Wireless LAN – WLAN
38
3.2
Development of WLAN security
BAT54-Rail/F..
Release
7.54
06/08
In the first phase, the client registers with the access point as usual, and en-
ters the state in which it can now send and receive over the access point in
normal WEP or WEPplus—but not with EAP, because in this state the client
still doesn't have a key to secure its data traffic from eavesdropping. Instead,
the client is in an 'intermediate state' from the point of view of the access
point, in which only particular packets from the client are forwarded, and
these are only directed to an authentication server. These packets are the
EAÜ/802.1x mentioned previously. The access point packs these packets in
RADIUS queries and sends them on to the authentication server. The access
point converts the replies coming from the RADIUS server back into EAP
packets, and sends them back to the client.
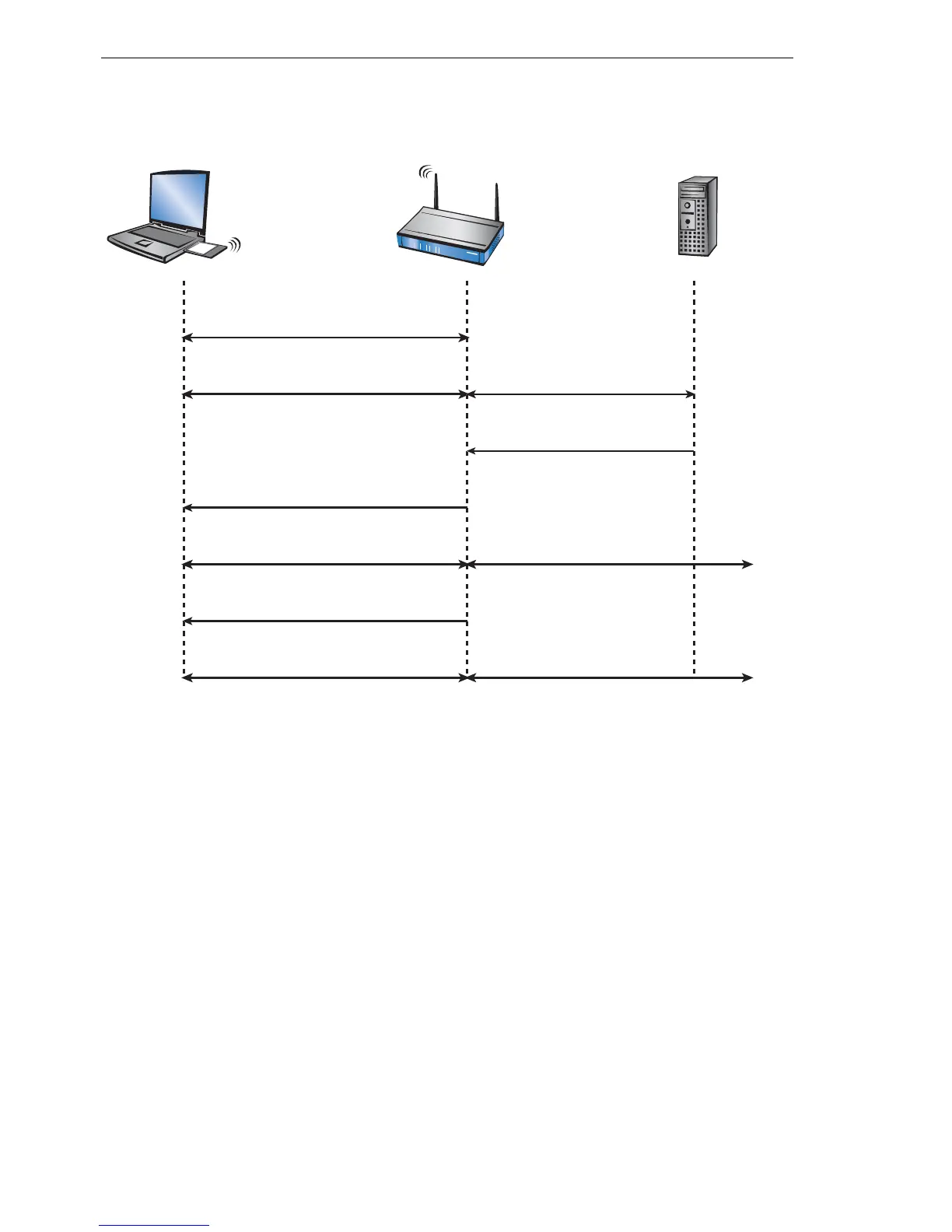
Figure 2: Schematic process of a WLAN session with EAP/802.1x
Access point
WLAN registration
EAP/802.1x negotiation
session key
sharing of Master Secret
Client RADIUS server
Normal data traffic
new session key
more normal data traffic
 Loading...
Loading...