1
K
KK
K Wiring
the
Main
Circuits
This
section
describes
wiring
connections
for
the
main
circuit
inputs
and
outputs.
nWiring
Main
Circuit
Inputs
Observe
the
following
precautions
for
the
main
circuit
power
supply
input.
Installing
a
Molded-case
Circuit
Breaker
Always
connect
the
power
input
terminals
(R,
S,
and
T)
and
power
supply
via
a
molded-case
circuit
breaker
(MCCB)
suitable
for
the
Inverter.
• Provide
one
MCCB
for
each
Inverter.
• Choose
an
MCCB
with
a
capacity
of
1.5
to
2
times
the
Inverter's
rated
current.
• For
the
MCCB's
time
characteristics,
be
sure
to
consider
the
Inverter's
overload
protection
(one
minute
at
150%
of
the
rated
output
current).
• If
the
same
MCCB
is
to
be
used
for
more
than
one
Inverter,
or
other
devices,
set
up
a
sequence
so
that
the
power
supply
will
be
turned
OFF
by
a
fault
output,
as
shown
in
Fig
2.9.
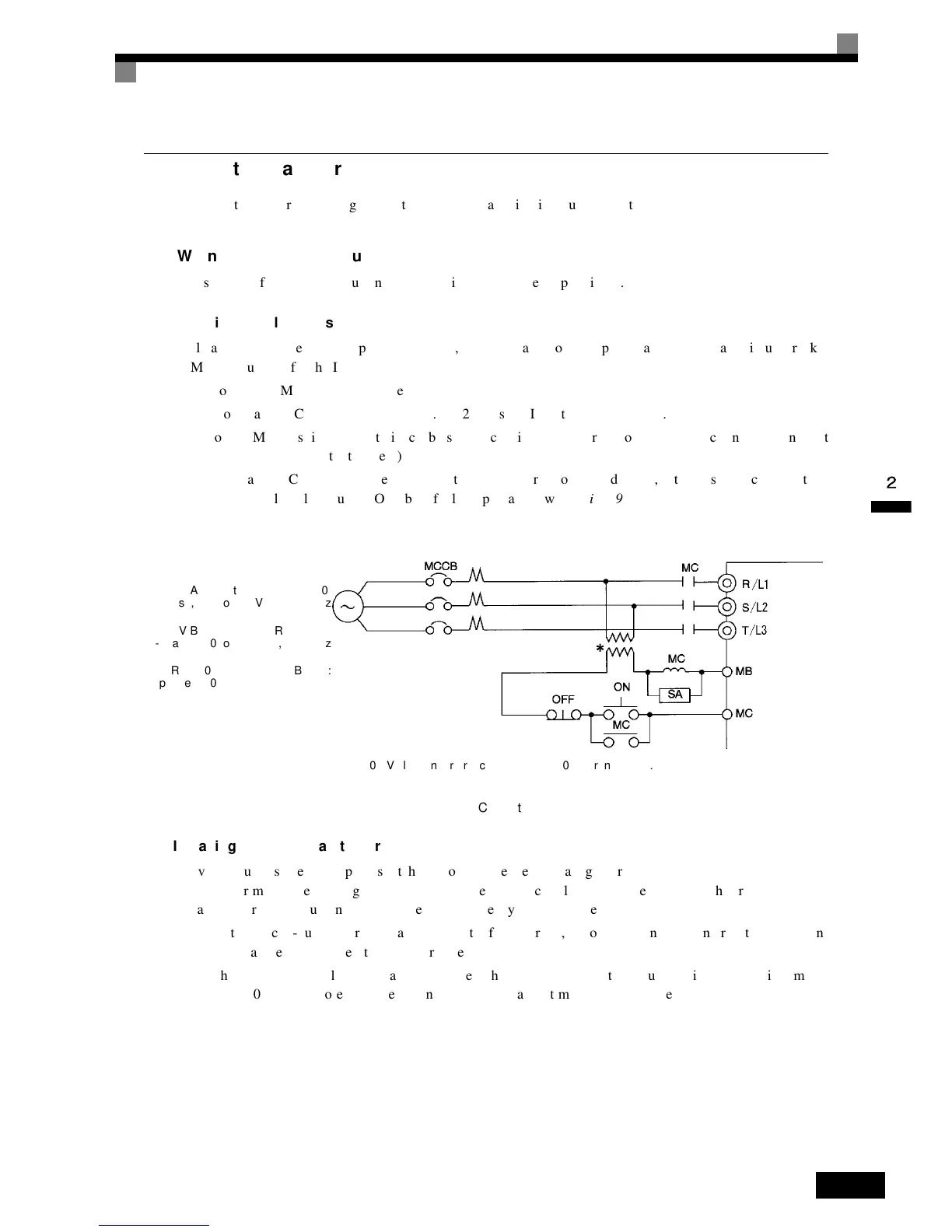
Fig 2.9 MCCB Installation
Installing
a
Ground
Fault
Interrupter
Inverter
outputs
use
high-speed
switching,
so
high-frequency
leakage
current
is
generated.
Therefore,
at
the
Inverter
primary
side,
use
a
ground
fault
interrupter
to
detect
only
the
leakage
current
in
the
frequency
range
that
is
hazardous
to
humans
and
exclude
high-frequency
leakage
current.
• For
the
special-purpose
ground
fault
interrupter
for
Inverters,
choose
a
ground
fault
interrupter
with
a
sen-
sitivity
amperage
of
at
least
10
mA
per
Inverter.
• When
using
a
general
ground
fault
interrupter,
choose
a
ground
fault
interrupter
with
a
sensitivity
amper-
age
of
200
mA
or
more
per
Inverter
and
with
an
operating
time
of
0.1
s
or
more.
* For 400-V class Inverters, connect a 400/200-V transformer.
3G3RV-A2004 to 3G3RV-B2300:
3-phase, 200 to 240 VAC, 50/60 Hz
3G3RV-B2370 to 3G3RV-B211K:
3-phase, 200 to 230 VAC, 50/60 Hz
3G3RV-A4004 to 3G3RV-B4300:
3-phase, 380 to 460 VAC, 50/60 Hz
Power
supply
Inverter
Fault output
(NC)

 Loading...
Loading...











