Routing and WAN connections
BAT54-Rail/F..
Release
7.54
06/08
11.6
Advanced Routing and Forwarding
383
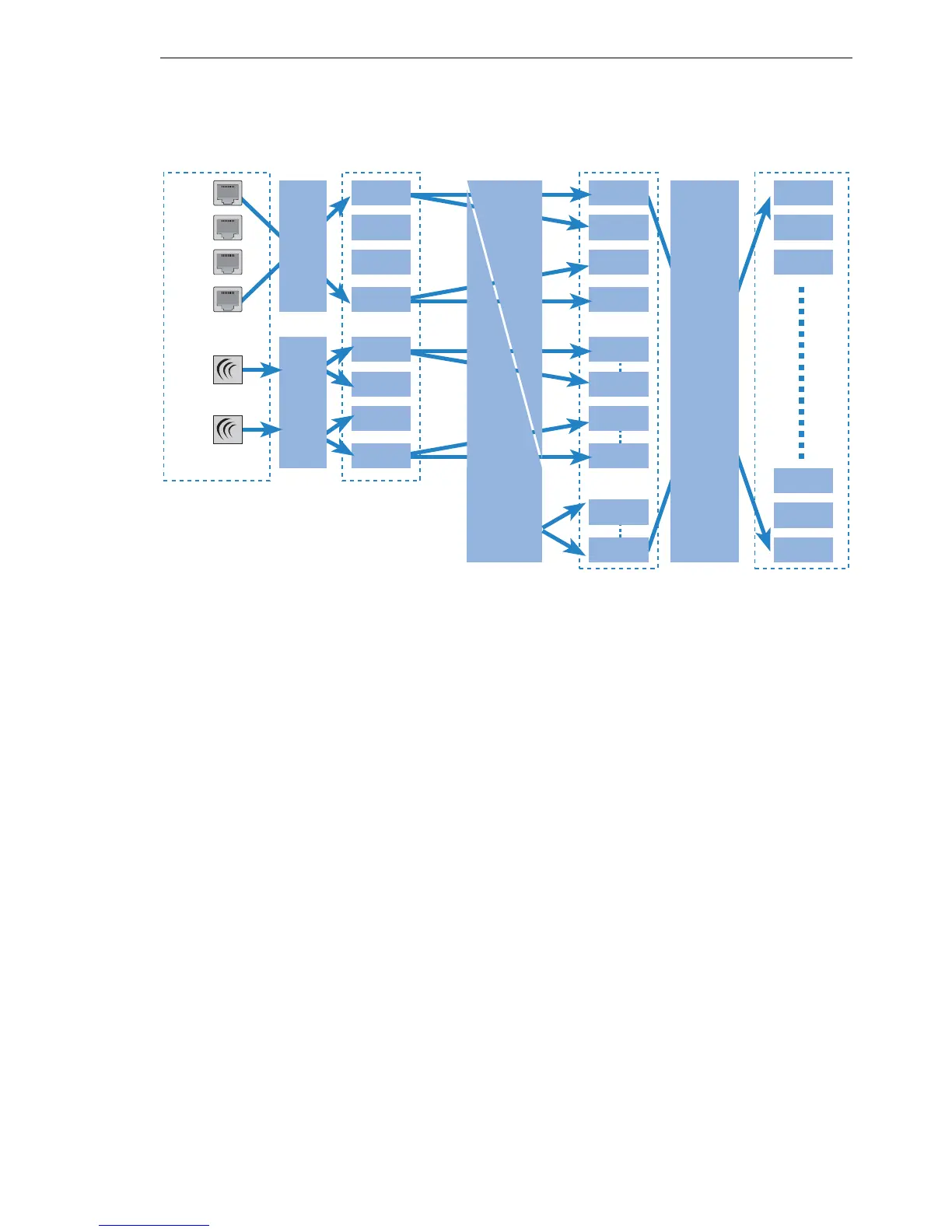
The assignment of IP networks to interfaces proceeds as follows:
D The various models have different numbers of physical interfaces, i.e.
Ethernet ports or WLAN modules.
D The logical interface(s) is/are assigned to the physical interface:
D For the Ethernet ports, Ethernet port mapping assigns the physical
ETH-1 to ETH-4 to the logical LAN-1 to LAN-4.
Note: For some but not all models, the number of logical LAN interfaces cor-
responds to the number of physically available Ethernet ports.
D In the case of the WLAN modules, the establishment of point-to-point
connections (P2P) and/or the use of Multi-SSID can mean that multi-
ple WLAN interfaces are assigned to each physical WLAN module:
Per module this may be up to eight WLAN networks and up to six P2P
connections.
D These logical interfaces are further specified and grouped in the next
stage:
LAN bridge
LAN -1
WLAN-1-1
to
P2P-1-6
Physical inter-
faces
WLAN-2-1
to
P2P-2-6
Multi-SSID, P2P
ETH-1
Virtual LANs (VLAN)
Ethernet port map-
ping
logical
Interfaces
IP networks
ETH-2
ETH-3
ETH-4
WLAN-1
WLAN-2
LAN -2
LAN -3
LAN -4
LAN-1,
VLAN-ID
WLAN-1-1
VLAN-ID
10
P2P-1-6
BRG-1
BRG-8
Advanced routing and forwarding
Logical interfaces with VLAN tags,
bridge groups
Network 1
Network 64
LAN-1,
VLAN-ID
LAN-4,
VLAN-ID
LAN-4,
VLAN-ID
WLAN-2-1
VLAN-ID
19
P2P-2-6

 Loading...
Loading...