26
5.2 Principles of Operation
The ‘Abacus 5’ analyzer uses a combination of methods to provide measurement results:
Volumetric impedance is used to determine the cellular concentrations and volume distributions of
leukocytes (WBC), erythrocytes (RBC), and platelets (PLT).
Photometric measurement of light absorbance is used to determine hemoglobin (HGB) concentration.
Optical measurement of light scattering and diffraction is used to determine five part leukocyte (LYM%,
MON%, NEU%, EOS%, BAS%) differential parameters.
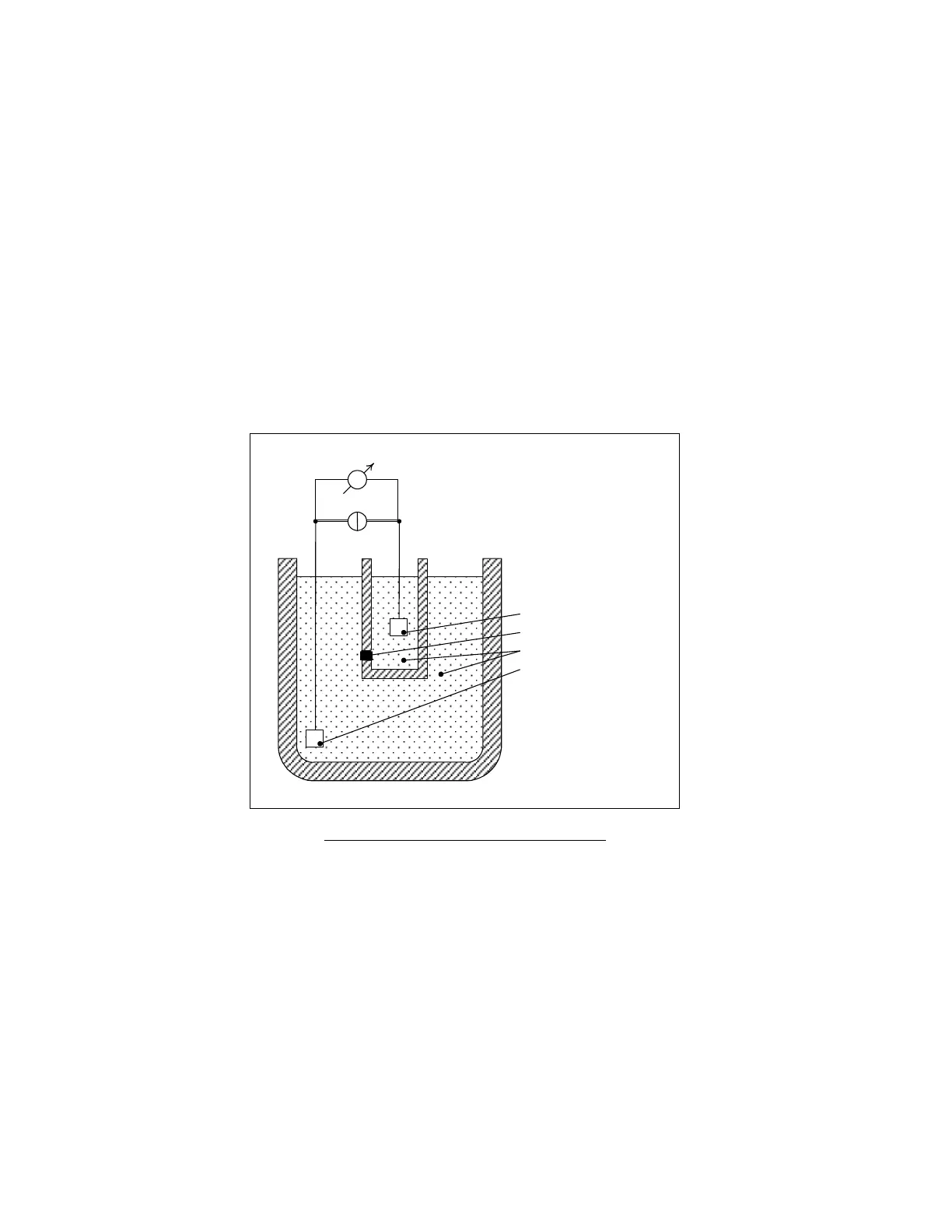
5.2.1 Volumetric Impedance Method
The volumetric impedance method determines cellular concentrations and volume distributions of cells by detecting
and measuring changes in electrical impedance when particles suspended in a conductive liquid pass through a small
aperture. The method is “volumetric” because a small known volume of blood is precisely diluted with a conductive
diluent and forced through the aperture at a fixed rate.
Figure 3. Volumetric Impedance Method
A constant direct current flows between the electrodes on either side of the aperture. Each cell passing through the
aperture causes a change in the electrical impedance of the conductive blood cell suspension. This change is sensed
by the ‘Abacus 5’ electronics and converted to an electrical pulse. The quantity of pulses is proportional to the
number of particles. The intensity of each pulse is proportional to the volume of the particle. The volume distribution
diagrams of the particles result in the WBC, RBC, and PLT histograms that measured in femtoliter volume units.
Electronic discrimination allows separation of erythrocytes (RBC) and platelets (PLT). A lytic reaction lyses
erythrocytes to clearly measure leukocytes (WBC).
5.2.2 Photometric Light Absorbance Method
A lysed blood sample dilution can be analyzed for hemoglobin (HGB) concentration based on its stable chromogen
content. The reagent lyses the red blood cells causing the release of cellular hemoglobin. The hemoglobin
 Loading...
Loading...