Introduction to the Fluorescence Detector 7
1100 Series FD Reference Manual 239
How the Detector Operates
Luminescence Detection
Luminescence, the emission of light, occurs when molecules change from an
excited state to their ground state. Molecules can be excited by different forms
of energy, each with its own excitation process. For example, when the
excitation energy is light, the process is called photoluminescence.
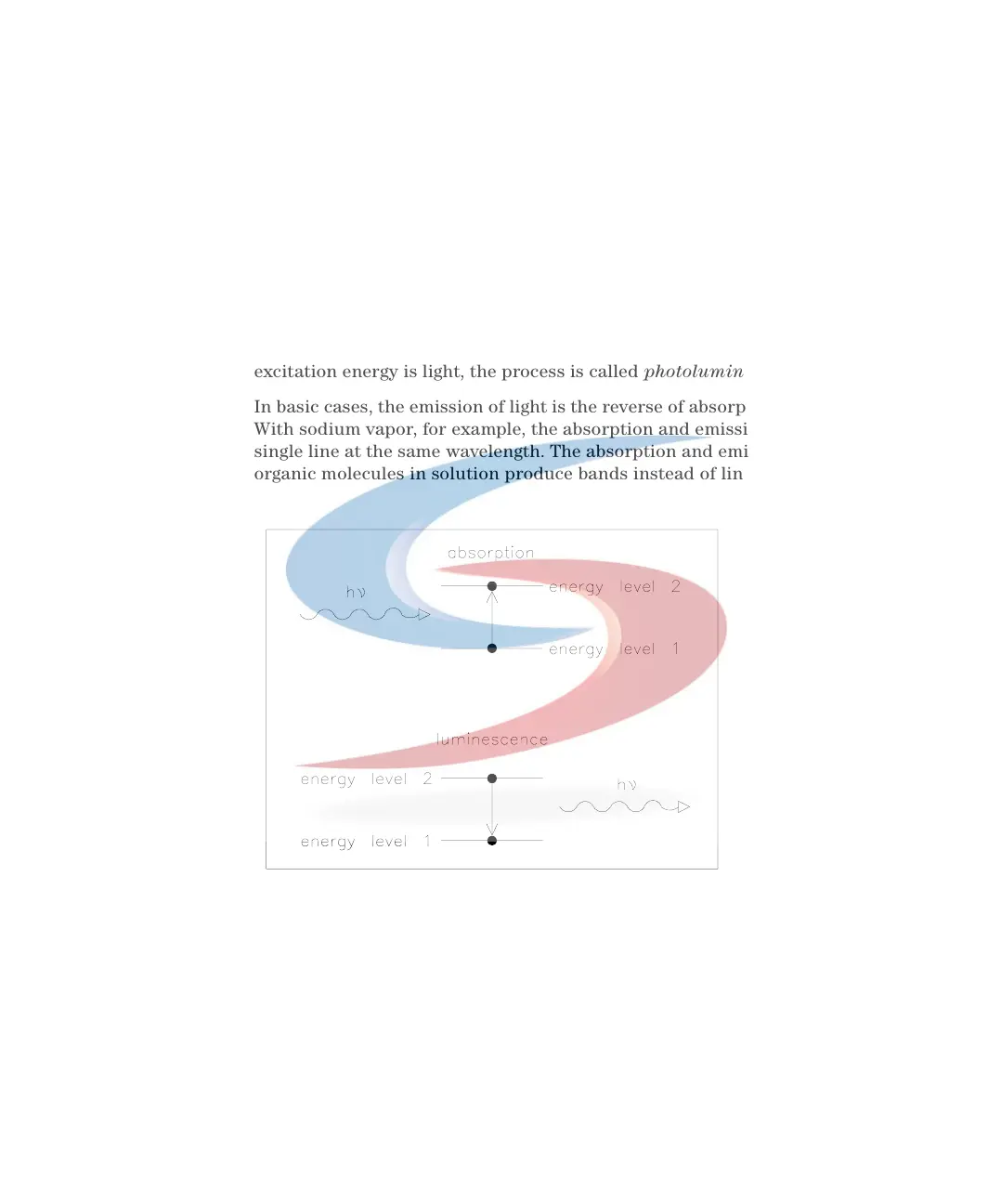
In basic cases, the emission of light is the reverse of absorption, see Figure 73.
With sodium vapor, for example, the absorption and emission spectra are a
single line at the same wavelength. The absorption and emission spectra of
organic molecules in solution produce bands instead of lines.
Figure 73 Absorption of Light Versus Emission of Light
 Loading...
Loading...
















