Sheet #673u – Definition, characteristics and measurement principles
Version 1.04a User guide ATEQ 6th series Page 3/7
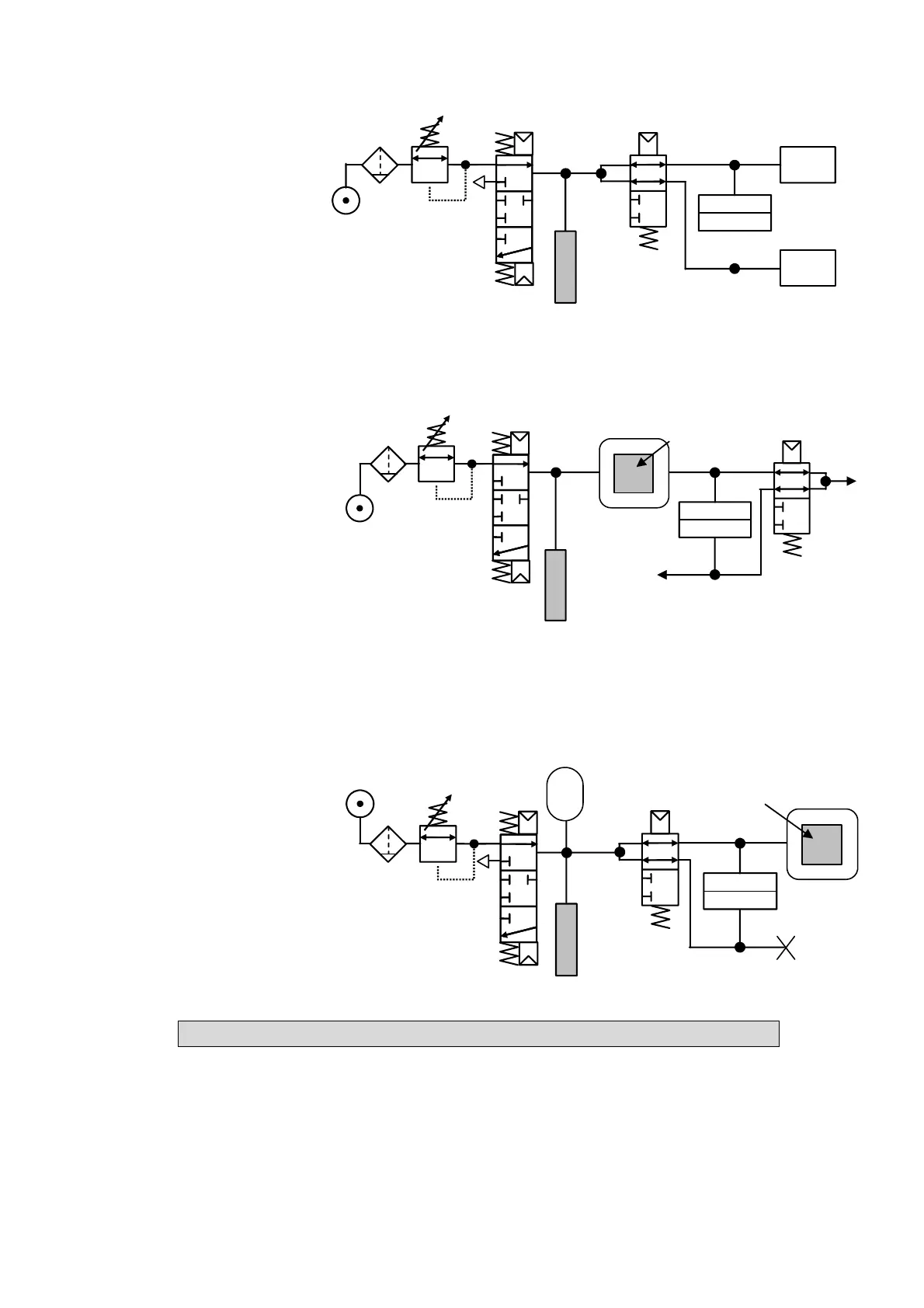
3.1.1. 1) Direct or pressure drop measurement
After filling the test and
reference parts to the required
pressure level, the instrument
measures the differential
pressure between the two
volumes which are separated
by the equalization valve.
Reference part
Test part
Electronic
ressure sensor
At the end of a cycle, the instrument empties the components via the dump valve.
3.1.1. 2) Indirect Pressure rise measurement
The test part is placed in a
sealed bell and the instrument
is pneumatically connected to
the bell. The part is externally
pressurized (with up to 20 MPa
or 200 bar) and the bell is
lightly pressurized. In the event
of a part leakage, the pressure
in the bell will rise.
P atm
Test part
Electronic
pressure sensor
P atm
Reclaimable
bell
Transducer
This method allows certain parts to be tested at high pressure levels whilst avoiding the
associated constraints. The instrument only tests and measures the pressure in the bell. In the
event of a large leak, electronic monitoring of the pressure in the bell will switch the instrument
to safety. A security valve must be installed on the bell.
3.1.1. 3) Sealed component measurement
This test is intended for sealed
parts which cannot be filled at
the test pressure. They are put
into the bell. The bell is
pressurized by dumping air
from an intermediary volume.
The difference in the amount of
air from a good to bad part can
be measured. The pressure in
the bell is controlled according
to the formula:
Test part
Electronic
pressure switch
Plugged ref.
output
Bell
Transducer
Internal volume
P1 V1 = P2 (V1 + V2) with V1 bell volume V2 internal volume
The first and the third measurements may be carried out in comparison with a reference,
without reference or in central zero.
Three kinds of sealed components are available, see sheet #613.

 Loading...
Loading...