8.2.8 2A Bias Current Source
8.3 Measurement accuracy
Test accuracy includes stability、temperature coefficient, linear degree, test repeatability and
calibration inter-error.
Check the accuracy of instrument should be under the following circumstances:
a. warm-up time: ≥ 60 minutes
b. cable:0m, 1m
c. correct open and short correction after warming up
d. DC bias is in the position of “OFF”
e. The range works in “AUTO” to select correct test range
8.3.1 Accuracy of│Z│,│Y│, L, C, R, X, G, B
The accuracy Ae of │Z│,│Y│, L, C, R, X, G and B are expressed as:
A
e
= ± [A
L
× A+(K
a
+K
b
+K
c
)×100+ K
d
+K
f
]×K
e
[%]
A: basic test accuracy(figure A)
A
L
: level correction factor(table A)
K
a
:impedance rate factor(table B)
K
b
:impedance rate factor(table B)
K
c
:calibrated interpolating factor(table E)
K
d
:cable length factor
K
e
:temperature factor(table G)
K
f
:scan fixture modification factor(no adding:K
f
= 0, adding:K
f
= 0.2)
Using condition of L, C, X, B accuracy A
e
:D
x
(test value of D)≤0.1
Using condition of R, G accuracy A
e
:Q
x
(test value of Q)≤0.1
When D
x
≥0.1, accuracy factor A
e
of L, C, X, B should be multiplied by
When Q
x
≥0.1, accuracy factor A
e
of R, G should be multiplied by
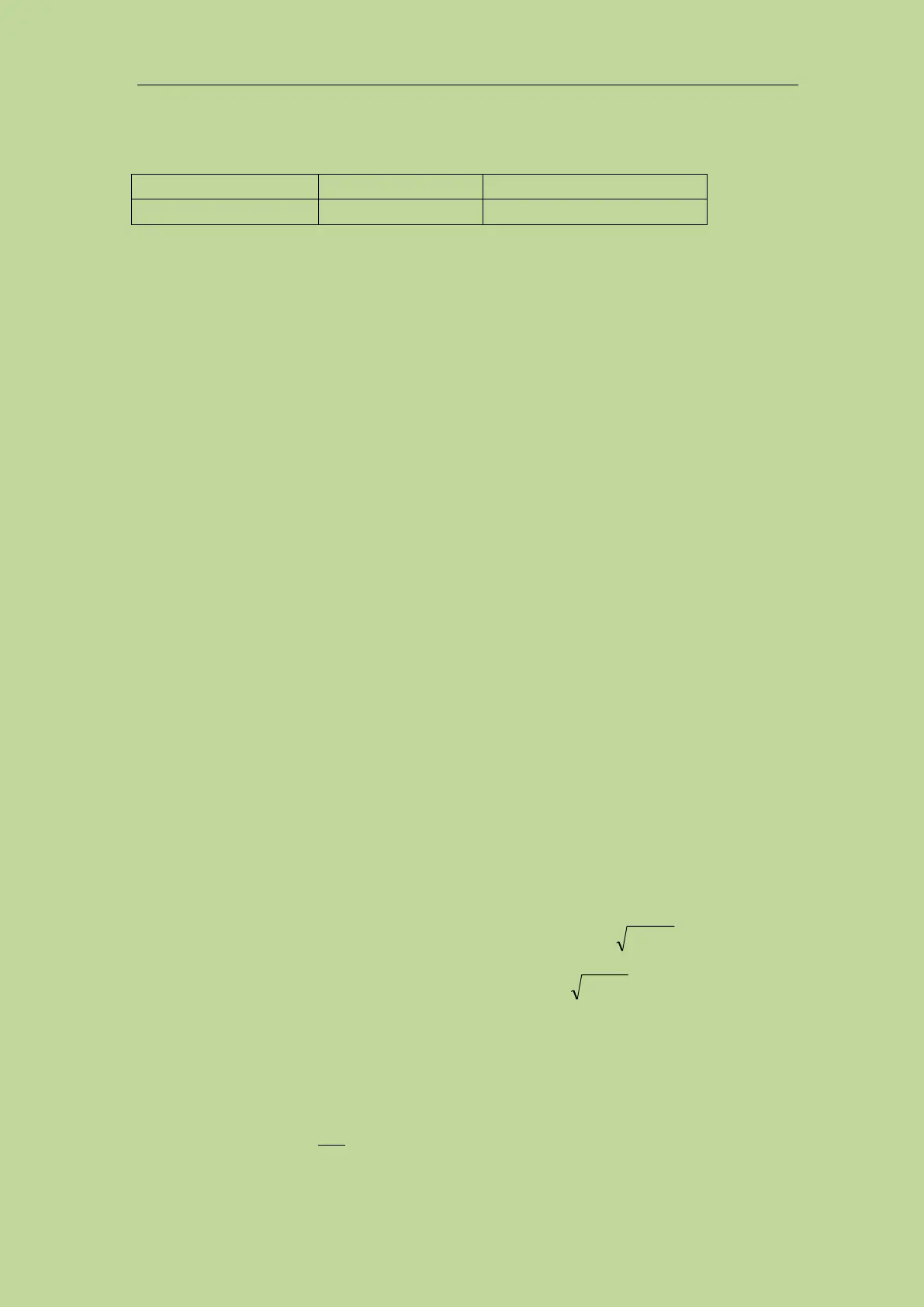
8.3.2 D accuracy
The accuracy of D is given by the formula below:
D
e
=
The formula is only available when D
x
≤0.1.

 Loading...
Loading...