Part B - System description cobas p 512
2-22 Operator's Manual - Version 1.6 - 10/2015
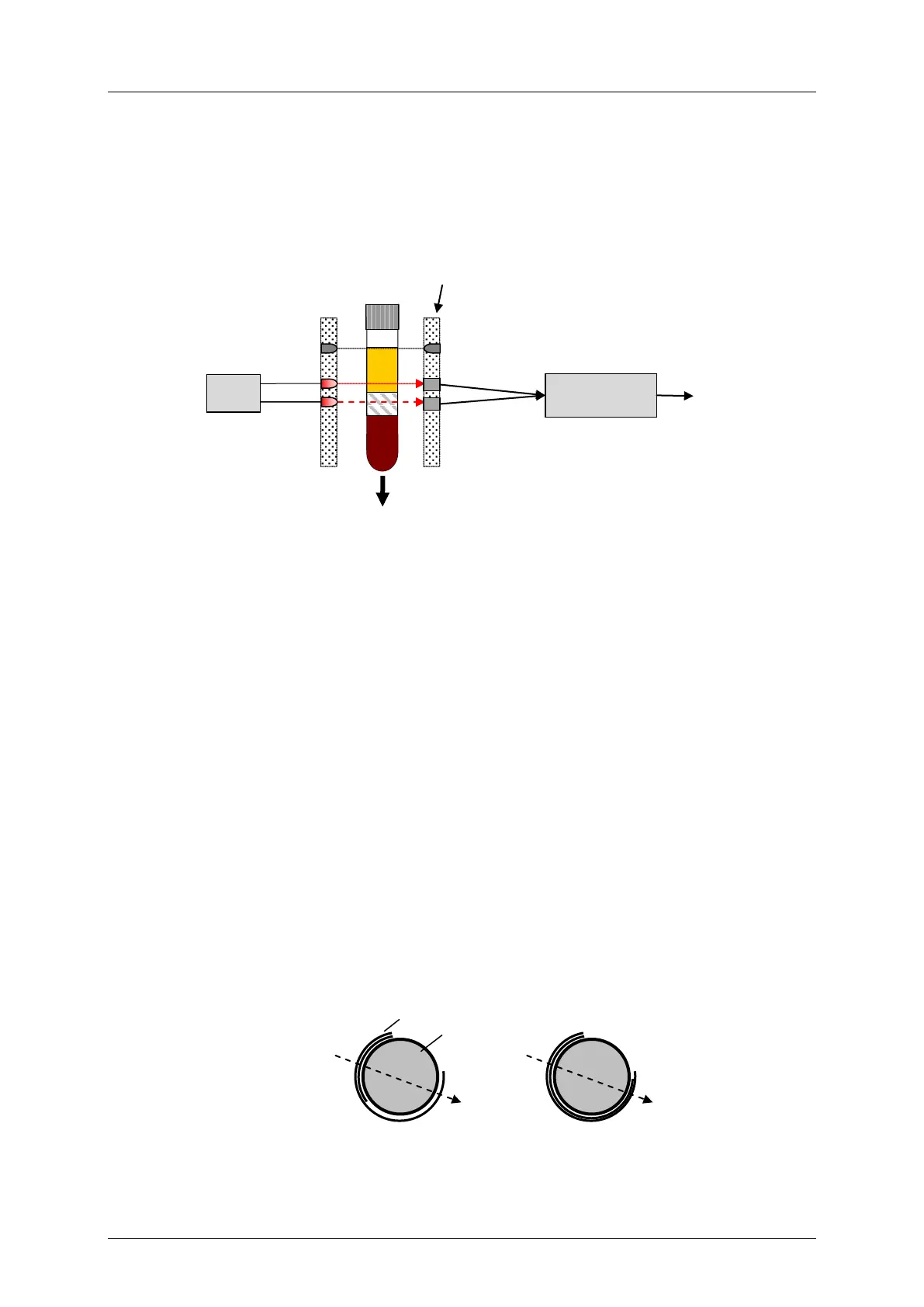
Measurement principle
The location of liquid within the tube is performed using an optical device which is able to
detect material transitions in the tube. The system comprises two infrared lasers of different
wavelengths which pass through the tube. The transmitted signals on the other side of the
tube are sent to the Laser-LLD control unit for processing (see next figure).
Figure 2-17: Schematic diagram
Barcode label
Only plastic labels and paper labels can be used. Metallic labels or reflective labels cannot be
used.
Labels must be pasted plane to the tube (wrinkle-free, no edges sticking out, no entrapped
air) otherwise the detection of liquid level may be erroneous. Residual adhesive from
removed labels may impair the liquid level detection as well.
The signal of the Laser-LLD module can pass through up to 5 layers of labels (supposing a
standard label thickness of 0.07 mm) altogether. The amount of layers includes the ones to be
passed by the beams on entering the tube plus the ones on leaving the tube again (see
Figure).
Having more than 5 layers of label or using thicker labels would affect the signal and lead to
an incorrect detection of the liquid level.
Figure 2-18: Layers of barcode label
transmission
moving direction of the tube
signal passes through
3 layers of label
signal passes through
4 layers of label
to the sorting
system

 Loading...
Loading...