Sheet #607u – ATR 0 – 1 – 2 – 3 function
Version 1.04a User guide ATEQ 6th series Page 1/6
ATR 0 - 1 - 2 - 3 FUNCTIONS
1. PRINCIPLE
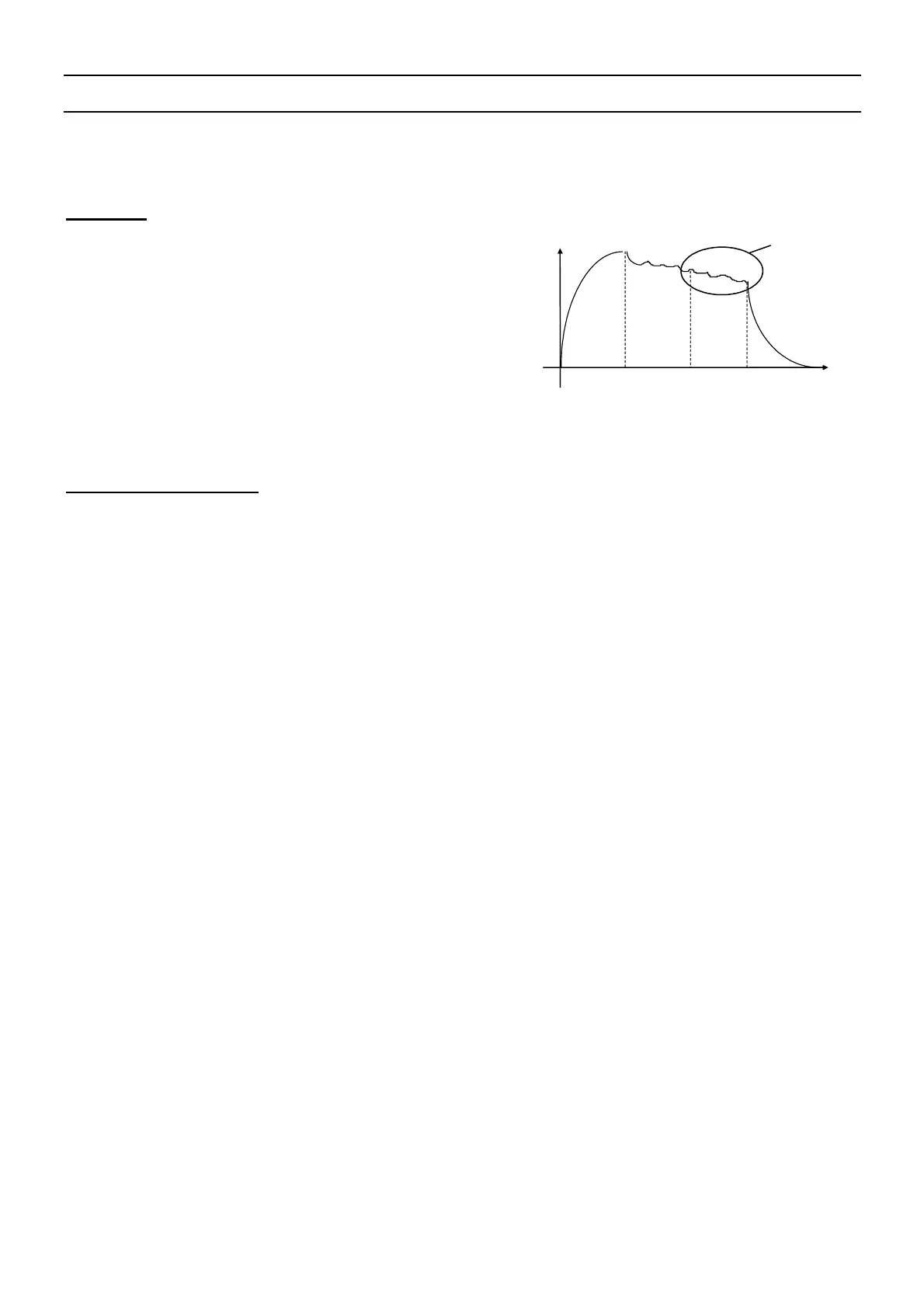
Problem:
Is the pressure drop occurring during the test time due
to a leak or a transient effect?
The test environment is not always ideal for the
measurement of pressure drops. There are several
momentary events (ex: temperature or volume
variations...) that can influence the measurement.
They are called transient effects.
Fill Stab. Test Dum
Time
Press
Pressure
drop
To avoid any interference, it is possible to increase the stabilization time to obtain the ideal
measurement conditions during the test phase. However, increasing the stabilization time for
each test may not be acceptable for optimal production speed.
Operational principle:
The principle consists of measuring the pressure variations caused by transient phenomena through
the use of a learning cycle and then removing these variations from the final test result for a part.
Three ATR (Attenuated Transient Reduction) functions are available: ATR0, ATR1, ATR2 and
ATR3. ATR1 and ATR2 are different because of their learning cycles.
1.1. ATR0
The initial value of the transient is known. Parameters must be set manually.
The ATR may only be used on parts that have identical behaviors during the test, in other
words, parts that have an identical transient.
Associated parameters to be set are:
¾Start (Initial value of the transient),
¾Transient
(actual, non modifiable value of the transient),
¾Per
centage drift (Percent of the reject level, the measurements used for transcient
calculation are less than this value).
¾Drift (Drift tolerance on acquisition of the transient, as a % of the Reject level).
The “start” value is saved and subtracted from the final result of the tests.

 Loading...
Loading...