5 - 26 WiNG 5.6 Access Point System Reference Guide
A captive portal is an access policy for providing temporary and restrictive access using a standard Web browser. Captive
portals provides authenticated access by capturing and re-directing a wireless user's Web browser session to a captive
portal login page where the user must enter valid credentials to access to the network. Once logged into the captive portal,
additional Terms and Agreement, Welcome, Fail and No Service pages provide the administrator with a number of options
on captive portal screen flow and user appearance. For information on configuring a captive portal policy, see Configuring
Captive Portal Policies on page 9-2.
12. Select OK to save the changes made to the Ethernet Port Basic Configuration. Select Reset to revert to the last saved
configuration.
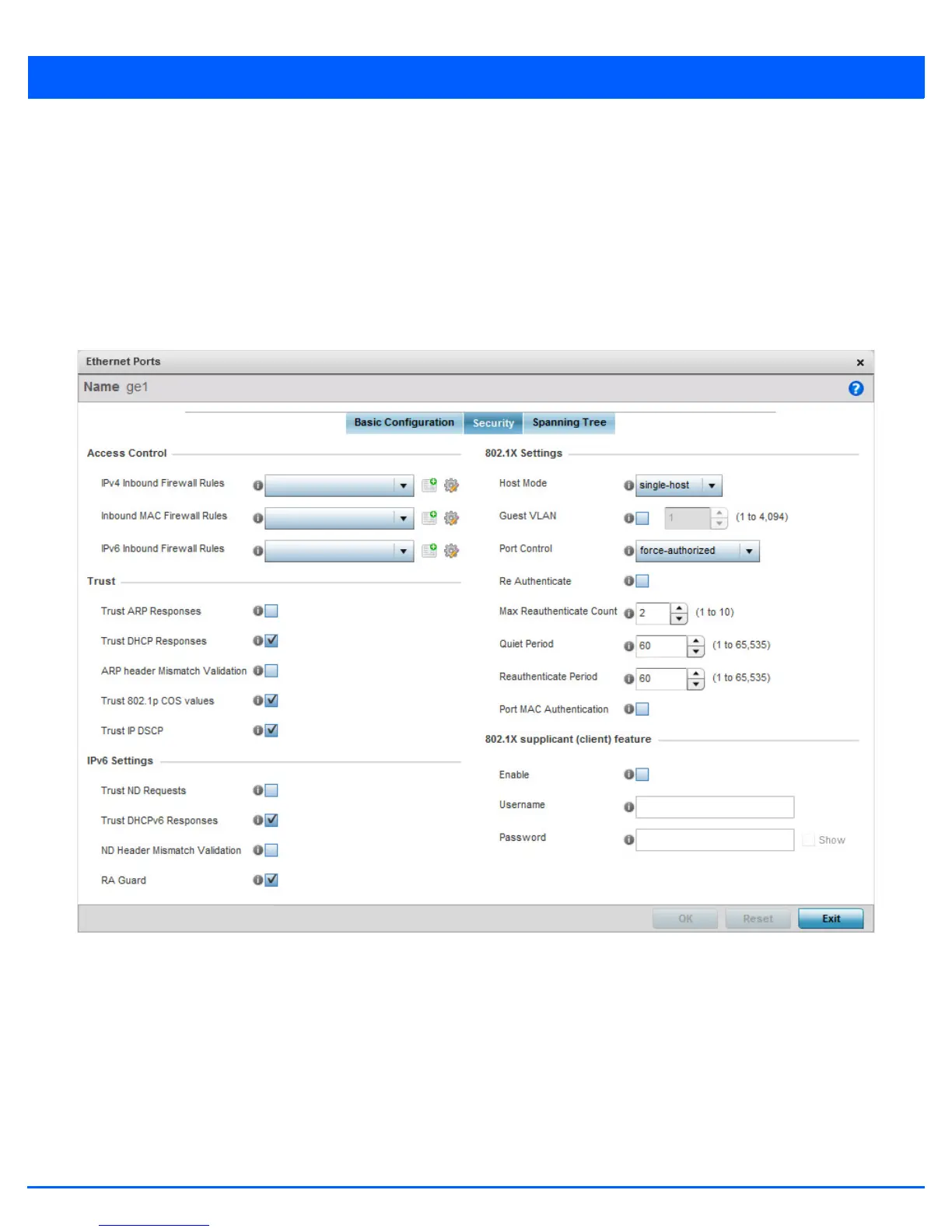
13. Select the Security tab.
Figure 5-15 Ethernet Ports - Security tab
14. Refer to the Access Control field. As part of the port’s security configuration, Inbound IP and MAC address firewall rules
are required.
Use the Inbound MAC Firewall Rules drop-down menus to select the firewall rules to apply to this profile’s Ethernet port
configuration. The firewall inspects MAC traffic flows and detects attacks typically not visible to traditional wired firewall
appliances.
Use the IPv4 Inbound Firewall Rules drop-down menu to select the IPv4 specific firewall rules to apply to this profile’s
Ethernet port configuration. IPv4 is a connection less protocol for packet switched networking. IPv4 operates as a best effort
delivery method, as it does not guarantee delivery, and does not ensure proper sequencing or duplicate delivery (unlike
(TCP). IPv4 hosts can use link local addressing to provide local connectivity.

 Loading...
Loading...











