Functions
2.36 Motor Starting Time Supervision (ANSI 48)
SIPROTEC, 7UM62, Manual
C53000-G1176-C149-7, Release date 03.2010
252
Therefore, if the starting current I actually measured is smaller (or larger) than the nominal starting current I
Start-
Curr
entered at address 6502 (parameter START. CURRENT), the actual tripping time t
TRIP
is lengthened (or
shortened) accordingly (see also Figure 2-114).
Definite-Time Overcurrent Tripping Characteristic (Locked Rotor Time)
If the motor starting time exceeds the maximum allowable blocked rotor time t
E
, tripping must be executed at
least with time t
E
when the rotor is blocked. The device can detect a blocked rotor condition via a binary input
(„>Rotor locked“) from an external rpm-counter. If the current in any of the phases exceeds the already
mentioned threshold I MOTOR START, a motor startup is assumed and in addition to the above inverse time
delay, a current-independent delay time (locked rotor time) is started. This happens every time the motor is
started and is a normal operating condition that is neither entered in the operational annunciations buffer, nor
output to a control centre, nor entered in a fault record.
The locked rotor delay time (LOCK ROTOR TIME) is ANDed with the binary input „>Rotor locked“. If the
binary input is still activated after the parameterized locked rotor time has expired, tripping is performed imme-
diately, regardless of whether the binary input was activated before or during the delay, or after the delay time
had elapsed.
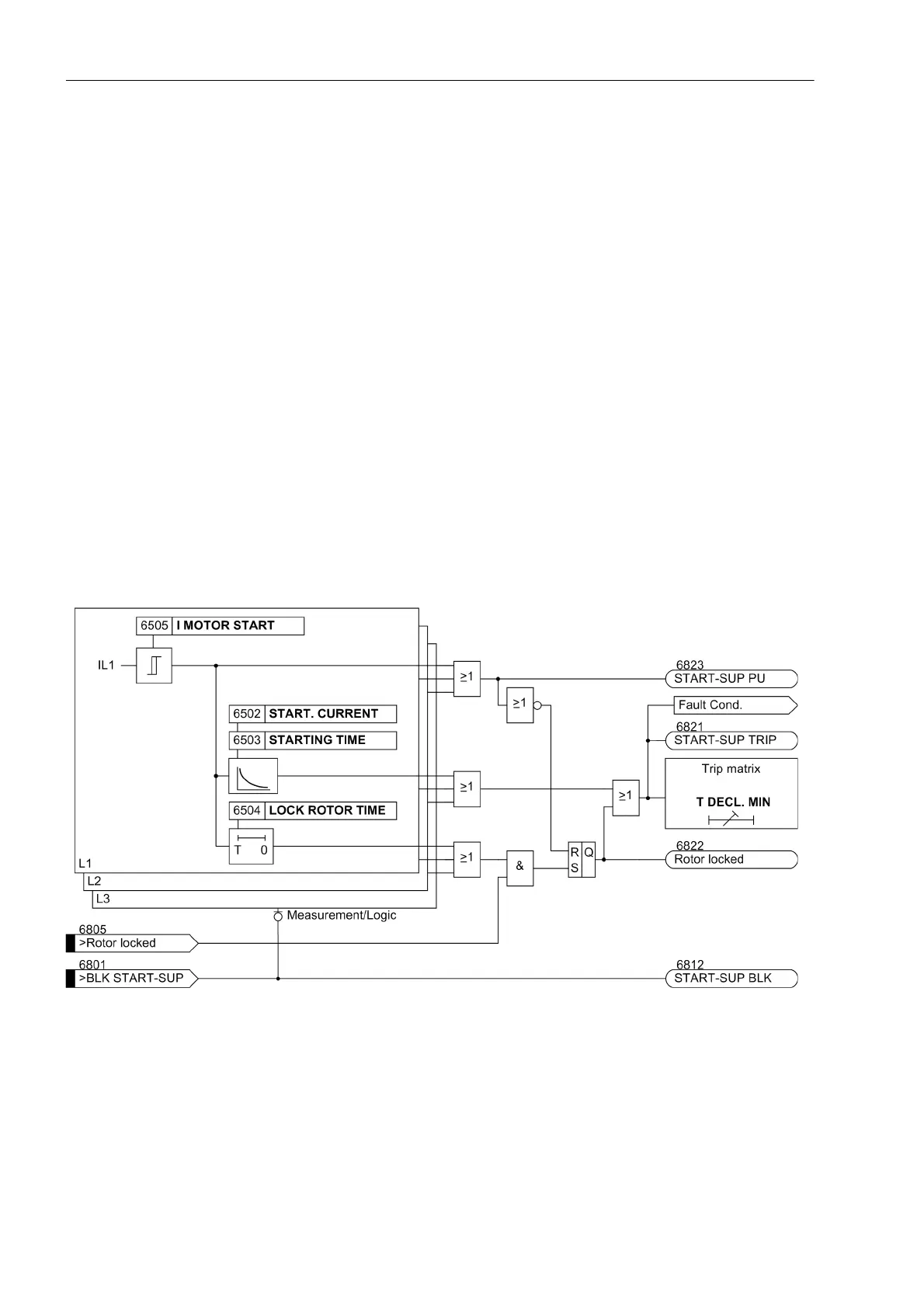
Logic
Motor startup monitoring may be switched on or off using a parameter. It may be blocked via binary input, i.e.
times and pickup indications are reset. The following figure shows the indication logic and fault administration.
A pickup does not result in a fault record. Fault recording is not started until a trip command has been issued.
Figure 2-115 Logic Diagram of the Motor Startup Time Monitoring

 Loading...
Loading...











