Functions
2.37 Restart Inhibit for Motors (ANSI 66, 49Rotor)
SIPROTEC, 7UM62, Manual
C53000-G1176-C149-7, Release date 03.2010
261
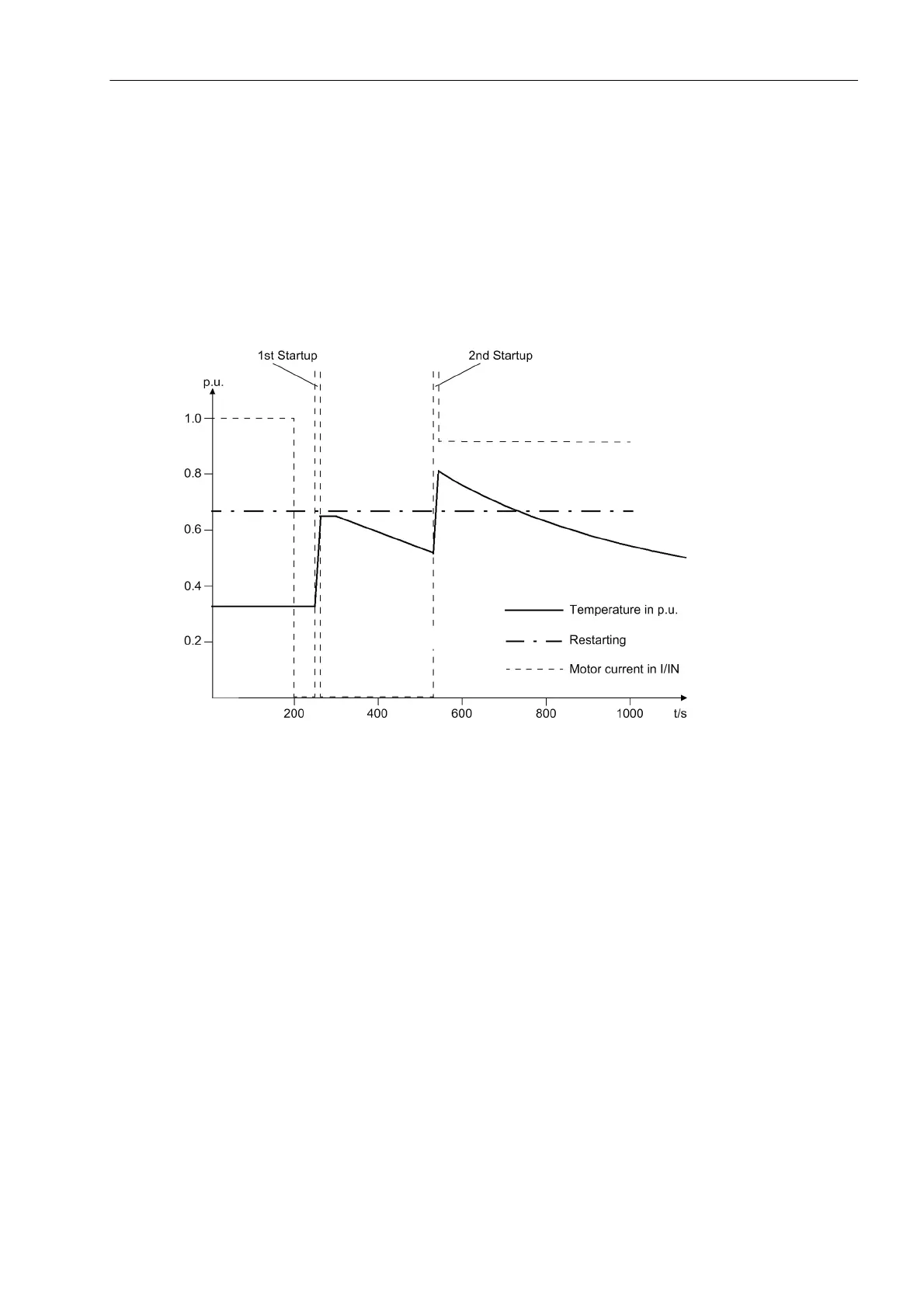
In Figure 2-119, the motor is also restarted twice in warm condition, but the pause between the restart attempts
is longer than in the first example. After the second restart attempt, the motor is operated at 90 % nominal cur-
rent. After the shutdown following the first startup attempt, the thermal profile is "frozen". After the temperature
leveling time (1 min), the rotor cools down with the time constant τ
R
· Kτ at STOP ≈ 5 · 204 s = 1020 s. During
the second restart, the starting current causes a temperature rise, whereas the subsequently flowing on-load
current of 0.9 I/I
Mot.Nom.
Kτ at RUNNING reduces the temperature. This time, the time constant τ
R
· Kτ at
STOP = 2 · 204 s = 408 s is effective.
The fact that the restart limit is exceeded for a short time does not mean a thermal overload. It rather indicates
that a thermal overload of the rotor would result if the motor were shut down immediately and restarted.
Figure 2-119 Two Warm Restarts Followed by Continuous Running

 Loading...
Loading...











