Version 7.2 353 Mediant 1000B Gateway & E-SBC
User's Manual 17. Control Network
Parameter Description
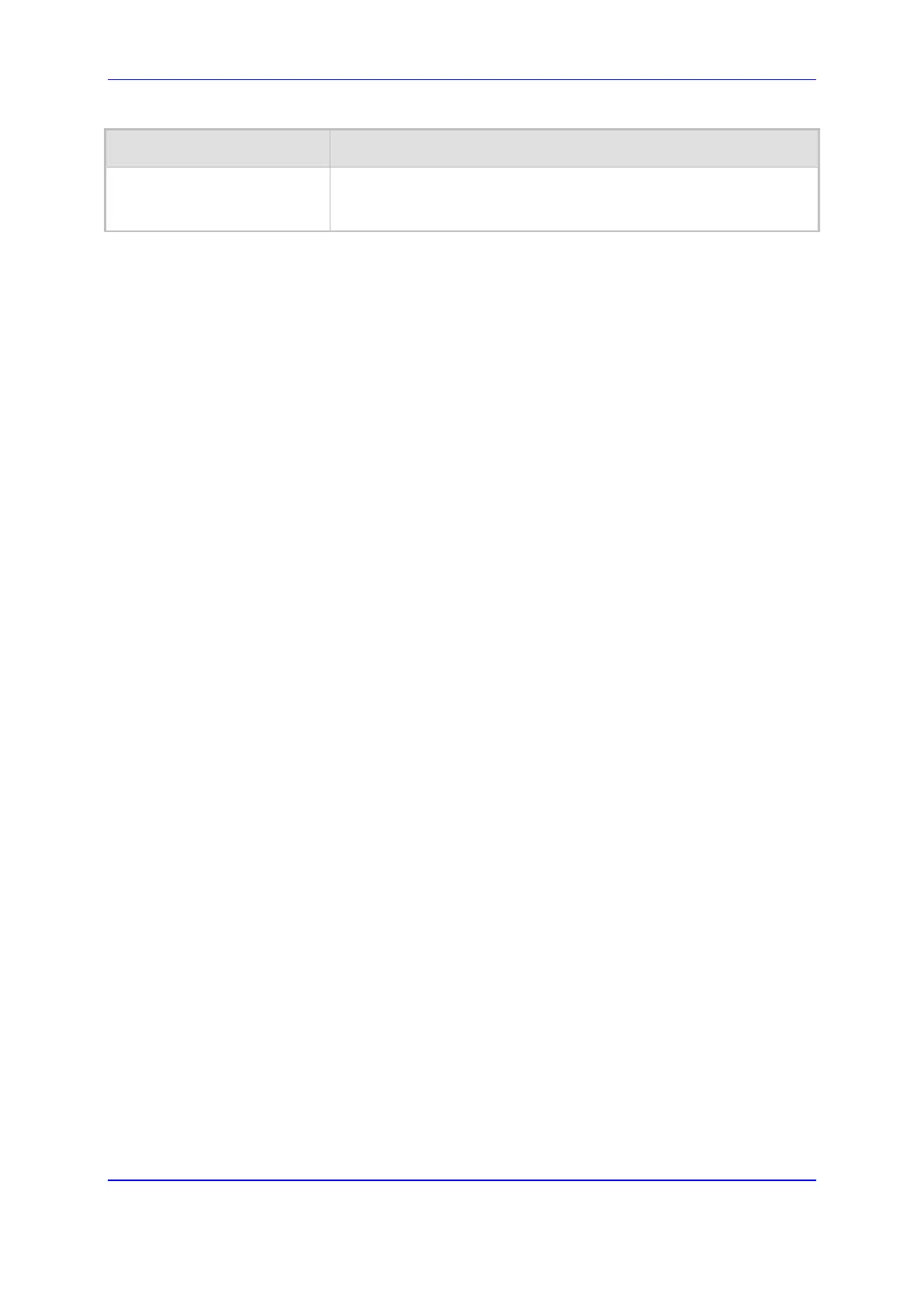
[SIPInterface_MaxNumOfReg
Users]
By default, no value is defined (i.e., the number of allowed user
registrations is unlimited).
Note: The parameter is applicable only to the SBC application.
17.4 Configuring IP Groups
The IP Groups table lets you configure up to 102 IP Groups. An IP Group represents a SIP
entity in the network with which the device communicates. This can be a server (e.g., IP
PBX or ITSP) or a group of users (e.g., LAN IP phones). For servers, the IP Group is
typically used to define the server's IP address by associating it with a Proxy Set (see
Configuring Proxy Sets on page 367).
You can use IP Groups for the following:
SBC application: Classification of incoming SIP dialog-initiating requests (e.g., INVITE
messages) to IP Groups based on Proxy Set. If the source address of the incoming
SIP dialog is defined for a Proxy Set, the device assigns ("bonds") the SIP dialog to
the IP Group associated with the Proxy Set. The feature is configured using the IP
Groups table's 'Classify by Proxy Set' parameter. For more information and
recommended security guidelines, see the parameter's description, later in this
section.
SBC application: Representing the source and destination of the call in IP-to-IP
Routing rules (see Configuring SBC IP-to-IP Routing Rules on page
695).
SIP dialog registration and authentication (digest user/password) of specific IP Groups
(Served IP Group, e.g., corporate IP-PBX) with other IP Groups (Serving IP Group,
e.g., ITSP). This is configured in the Accounts table (see ''Configuring Registration
Accounts'' on page
383).
Gateway application: Call routing rules:
• Tel-to-IP calls: The IP Group is used as the destination of the outgoing IP call and
is used in Tel-to-IP call routing rules (see Configuring Tel-to-IP Routing Rules on
page 511).
• IP-to-Tel calls: The IP Group identifies the source of the IP call and is used in IP-
to-Tel call routing rules (see Configuring IP-to-Tel Routing Rules on page 520).
• Number manipulation: The IP Group can be associated with a number
manipulation rule (see Configuring Number Manipulation Tables on page 541).
Included in routing decisions by a third-party routing server. If deemed necessary for
routing, the routing server can even create an IP Group. For more information, see
Centralized Third-Party Routing Server on page
279.
You can also apply the device's Quality of Experience feature to IP Groups:
Quality of Experience Profile: Call quality monitoring based on thresholds for voice
metrics (e.g., MOS) can be applied per IP Group. For example, if MOS is considered
poor, calls belonging to this IP Group can be rejected. To configure Quality of
Experience Profiles, see ''Configuring Quality of Experience Profiles'' on page
315.
Bandwidth Profile: Bandwidth utilization thresholds can be applied per IP Group. For
example, if bandwidth thresholds are crossed, the device can reject any new calls on
this IP Group. To configure Bandwidth Profiles, see ''Configuring Bandwidth Profiles''
on page
320.

 Loading...
Loading...















