Routing and WAN connections
462
11.17
The rapid spanning tree protocol
BAT54-Rail/F..
Release
7.54
06/08
D Disabled: no packets can be sent or received through this port. This
occurs when the port has either been disabled manually or when it has
a negative link status.
D Listening: Intermediate state on the way to enabling. Only Spanning
Tree packets are listened to, data packets are ignored and are also not
forwarded to this port.
D Learning: Further intermediate state. As opposed to 'listening' addi-
tional MAC addresses from data packets entering this port are learned
but data packets are still not forwarded.
D Forwarding: the port is completely active, data packets are received
and forwarded in both directions.
D Blocking: Spanning Tree has identified this port to be redundant and
disabled it for data traffic.
D Root
The ID for the root bridge that can be reached through this port.
D Bridge
This is the ID for the bridge through which the root bridge can be reached.
D Costs
This value defines the 'costs' for this port. The value is determined by the
port technology (Ethernet, WLAN, etc.) and the bandwidth. Examples of
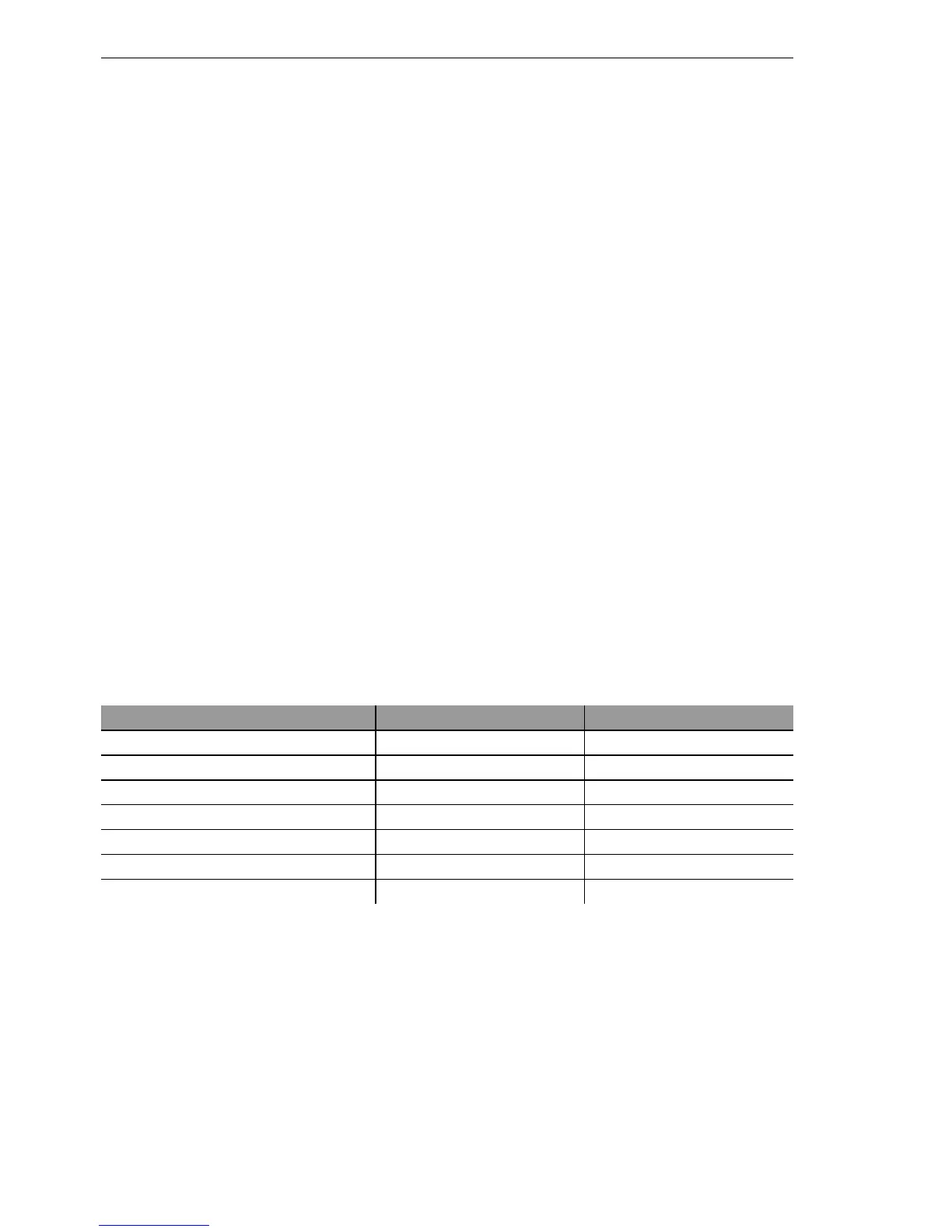
values used are:
Note: If path costs for a port were manually entered, then the configured val-
ue appears in this column.
U Information in the RSTP port statistics
The RSTP port table can be used to inspect the following values for all avail-
able ports (LAN, wireless LAN, point-to-point connections).
Transfer technology Costs of Classic Spanning Tree Costs of Rapid Spanning Tree
Ethernet 10 MBit 100 2000000
Ethernet 100 MBit 19 200000
Ethernet 1000 MBit 4 200000
WLAN 2 MBit 500 12500000
WLAN 11 MBit 140 4000000
WLAN 54 MBit 35 900000
WLAN 108 MBit 25 450000

 Loading...
Loading...