Virtual LANs (VLANs)
350
10.8
VLAN Q-in-Q tagging
BAT54-Rail/F..
Release
7.54
06/08
10.8VLAN Q-in-Q tagging
VLANs compliant with IEEE302.1q are generally used to connect multiple
networks that share a common physical medium but which are to be kept
separate from one another. In some cases VLANs are operated on public
networks that are operated by providers in order to keep the various compa-
ny networks separate. Consequently VLAN tags may be used both in the
LAN and over the WAN path—VLAN tagged LAN packets therefore require
an additional VLAN tag for transmission over WAN. For control over VLAN
tagging, the actions performed by each port can be defined separately.
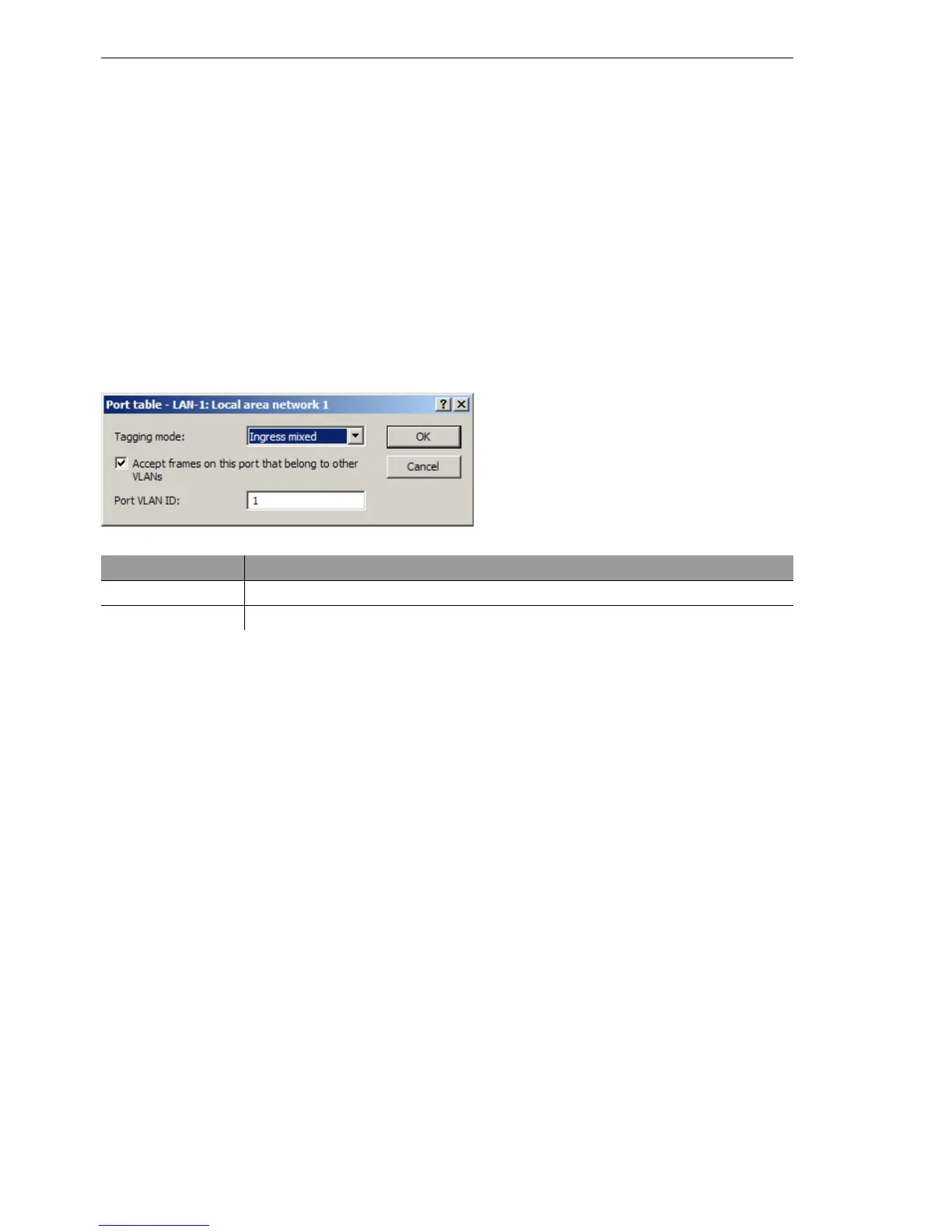
D Tagging mode
Controls the processing and assignment of VLAN tags at this port.
D Never: Outbound packets are not given a VLAN tag at this port. Incom-
ing packets are treated as though they have no VLAN tag. If incoming
packets have a VLAN tag, it is ignored and treated as though it were
part of the packet's payload. Incoming packets are always assigned to
the VLAN defined for this port.
D Unconditional: Outgoing packets at this port are always assigned with
a VLAN tag, irrespective of whether they belong to the VLAN defined
for this port or not. Incoming packets must have a VLAN tag, otherwise
they will be dropped.
D Mixed: Allows mixed operation of packets with and without VLAN tags
at the port. Packets without a VLAN tag are assigned to the VLAN
defined for this port. Outgoing packets are given a VLAN tag unless
they belong to the VLAN defined for this port.
D Ingress-mixed: Arriving (ingress) packets may or may not have a
VLAN tag; outbound (egress) packets are never given a VLAN tag.
D Default: Ingress mixed
Configuration tool Call
LANconfig Interfaces
VLAN Port table
WEBconfig, Telnet Expert configuration > Setup > VLAN > Port table

 Loading...
Loading...