Device Configuration 5 - 105
5.2.6.10 Forwarding Database
Profile Network Configuration
A Forwarding Database is used by a bridge to forward or filter packets. The bridge reads the packet’s destination MAC address
and decides to either forward the packet or drop (filter) it. If it is determined the destination MAC is on a different network
segment, it forwards the packet to the segment. If the destination MAC is on the same network segment, the packet is dropped
(filtered). As nodes transmit packets through the bridge, the bridge updates its forwarding database with known MAC
addresses and their locations on the network. This information is then used to decide to filter or forward the packet.
To define a forwarding database configuration:
1. Select the Configuration tab from the Web UI.
2. Select Devices.
3. Select System Profile from the options on left-hand side of the UI.
4. Expand the Network menu and select Forwarding Database.
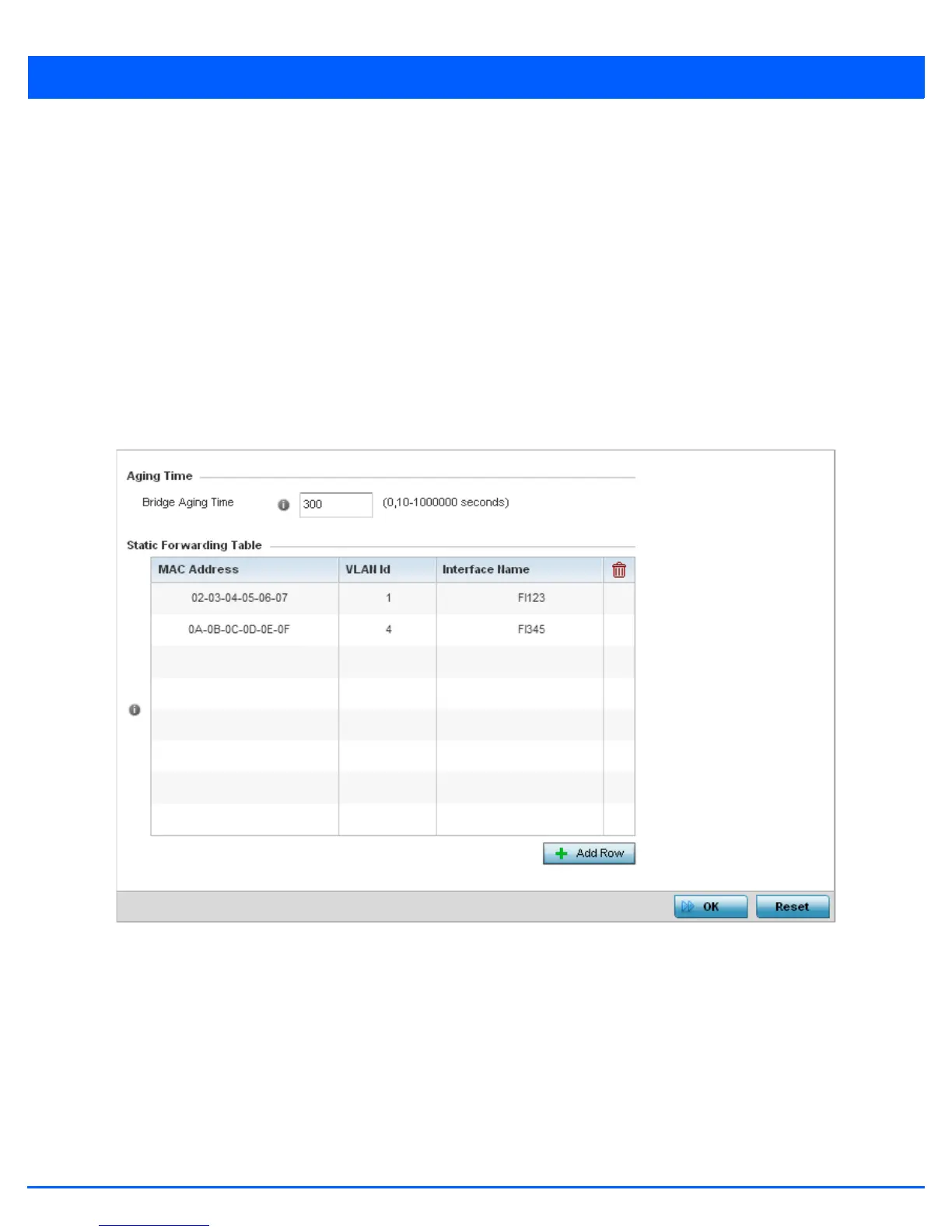
Figure 5-67 Network - Forwarding Database screen
5. Define a Bridge Aging Time from 0, 10-1,000,000 seconds.
The aging time defines the length of time an entry will remain in the bridge’s forwarding table before it is deleted due to
lack of activity. If an entry replenishments a destination, generating continuous traffic, this timeout value will never be
invoked. However, if the destination becomes idle, the timeout value represents the length of time that must be exceeded
before an entry is deleted from the forwarding table. The default setting is 300 seconds.
6. Use the + Add Row button to create a new row within the Static Forwarding Table.
7. Set a destination MAC Address address. The bridge reads the packet’s destination MAC address and decides to forward
the packet or drop (filter) it. If it’s determined the destination MAC is on a different network, it forwards the packet to the
segment. If the destination MAC is on the same network segment, the packet is dropped (filtered).

 Loading...
Loading...











