440
Precautions The same block number cannot be used more than once.
Block programs cannot be nested.
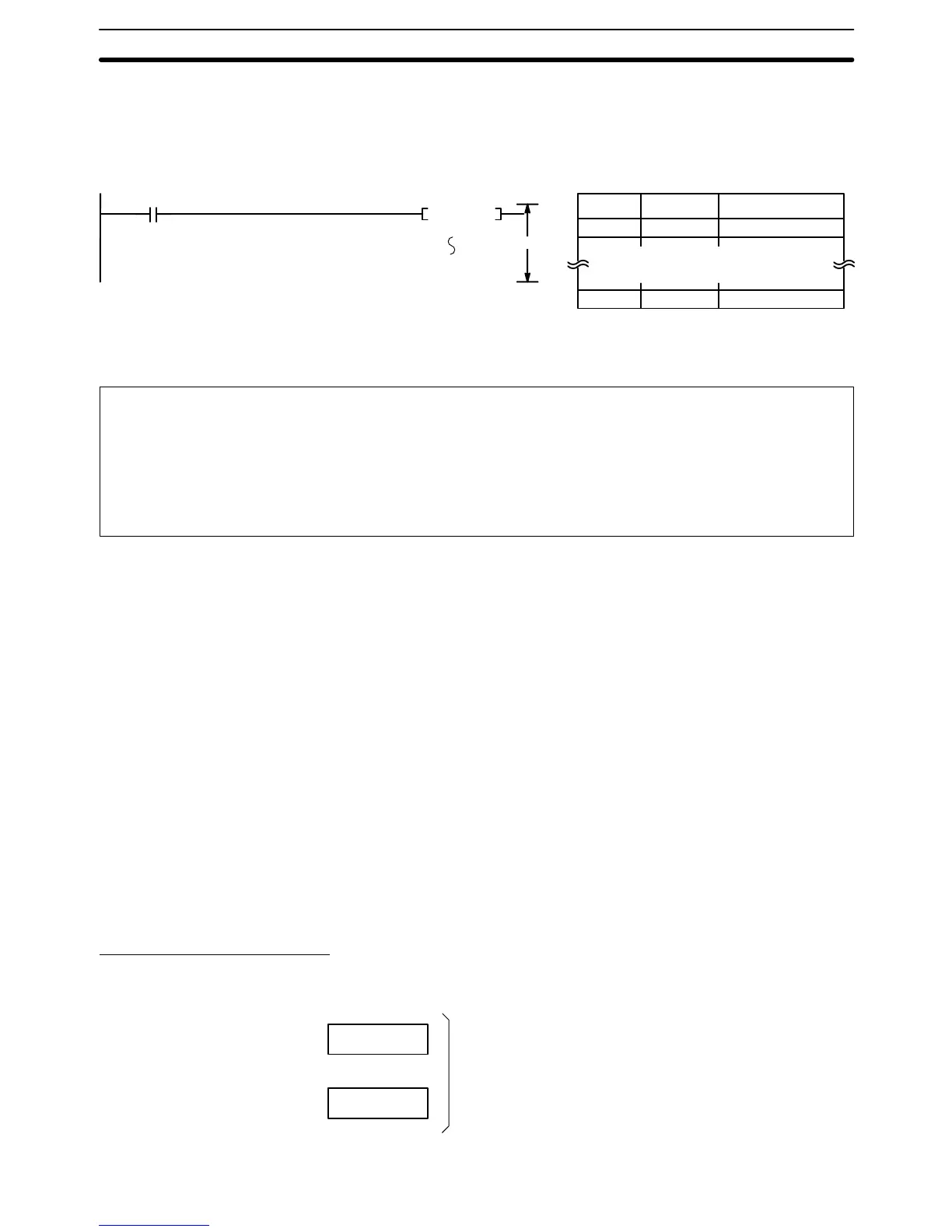
Example When CIO 000000 is ON in the following diagram, the block program between
program addresses 000501 and 000600 will be executed.
(250)
BPRG 99
000500 BPRG(250) 99
Block program.
000600 BEND<001>
BEND<001>
Block program
Address Instruction Operands
0000
00
5-38-3 Branching–IF<002>, ELSE<003>, and IEND<004>
B: Bit CIO, G, A, T, C
Operand Data AreaLadder Symbol
IF<002> B
IF<002>
IF<002> NOT B
ELSE<003>
IEND<004>
Branching instructions are used to branch according to either the current
execution condition or the status of a designated bit. IF<002> and IF<002>
NOT must be used in combination with IEND<004). ELSE<003> may be
used in between them, but is optional.
Branching is initiated with any of the following: IF<002> with a bit operand,
IF<002> without a bit operand, or IF<002> NOT with a bit operand.
If the IF condition is YES, the instructions immediately following the IF<002>
or IF<002> NOT will be executed. A YES execution condition is produced by
an ON bit or ON execution condition for IF<002> or an OFF bit for
IF<002>NOT.
If ELSE<003> is encountered following IF<002> or IF<002>NOT, execution
will jump to IEND<003> without executing any instruction in between. If
ELSE<003> is not encountered, execution will continue as normal.
If the IF condition is NO, execution will jump to ELSE<003> or to IEND<004>,
whichever appears first after the IF<002> or IF<002> NOT.
LD, possible in combination with AND or OR, must be used to establish the
execution condition for IF<002> without an operand or IF<002> NOT without
an operand.
Execution Flow Examples
IF<002> to ELSE to IEND
A
IF<002> B
ELSE<003>
C
IEND<004>
When B is ON, A is executed.
When B is OFF, C is executed.
Description
IF<002> with an Operand
(CVM1 V2)
Block Programming Instructions Section 5-38
 Loading...
Loading...











