Rexroth IndraDrive Calculations 15-11
DOK-INDRV*-SYSTEM*****-PR02-EN-P
Note: For calculating the inrush current take all devices connected to
mains voltage into account.
Mains Contactor and Fusing
To facilitate the selection of an appropriate mains contactor and fusing
device for power connection there are selection tables available in chapter
"Fusing and Selecting the Mains Contactor".
Calculating the Mains Harmonics
Harmonic Load THD
The harmonic load of the mains is described by the THD (total harmonic
distortion):
∑
=
=
40
2
2
1
n
n
I
I
THD
I
n
: harmonic current of the n-th harmonic
I
1
: rms value of the 1
st
harmonic (fundamental wave)
I
2
: rms value of the 2
nd
harmonic
I
n
: rms value of the n-th harmonic
Fig. 15-29: THD (total harmonic distortion)
Harmonic Content / Distortion Factor k
The harmonic content of, for example, the mains current is described by
the distortion factor k. The distortion factor contains all alternating
components, both those of the fundamental wave (I
1
) and of the
harmonics (I
k
). Direct components (I
0
) are not contained.
...
...
2
3
2
2
2
1
2
3
2
2
1
2
2
2
III
II
I
I
k
n
k
k
n
k
k
++
++
==
∑
∑
=
=
k: distortion factor or harmonic content
I
k
: harmonic current of the k-th harmonic
I
1
: rms value of the 1
st
harmonic (fundamental wave)
I
2
: rms value of the 2
nd
harmonic
I
n
: rms value of the n-th harmonic
Fig. 15-30: Distortion factor k or harmonic content
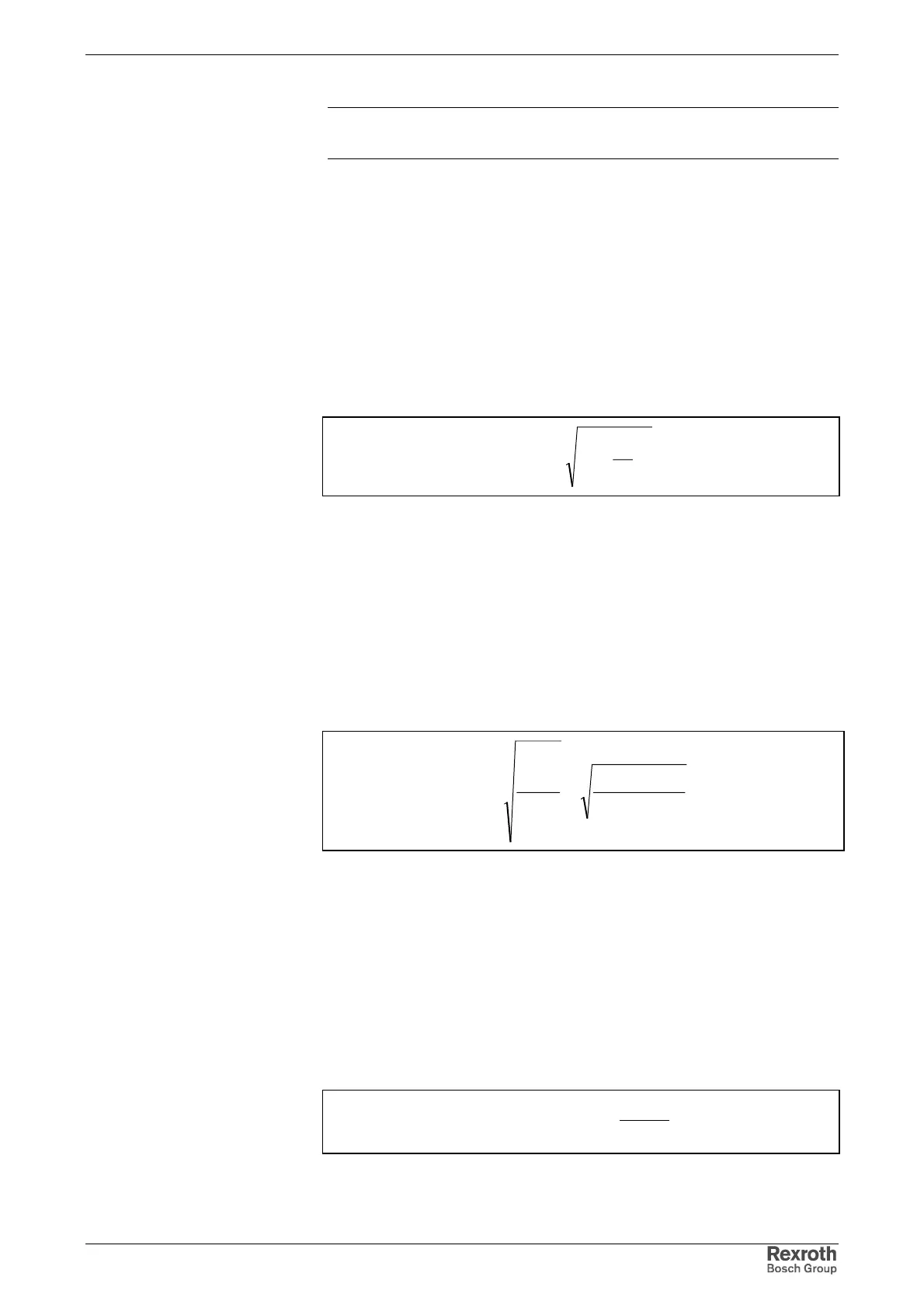
Power Factor cosϕ1 or DPF for Calculating the Reactive
Power Load of the Mains
The power factor cosϕ1 or DPF (Distortion Power Factor) is used to
calculate the reactive power load of the mains:
netzS
Pnetz
DPF
1
1
cos ==
ϕ
Pnetz: effective mains power
S1netz: apparent mains power of fundamental wave
Fig. 15-31: Power factor cos ϕ
1
/ DPF
 Loading...
Loading...











