27
concentration is measured by taking a photometric reading across the ‘Abacus 5’ WBC chamber. The HGB
measurement is calculated as the difference between and blank and a sample measurement with and without
illumination to reduce the effect of liquid refraction and incident light.
Figure 4. Photometric Light Absorbance Method
5.2.3 Optical Light Scatter and Diffraction Method
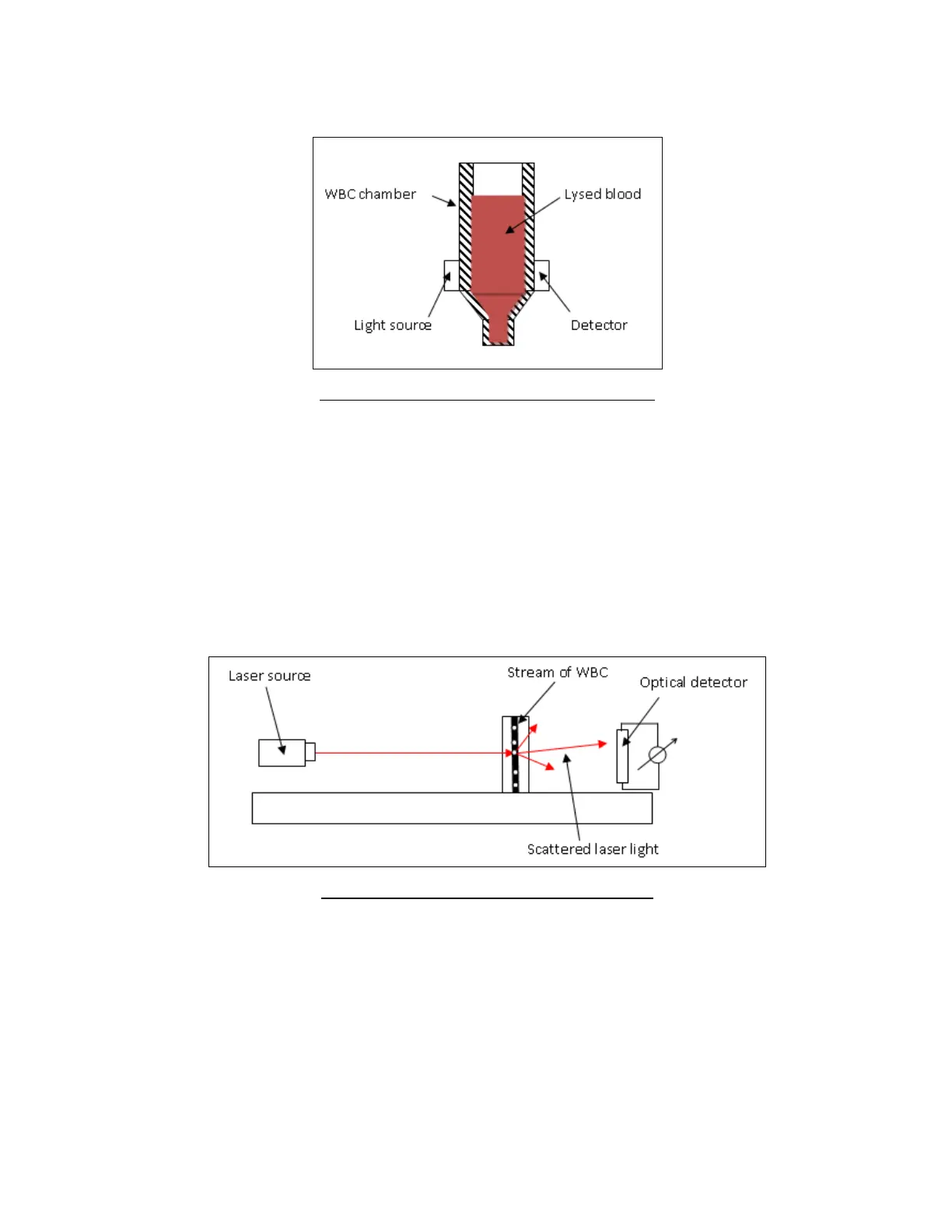
Optical measurement of light scattering and diffraction is used to determine five part leukocyte (LYM%, MON%,
NEU%, EOS%, BAS%) differential parameters. An optical measuring head contains a focused laser source that is used
to illuminate a stream of leukocytes (WBC) suspended in an optically clear diluent moving through a flow cell.
The cells scatter light as they flow through the path of the laser beam. An optical detector senses changes in the
intensity of the scattered laser light which are proportional to the cell volume and granularity of the cell’s internal
structure. The ‘Abacus 5’ electronics convert these changes to electrical pulses which are gathered and stored for
analysis. Five part population discrimination is based on analysis of the two dimensional volume and granularity
distribution scatter diagram.
Figure 5. ‘Abacus 5’ Optical Head Block DIagram
Cells with greater volume or size or more granularity will tend to scatter greater amounts of light. The intensity of
scattered light is detected by an optical signal processing system.
 Loading...
Loading...