470
The following CVSS/SSS operations are instruction execution events:
Monitoring, data modification, set, reset, online edit, DM edit, search,
transfer block (CVSS/SSS to PC), save block (CVSS/SSS to PC), I/O table
change, PC Setup, PC Setup information transfer, data trace execution,
program trace execution, setting program memory protect, clearing
program memory protect, Memory Card (program, I/O memory)
The following host interface operations are writing events:
Data area block write, data area transfer, parameter area write, parameter
area block write, start program area protect, clear protect area, program
area read, program area write, program area clear, cycle time read, program
area to file transfer, force set/reset, force set/reset for all bits
When SFC online editing is selected from the CVSS, all writing events will be
suspended until the online editing has been completed.
6-3 Calculating Cycle Time
The PC configuration, the program, and program execution conditions must
be taken into consideration when calculating the cycle time. This means tak-
ing into account such things as the number of I/O points, the programming
instructions used, and whether or not Peripheral Devices are being used.
This section shows a basic example of cycle time calculation. Operating
times are given in the tables in
6-2 Cycle Time
.
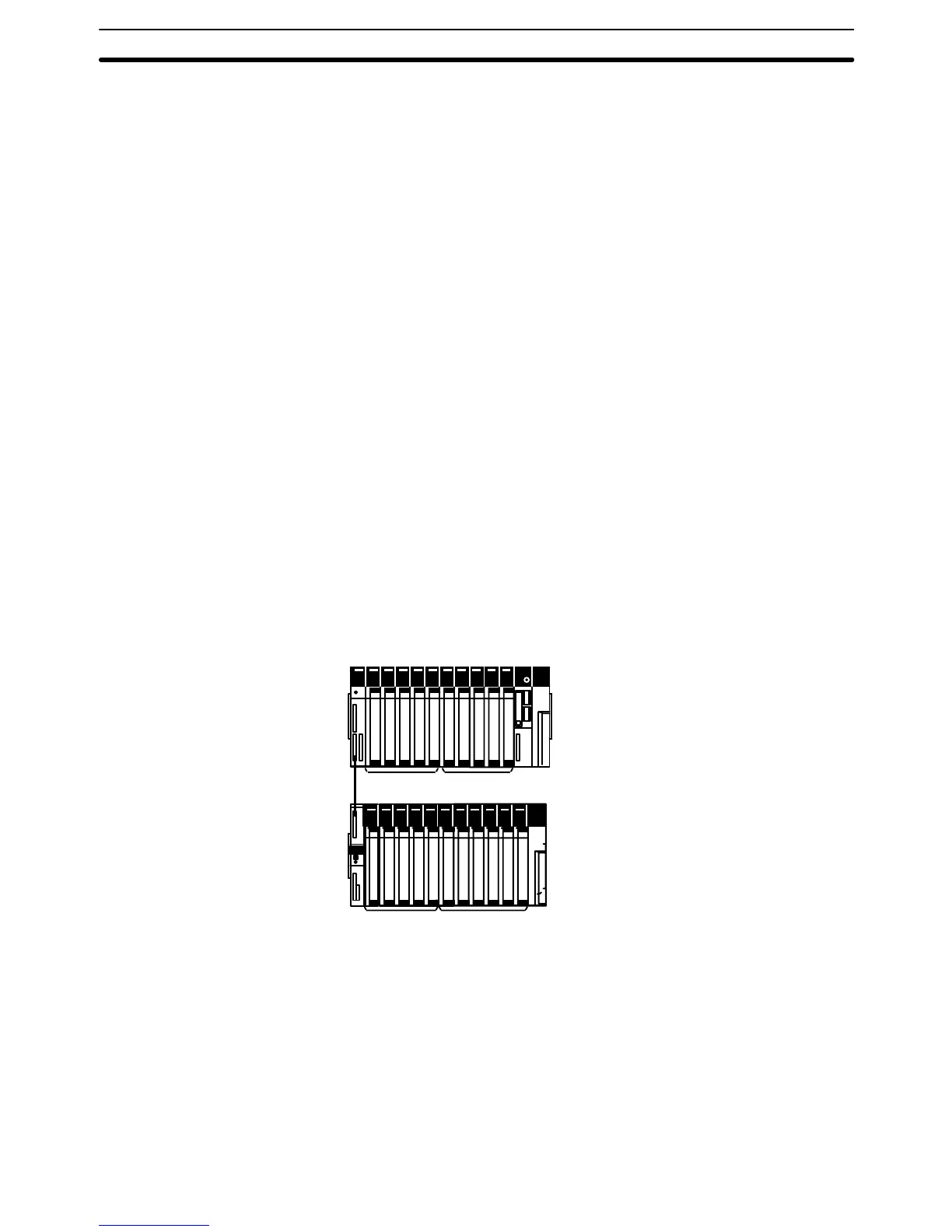
Here, we’ll compute the cycle time for a CV1000 or CV2000 set for cyclic re-
freshing. The PC controls only I/O Units, ten on the CPU Rack and eleven on
an Expansion I/O Rack. The PC configuration for this is shown below. It is
assumed that the program contains 20,000 instructions requiring an average
of 0.3 µs each to execute.
Refer to the next section for instruction execution times. Using the cycle time
in calculating the I/O response time is described in the last part of
Section 6
.
32-point Output Units
16-point Input
Units
32-point Input Units
16-point Output
Units
CPU Rack
Expansion I/O
Rack
The equation for the cycle time from above is as follows:
Cycle time = overseeing time (basic processes)
+ program execution
+ output refreshing
+ input refreshing time
The overseeing time is fixed at 0.5 ms for nonsynchronous processing.
The program execution time is 6 ms (0.3 µs/instruction times 20,000 instruc-
tions).
SFC Online Editing
Calculations
Calculating Cycle Time Section 6-3
 Loading...
Loading...











