Functions
2.14 Differential Protection and Its Protected Objects
SIPROTEC, 7UM62, Manual
C53000-G1176-C149-7, Release date 03.2010
107
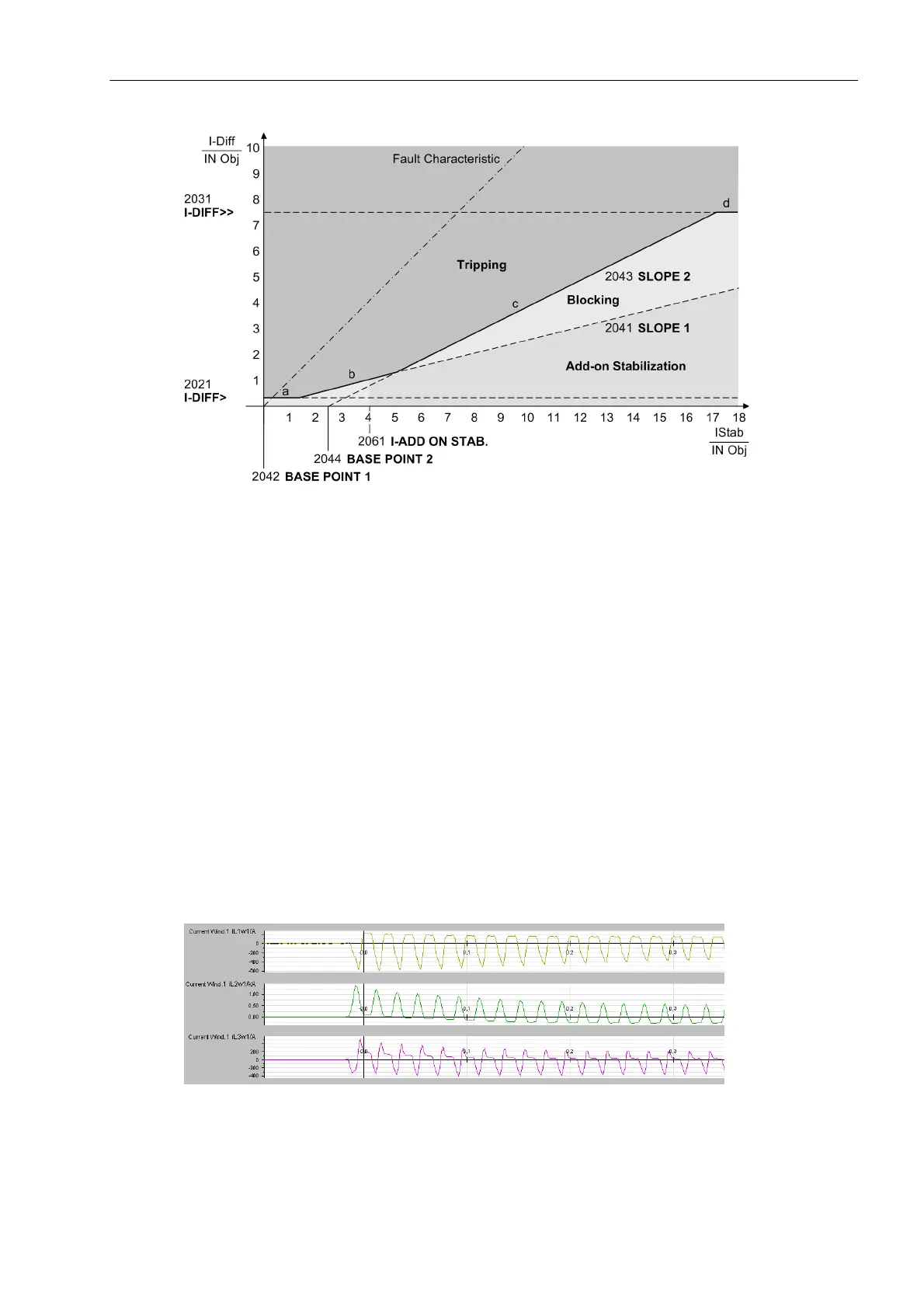
Figure 2-35 Add-on Stabilization During Current Transformer Saturation
Identification of DC Components
A further stabilization (restraint) comes into effect when differential secondary currents are simulated by differ-
ent transient behaviour of the current transformer sets. This differential current is caused by different DC time
constants in the secondary circuits during through-current conditions, i.e. the equal primary DC components
are transformed into unequal secondary DC components due to different time constants of the secondary cir-
cuits. This produces a DC component in the differential current which increases the pickup values of the differ-
ential stage for a short period.
Harmonic Stabilization
In transformers in particular, high short-time magnetizing currents may be present during power-up (inrush cur-
rents). These currents enter the protected zone but do not exit it again, so that they produce differential quan-
tities as they seem like single-end fed fault currents. Unwanted differential currents may also be caused by par-
allel connection of transformers or by transformer overexcitation due to excessive voltage.
The inrush current can amount to a multiple of the rated current and is characterized by a considerable 2nd
harmonic content (double rated frequency) which is practically absent during a short-circuit. If the second har-
monic content in the differential current exceeds a selectable threshold, tripping is blocked.
Figure 2-36 Inrush current - Recording Example of the Three Higher-Voltage Currents

 Loading...
Loading...











