Wireless LAN – WLAN
114
3.8
Establishing outdoor wireless networks
BAT54-Rail/F..
Release
7.54
06/08
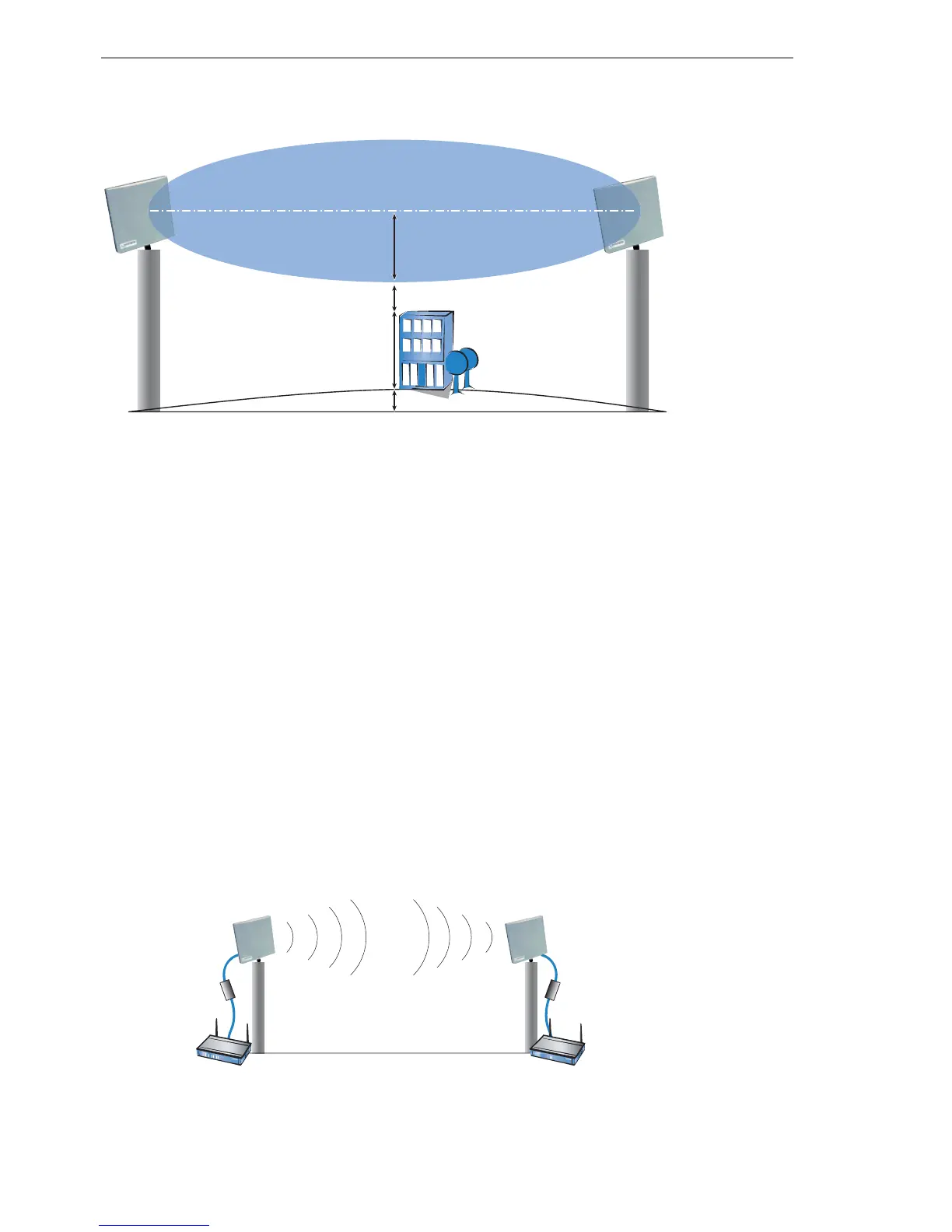
M = R + 1m + H + E (Earth's curvature)
The height of the Earth's curvature (E) is calculated from the distance (d) E
= d² * 0,0147 – even at a distance of 8 km that results in almost 1m!
Example: With a distance of 8 km between the antennae, the result in the
2.4-GHz band is a mast height above the level of the highest obstruction of
approx. 13 m, in the 5-GHz band 9 m.
3.8.2 Antenna power
The power of the antenna must be high enough to ensure acceptable data
transfer rates. On the other hand, the country's legal limitations on transmis-
sion power should not be exceeded.
The calculation of effective power considers everything from the radio mod-
ule in the transmitting access point to the radio module in the receiving ac-
cess point. In between there are attenuating elements such as the cable, plug
connections, and even the air, and amplifying elements such as the external
antennae.
Fresnel zone 1
Radius R
Safety margin: 1m
Obstruction height H
Earth's curvature E
ree-space
oss
Amplification with antenna
gain
Output power of the ra-
dio module
Loss through ca-
ble, plugs and light-
ning protection
Amplification with antenna
gain
Input signal at the ra-
dio module
Loss through ca-
ble, plugs and
lightning protec-
tion
 Loading...
Loading...