135
If the execution condition for IL(002) is OFF, the interlocked section between
IL(002) and ILC(003) will be treated as shown in the following table:
Instruction Treatment
OUT and OUT NOT Designated bit turned OFF.
TIM, TIMH(015), and TIML(121) Reset.
CNT, CNTR(012), TTIM(120), and MTIM(122) PV maintained.
KEEP(011), SFT(050) Bit status maintained.
DIFU(013) and DIFD(014) Not executed (see below).
All others Not executed.
IL(002) and ILC(003) do not necessarily have to be used in pairs. IL(002) can be
used several times in a row, with each IL(002) creating an interlocked section
through the next ILC(003). ILC(003) cannot be used unless there is at least one
IL(002) between it and any previous ILC(003).
Differentiation in Interlocks Changes in the execution condition for DIFU(013), DIFD(014), or a differen-
tiated instruction are not recorded if the DIFU(013) or DIFD(014) is in an inter-
locked section and the execution condition for the IL(002) is OFF. When
DIFU(013), DIFD(014), or a differentiated instruction is executed in an inter-
locked section immediately after the execution condition for the IL(002) has
gone ON, the execution condition for the DIFU(013), DIFD(014), or differen-
tiated instruction will be compared to the execution condition that existed before
the interlock became effective (i.e., before the interlock condition for IL(002)
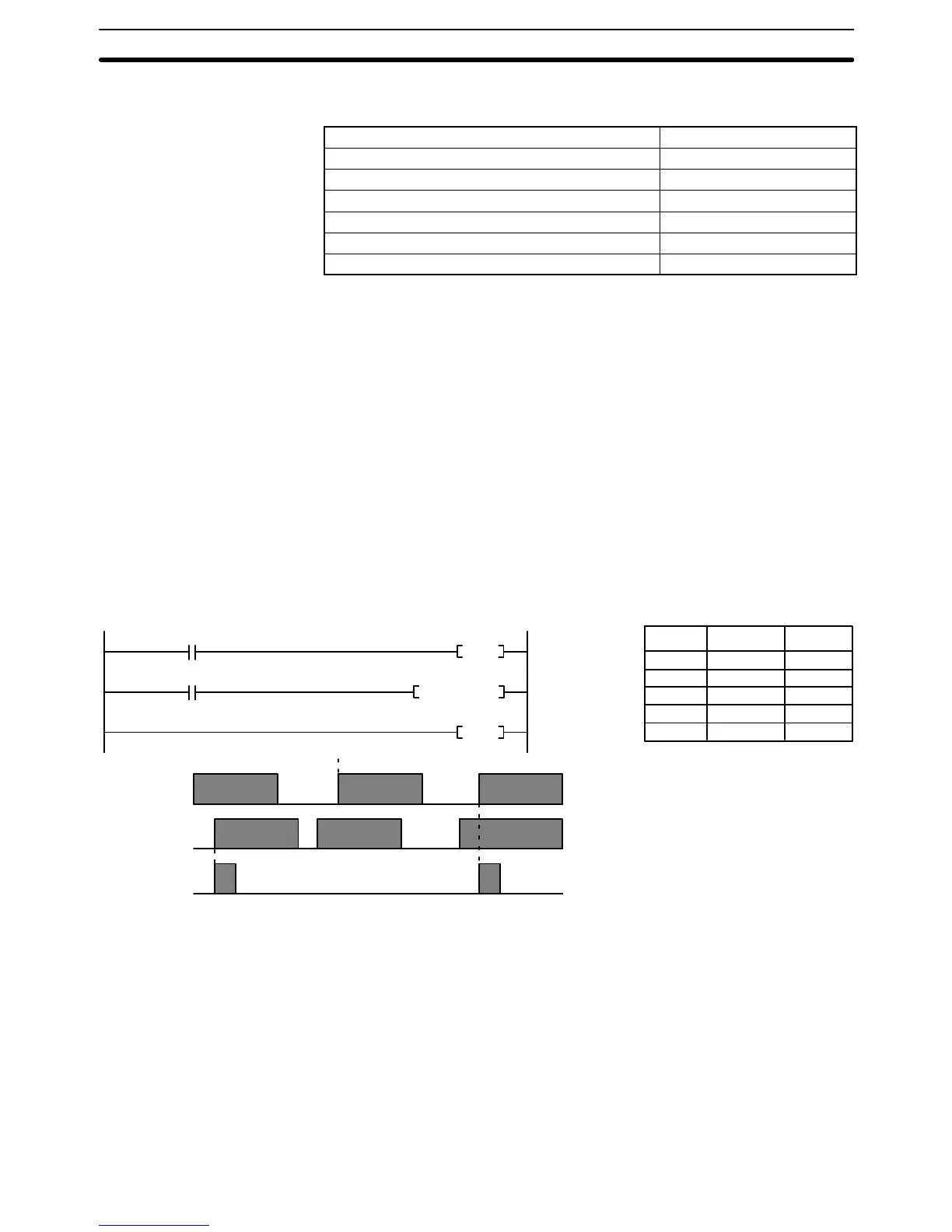
went OFF). The ladder diagram and bit status changes for a DIFU(013) instruc-
tion in an interlock are shown below. The interlock is in effect while 000000 is
OFF. Bit 001000 is not turned ON at the point labeled A even though 000001 has
turned OFF and then back ON because the OFF status of 000001 just before A
was not detected while the interlock condition was OFF.
000000
000001
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
001000
ON
OFF
A
Address Instruction Operands
0000
00
0000
01
(002)
IL
(013)
DIFU 001000
(003)
ILC
00000 LD 000000
00001 IL(002)
00002 LD 000001
00003 DIFU(013) 001000
00004 ILC(003)
There must be an ILC(003) following any one or more IL(002).
Although as many IL(002) instructions as are necessary can be used with one
ILC(003), ILC(003) instructions cannot be used consecutively without at least
one IL(002) in between, i.e., nesting is not possible. Whenever a ILC(003) is
executed, all interlocks between the active ILC(003) and the preceding ILC(003)
are cleared.
When more than one IL(002) is used with a single ILC(003), an error message
will appear when the program check is performed, but execution will proceed
normally.
Note: Refer to page 115 for general precautions on operand data areas.
There are no flags affected by these instructions.
Precautions
Flags
INTERLOCK and INTERLOCK CLEAR: IL(002) and ILC(003) Section 5-8
 Loading...
Loading...











