Device Roles
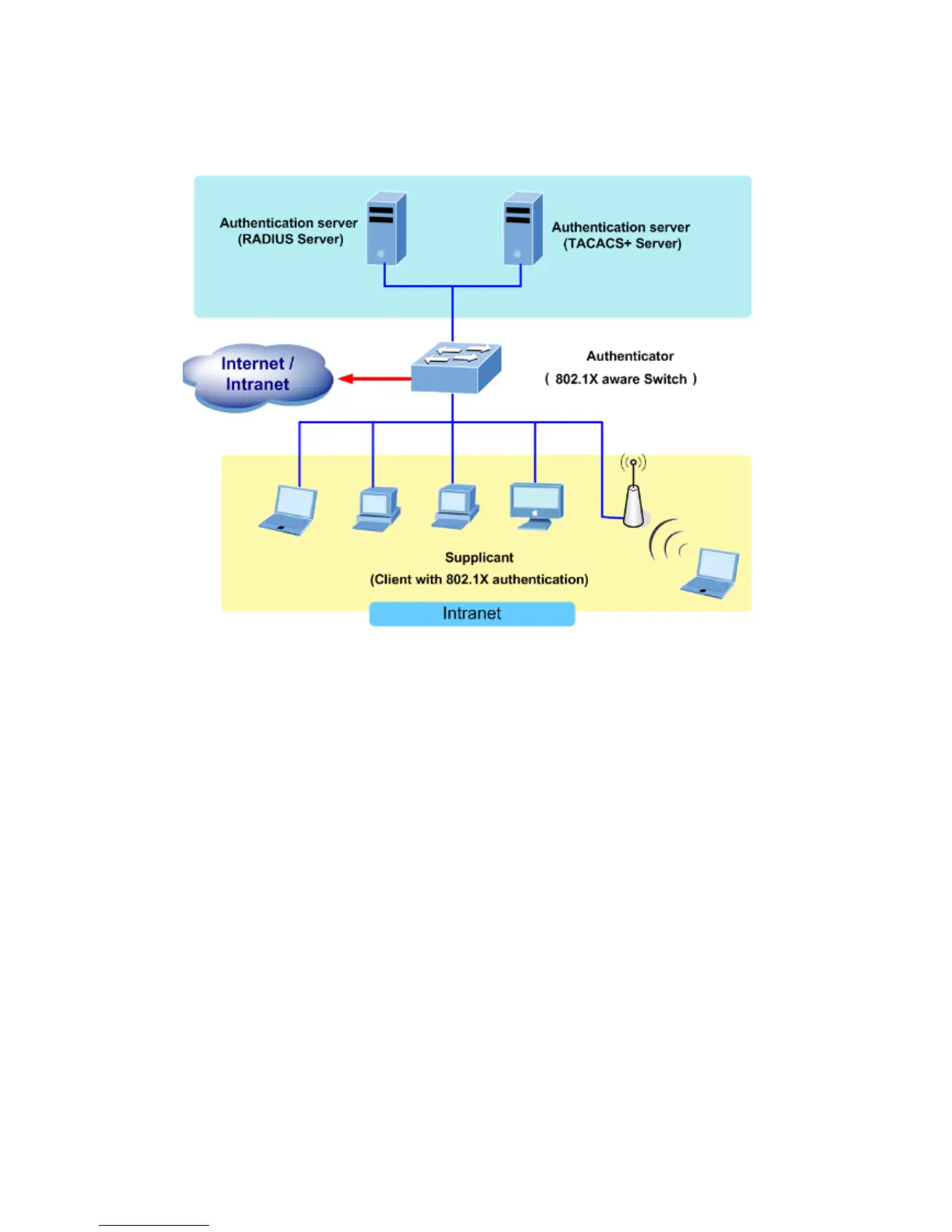
With 802.1X port-based authentication, the devices in the network have specific roles as shown below.
Figure 4-11-1
Client—the device (workstation) that requests access to the LAN and switch services and
responds to requests from the switch. The workstation must be running 802.1X-compliant
client software such as that offered in the Microsoft Windows XP operating system. (The
client is the supplicant in the IEEE 802.1X specification.)
Authentication server—performs the actual authentication of the client. The authentication
server validates the identity of the client and notifies the switch whether or not the client is
authorized to access the LAN and switch services. Because the switch acts as the proxy, the
authentication service is transparent to the client. In this release, the Remote Authentication
Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) security system with Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP)
extensions is the only supported authentication server; it is available in Cisco Secure Access
Control Server version 3.0. RADIUS operates in a client/server model in which secure
authentication information is exchanged between the RADIUS server and one or more RADIUS
clients.
Switch (802.1X device)—controls the physical access to the network based on the
authentication status of the client. The switch acts as an intermediary (proxy) between the

 Loading...
Loading...