Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) | 577
33
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
Overview
The spanning tree protocol (STP) is a Layer 2 protocol—specified by IEEE 802.1d—that eliminates loops
in a bridged topology by enabling only a single path through the network. By eliminating loops, the
protocol improves scalability in a large network and allows you to implement redundant paths, which can
be activated after the failure of active paths. Layer 2 loops, which can occur in a network due to poor
network design and without enabling protocols like xSTP, can cause unnecessarily high switch CPU
utilization and memory consumption.
Table 33-1 lists the variations of STP that FTOS supports.
This chapter contains the following sections:
• Configuring Spanning Tree
• Configuring Interfaces for Layer 2 Mode
• Enabling Spanning Tree Protocol Globally
• Adding an Interface to the Spanning Tree Group
• Removing an Interface from the Spanning Tree Group
• Modifying Global Parameters
• Modifying Interface STP Parameters
• Enabling PortFast
• BPDU Filtering
• STP Root Selection
• STP Root Guard
• SNMP Traps for Root Elections and Topology Changes
• Displaying STP Guard Configuration
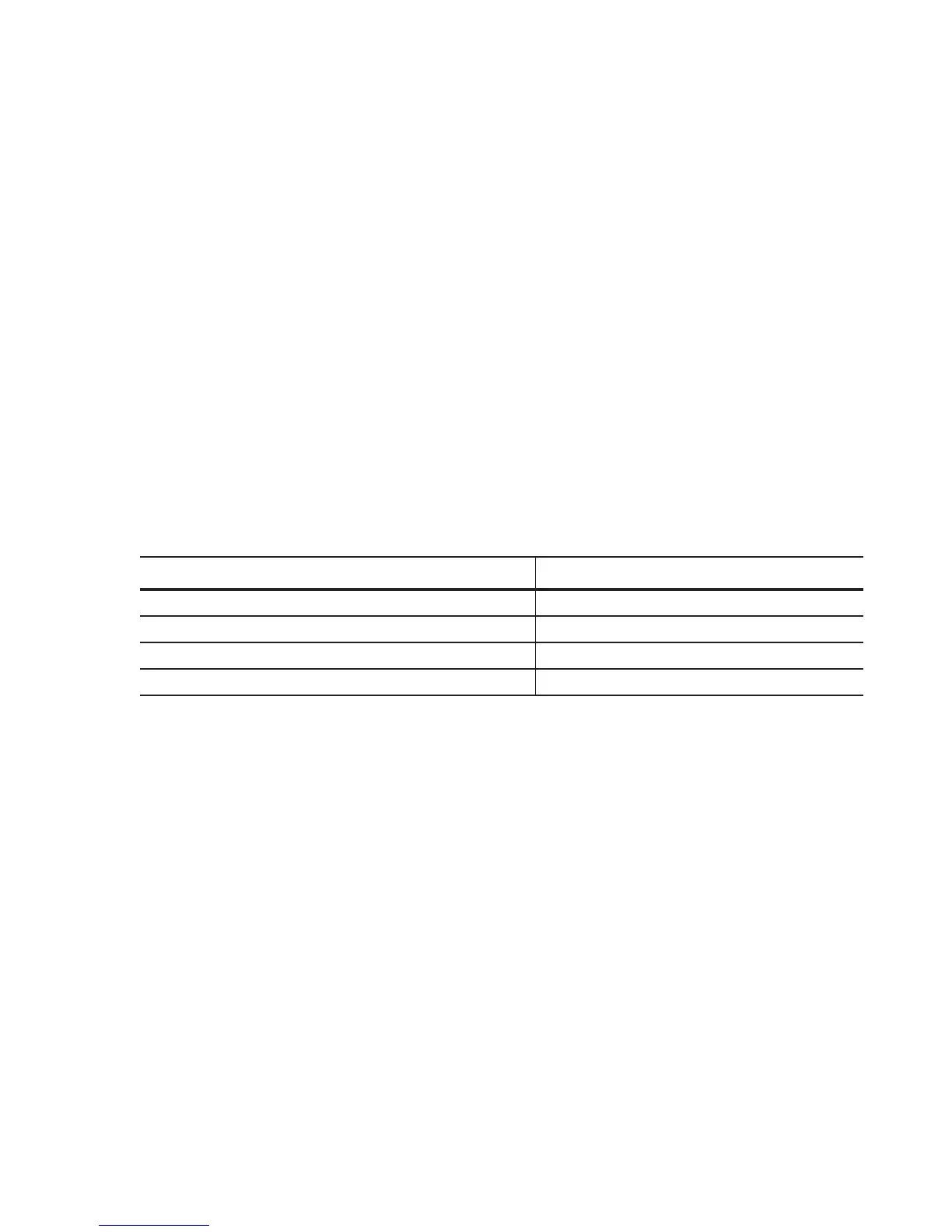
Table 33-1. FTOS Supported Spanning Tree Protocols
Dell Force10 Term IEEE Specification
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) 802.1d
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) 802.1w
Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) 802.1s
Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Plus (PVST+) Third Party

 Loading...
Loading...











