release date 03.2010
256
Although the heat distribution at the rotor cage bars can range widely during motor startup, the different
maximum temperatures in the rotor do not necessarily affect the motor restart inhibit (see Figure 2-116). It is
much more important to establish a thermal profile, after a complete motor startup, that is appropriate for pro-
tection of the motor's thermal state. The figure shows, as an example, the heating processes during repeated
motor starts (three startups from cold operating condition), as well as the thermal replica of the protection
device.
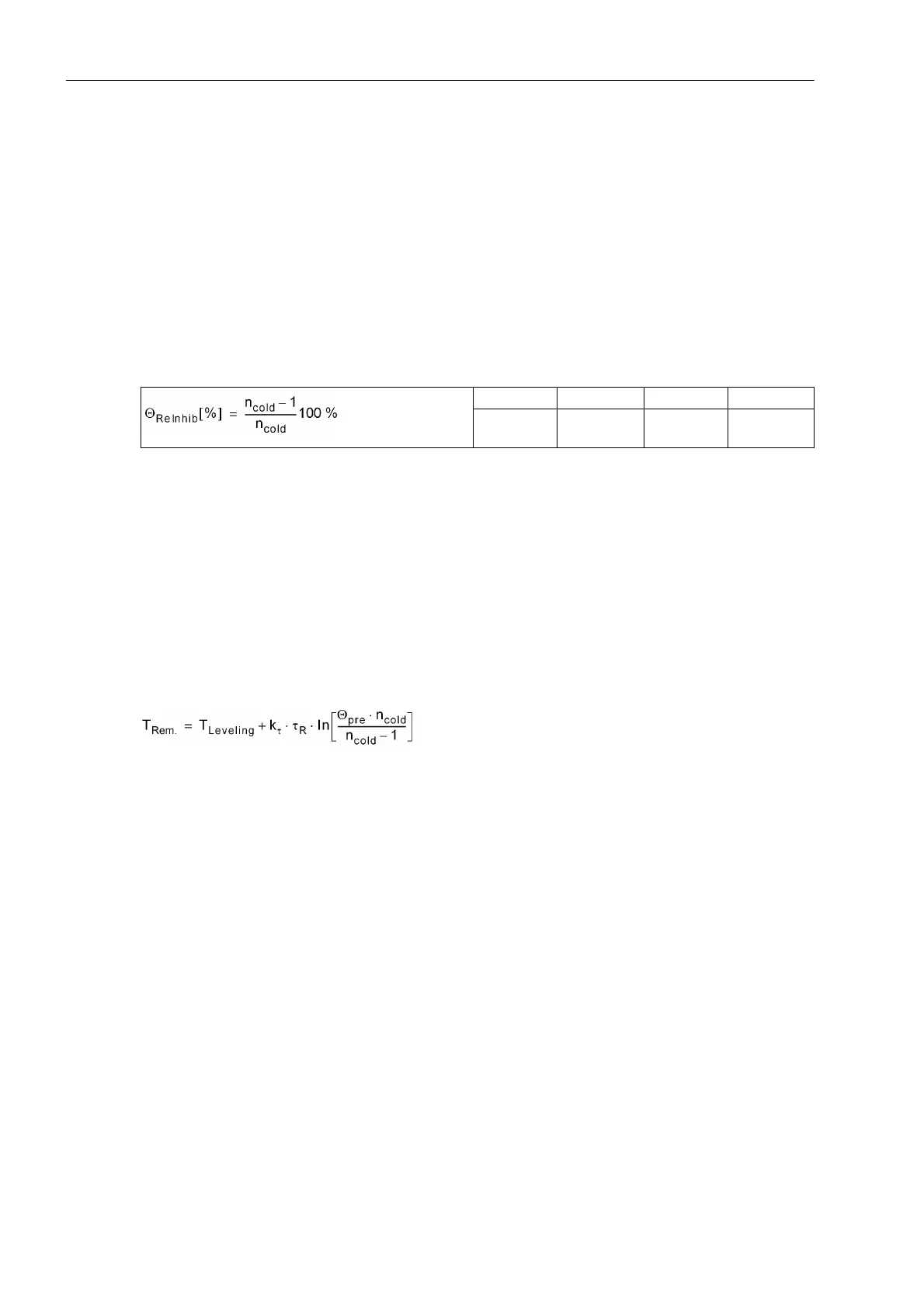
Restart Threshold
If the rotor temperature has exceeded the restart threshold, the motor cannot be restarted. Only when the rotor
temperature goes below the restart threshold, i.e. just when a startup becomes possible without exceeding the
rotor overtemperature limit, the blocking signal is retracted. Therefore, the following applies for the restart
threshold Θ
Re.Inh.
, related to maximum admissible rotor overtemperature:
Restart Times
The motor manufacturer allows a number of cold (n
cold
) and warm (n
warm
) startups. No subsequent renewed
startup is allowed. A corresponding time — the restart time — must expire to allow the rotor to cool down.
Thermal behaviour is allowed for as follows: Each time the motor is shutdown, a leveling timer is started (ad-
dress 6604 T EQUAL). This takes into account the different temperatures of the individual motor components
at the moment of shutdown. During the leveling time the thermal profile of the rotor is not updated but main-
tained constant to replicate the leveling processes in the rotor. Then the thermal model cools down with the
corresponding time constant (rotor time constant x extension factor). During the leveling time the motor cannot
be restarted. As soon as the restart threshold is undershot, a new restart may be attempted.
The total time that must expire before motor restart equals to the leveling time and the time calculated using
the thermal model required for the rotor temperature to decrease below the restart threshold:
with
T
Leveling
Rotor temperature equilibrium time address 6604
k
τ
extension factor for the time constant = Kτ at RUNNING address 6609 or Kτ at STOP
address 6608
τ
R
rotor time constant, internally calculated:
τ
R
= t
Start
· (n
cold
– n
warm
) · I
on
2
where:
t
Start
= Startup time in s
I
on
= Startup current in pu
Θ
pre
thermal profile at the moment of motor shutdown (depends on the operating state)
The operational measured value T
Rem.
= (to be found in the thermal measured values) shows the time remaining
until the next restart is allowed.
n
cold
234
Θ
Re.Inh.
[%] 50 % 66.7 % 75 %

 Loading...
Loading...











